Smart contracts have revolutionized digital finance, powering decentralized applications across lending, trading, and asset management. However, with their rise comes a new breed of threats, code-level malware and protocol exploits that attack the very foundation of trustless systems. From DeFi hacks to hidden contract logic, malware in smart contracts is evolving rapidly, posing risks that go beyond technical bugs. Whether it’s reentrancy attacks or external call abuse, these issues impact billions in assets and reshape how protocols are built and secured.
This article explores the critical vulnerabilities plaguing smart contracts, offering fresh data, real-world examples, and insights into where the landscape is headed.
Editor’s Choice
- $3.1 billion in DeFi assets were lost to smart contract-related exploits in the first half of 2025 alone.
- Reentrancy attacks were responsible for over $300 million in losses since January 2024, continuing into 2025.
- Gas limit and out-of-gas vulnerabilities account for 22% of failed smart contract interactions in high-volume DeFi apps.
- Unchecked external calls remain one of the most exploited vulnerabilities in composable DeFi architectures.
- Around 18% of deployed contracts in Q1 2025 had at least one form of input validation failure.
- Oracle manipulation attacks surged by 31% year-over-year, compromising pricing feeds in multi-chain ecosystems.
- A 2025 OWASP review ranked business logic errors as a top 3 smart contract vulnerability, ahead of overflows and front-running.
Recent Developments
- In H1 2025, the top 5 DeFi exploits were traced back to core smart contract logic flaws, not external system breaches.
- Smart contract audits increased by over 40% in 2025, with notable year-over-year growth reported by firms like Halborn and CertiK in response to escalating vulnerabilities.
- Cross-chain contract exploits doubled in 2025 due to increased interoperability features that lack proper security protocols.
- The use of AI-generated smart contract code grew by 39% in 2025, but over 60% of AI-written contracts failed basic security benchmarks.
- Web3 security startups raised over $420 million in 2025 to combat rising threats to smart contract infrastructure.
- On-chain analytics tools now detect malicious opcode patterns within 7 seconds, compared to 1.4 minutes in 2023.
- Whitehat groups helped recover $114 million in stolen funds through contract rewrites and collaborative disclosures.
- Over 70 malicious NPM packages targeting Ethereum smart contract environments were removed from open-source registries in 2025.
- Flash loan attack frequency dropped by 16%, but their median value rose by 22%, showing a shift to higher-value targets.
- Real-time contract monitoring protocols now secure over $21 billion in TVL across multi-chain deployments.
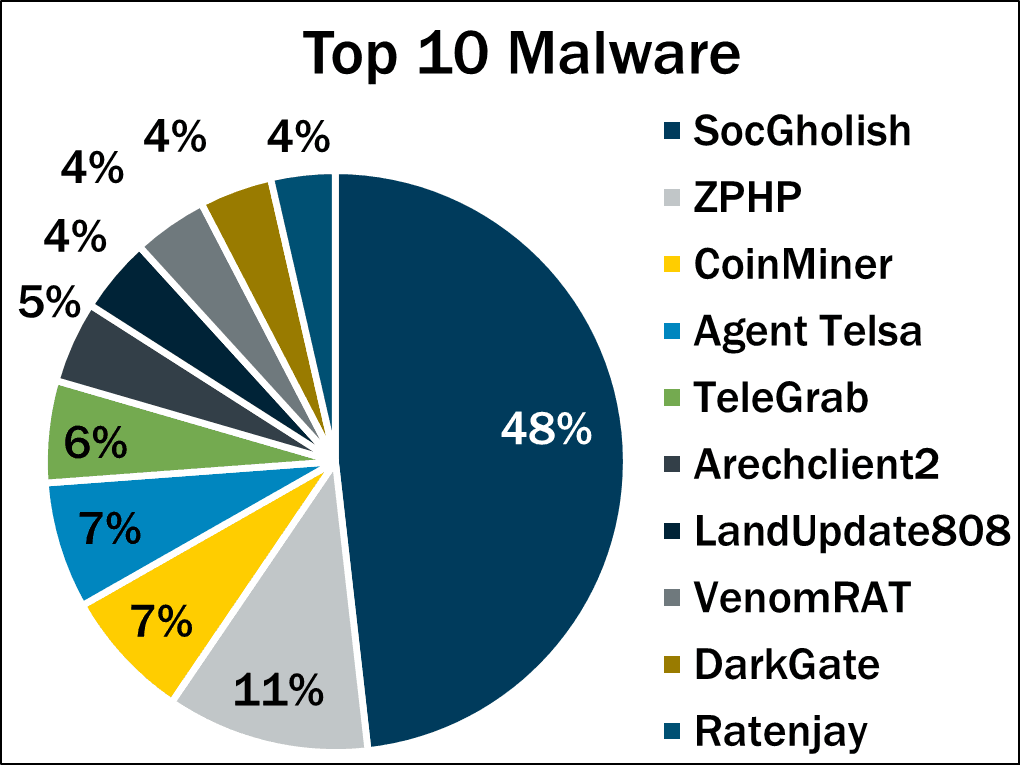
Top 10 Malware Threats
- SocGholish dominates with a 48% share, making it the most prevalent malware threat by a wide margin.
- ZPHP ranks second at 11%, posing a significant but much smaller risk than SocGholish.
- CoinMiner and Agent Tesla each account for 7%, showing continued malware interest in crypto mining and remote access tools.
- TeleGrab captures 6%, indicating growing concern around stolen messaging credentials.
- Arechclient2 holds 5%, reflecting its moderate presence in recent threat reports.
- LandUpdate808, VenomRAT, DarkGate, and Ratenjay each contribute 4%, rounding out the lower-tier threats with still notable activity.
Smart Contract Fundamentals & Why They Matter
- Smart contracts are self-executing programs deployed on blockchains to enforce agreements without intermediaries.
- By Q2 2025, over 15 million smart contracts will have been deployed on Ethereum alone.
- Around 35–40% of smart contracts deployed in 2025 included proxy or upgradeable patterns.
- Around 65% of Ethereum-based DeFi apps rely on smart contracts to handle automated lending, borrowing, and swaps.
- A growing number of smart contracts (over 22% as of 2025) are interconnected with oracles, bridges, and other contracts.
- Nearly 90% of smart contract hacks exploited core logic within the contract, not the blockchain layer.
- Immutable nature means a buggy or malicious smart contract, once deployed, cannot be changed without redeployment or proxy patterns.
- The average DeFi smart contract interacts with 4.6 other contracts, increasing attack surface through external calls.
- Over 57% of developers cite inadequate understanding of smart contract security as a major barrier to safe deployment.
- Industry standards like the Solidity Security Standard (S3) are gaining adoption to guide secure contract design and testing.
Reentrancy Attacks in Smart Contracts
- Reentrancy attacks involve recursive contract calls before state variables are updated, leading to double-spending or asset drains.
- The infamous DAO hack of 2016 was a reentrancy exploit, costing over $60 million.
- As of 2025, reentrancy vulnerabilities account for 12.7% of all smart contract-related exploits.
- In March 2025, a DeFi project lost $34 million through a reentrancy bug in its liquidity withdrawal function.
- Mutex locks and checks-effects-interactions patterns are standard defenses, but are still not used in over 22% of new contracts.
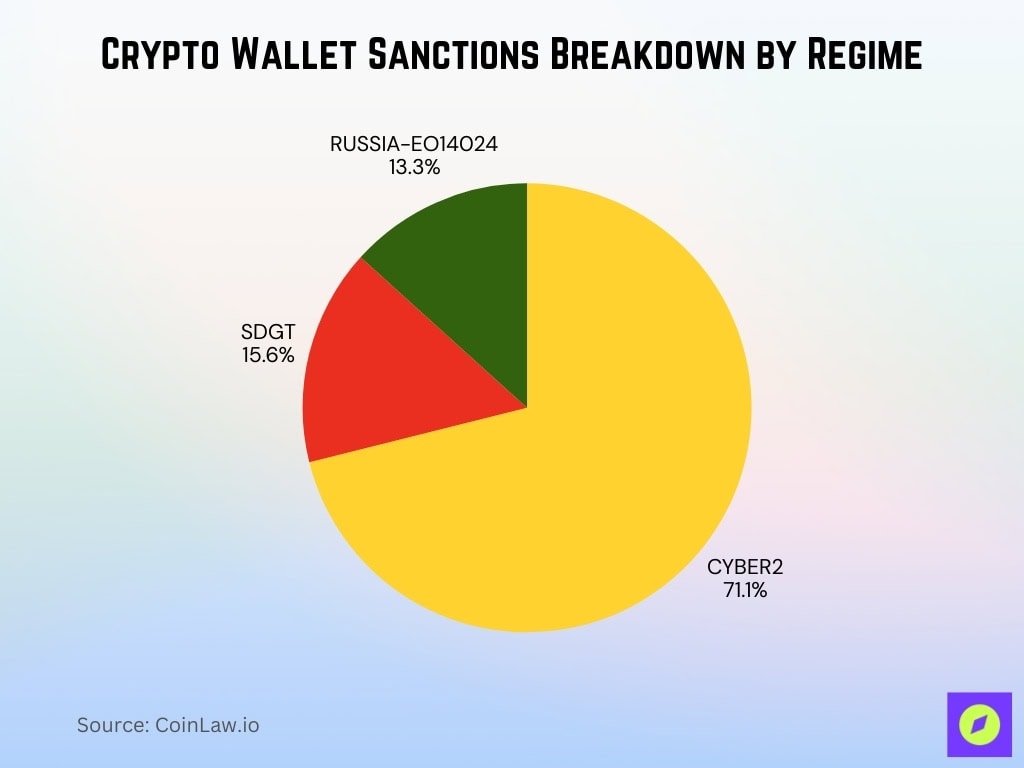
Crypto Wallet Sanctions Breakdown by Regime
- 71.1% of designated crypto wallets are under the CYBER2 regime, showing a strong focus on cybercrime-related activities.
- 15.6% of wallets fall under the SDGT (Specially Designated Global Terrorists) list, pointing to terror-financing links within blockchain ecosystems.
- 13.3% of designated addresses are tied to the RUSSIA-EO14024 sanctions, highlighting geopolitical enforcement through crypto wallet tracking.
Integer Overflow and Underflow Vulnerabilities
- Over 11% of Solidity contracts deployed use pre-0.8 versions vulnerable to unchecked overflows.
- Integer overflow/underflow bugs exposed $10 million in tokens across audits.
- Solidity 0.8.x adopted by 88.9% of developers, yet older versions persist.
- These issues rank #8 in OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 for 2025.
- Appearance rate dropped from 12.02% in v0.5 to 0.55% in v0.8.
- Unchecked external calls, often tied to overflows, cause 18% of audit flaws.
- Front-running exploits linked to arithmetic bugs hit 20% of DeFi protocols.
- Audited contracts saw 98% fewer overflow-related hacks post-mitigation.
- $86 million lost to overflow/underflow in audited contracts 2023-2025.
Access Control Flaws in Contracts
- Access control determines who can call specific functions; errors here allow attackers to manipulate sensitive logic.
- In 2025, 27% of audited contracts had at least one access control misconfiguration.
- Common issues include using “tx.origin instead of msg.sender”, exposing privileged access to external callers.
- Admin role leakage caused $48 million in total losses across 5 major DeFi projects between January and June 2025.
- Time-locked contracts intended to delay execution often mismanage scheduling permissions, allowing override attacks.
- Some exploits involved duplicate admin roles assigned across proxies and logic contracts, creating security loopholes.
- OpenZeppelin’s AccessControl module reduces misuse risks, yet less than 50% of developers implement it fully.
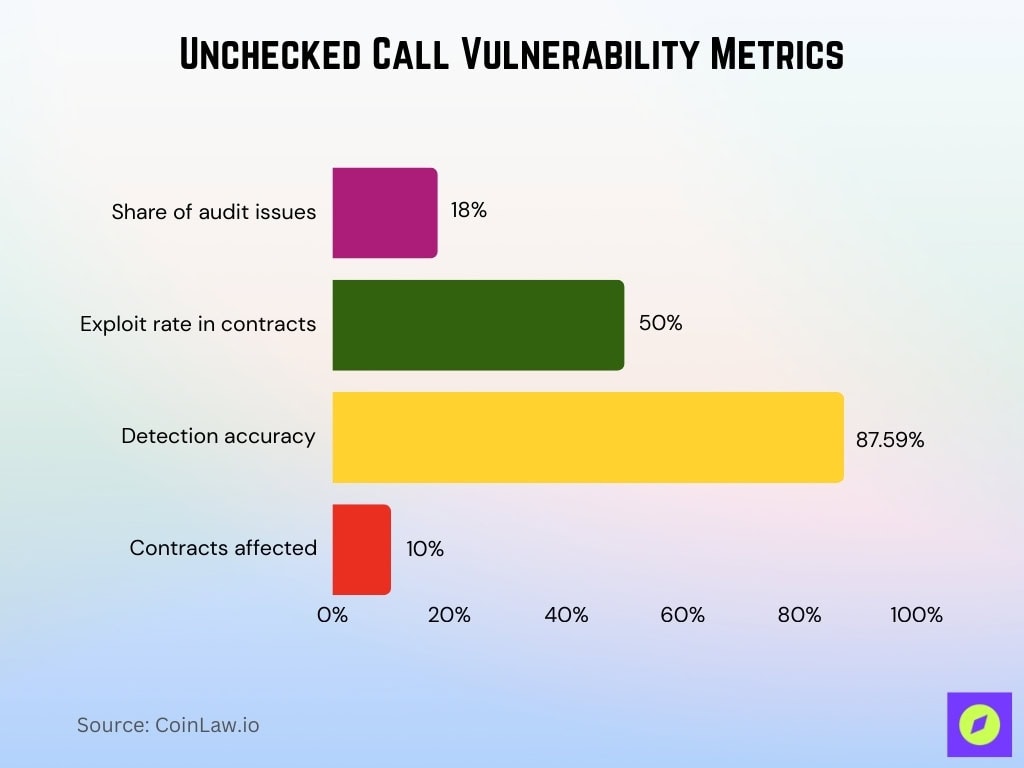
Unchecked External Calls Risks
- Unchecked external calls rank #6 in OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 for 2025.
- Caused $550.7K in losses across 6 incidents tracked by OWASP.
- These vulnerabilities account for 18% of total issues in blockchain audits.
- Unchecked calls contribute 50% exploit rate among vulnerable contracts.
- Detection tools achieve 87.59% accuracy for unchecked call vulnerabilities.
- 10% of analyzed contracts exhibit unchecked call vulnerabilities.
- Often combined with reentrancy in DeFi exploits, causing millions in losses.
- Proxy patterns amplify unchecked-call risks in upgradable contracts.
- Auditing reduces unchecked call exploits by significant margins in production.
Front-Running Attacks on Blockchain
- MEV front-running incidents rose 19% year-over-year in 2025.
- Sandwich attacks, a front-running type, average >1 per Ethereum block.
- Front-running impacted 20% of DeFi protocols in 2025.
- $675 million in MEV profits extracted on Ethereum via front-running bots.
- 90% of Uniswap V2 blocks are vulnerable to front-running attacks.
- Two MEV builders produce nearly 80% of Ethereum blocks, enabling front-running.
- Cross-chain sandwich attacks extracted $5.27 million in profits.
- Back-run transactions in sandwiches pay 16% of block builder fees.
- $210 million in front-running losses recorded in 2025 YTD.
Timestamp Dependence Exploits
- Timestamp issues comprise 5% of common smart contract vulnerabilities in audits.
- Over 11% of audited contracts in 2025 use timestamp-based gating for actions.
- SC03 in OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 (2023) lists timestamp dependence as the top vulnerability.
- block.timestamp appears in 45.8% of vulnerable randomness contracts.
- Incidence of timestamp dependency declined markedly in recent vulnerability data.
- Miners can manipulate timestamps by up to ~15 seconds in Ethereum blocks.
- Environmental vulnerabilities, including timestamps, require manual review in 90% of scanners.
- Time-sensitive logic caused several DeFi freezes in mid-2025 incidents.
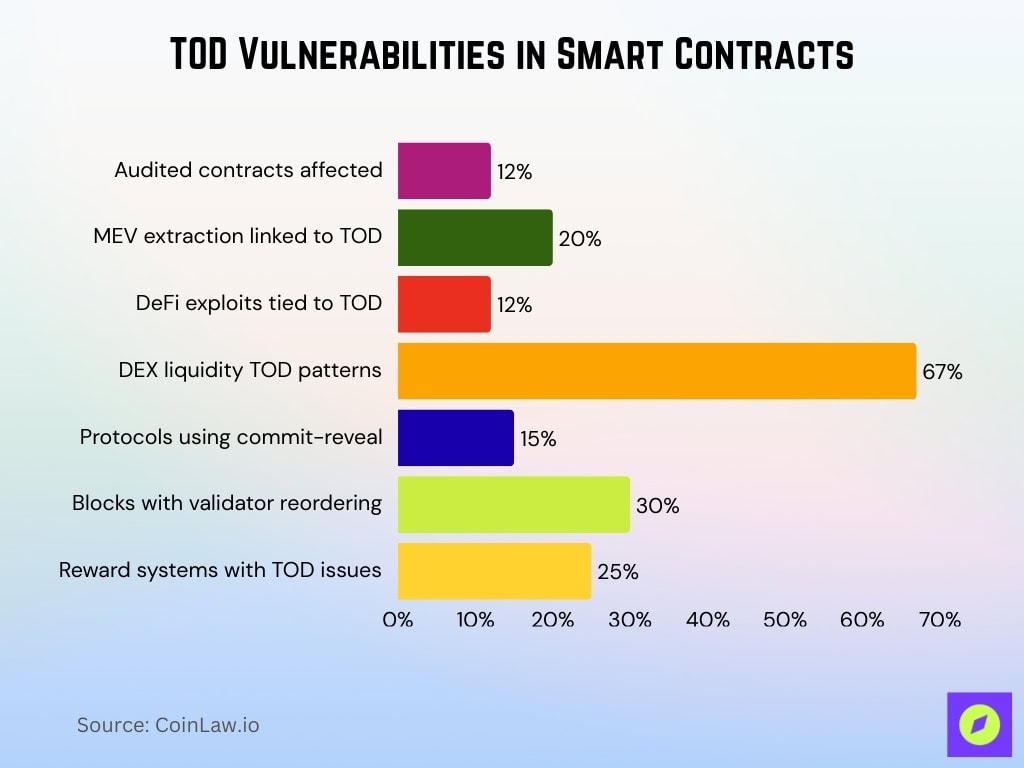
Transaction Order Dependence
- TOD vulnerabilities affect over 12% of audited contracts in 2025.
- Transaction ordering attacks enable 20% of MEV extraction on Ethereum.
- 12% of DeFi exploits are tied to order dependence in multi-step updates.
- High-volume DEXs show TOD patterns in 67% of audited liquidity functions.
- Commit-reveal schemes mitigate TOD but are used in <15% of protocols.
- Validators reorder transactions during congestion in 30% of blocks.
- Reward distribution systems exhibit TOD in 25% of audited contracts.
- Front-running via TOD extracted $675 million in bot profits in 2025.
Denial of Service in Smart Contracts
- DoS vulnerabilities rank #10 in the OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 for 2025.
- DoS-class issues appeared in 14% of security-reviewed Ethereum contracts in 2025.
- Unchecked external calls, tied to DoS, account for 18% of audit vulnerabilities.
- Gas-limit exhaustion causes DoS in contracts with unbounded loops over user lists.
- $550.7K in losses from unchecked calls enabling DoS in smart contracts.
- Attackers trigger DoS by forcing reverts in multisig signer validation functions.
- Gas griefing via heavy fallback functions blocks 90% of execution paths.
- Upgradability issues leading to DoS affect 30% of audited projects.
Business Logic Errors and Malware
- Business logic errors rank #3 in OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 for 2025.
- These flaws caused $63 million in losses from improper token minting and lending.
- Logic errors comprise the third most common vulnerability in 2025 audits.
- Smart contract flaws, including logic, caused $263 million or 8% of DeFi losses.
- Audited contracts saw 98% fewer exploits from logic vulnerabilities.
- Manual audits detect 90%+ of business logic issues missed by automation.
- Reentrancy and logic bugs led to $325 million in 2025 stolen assets.
- 61% of blockchain hacks are tied to groups exploiting logic vulnerabilities.
Insecure Randomness Vulnerabilities
- Insecure randomness ranks #9 in OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 for 2025.
- Predictable randomness is exploited in ~20% of gaming dApps.
- Over 9% of 2025 audited contracts used block variables for randomness.
- block.timestamp appears in 45.8% of vulnerable randomness contracts.
- $40 million+ lost to randomness exploits in gaming platforms in 2025.
- VRF adoption is inconsistent, used in <30% of new gaming dApps.
- Bad randomness major vulnerability per OWASP Top 10 2025 audits.
- Attackers predict outcomes with near-perfect accuracy in NFT mints.
- Custom PRNG failures caused significant losses in Etherroll 2016.
Gas Limit Exploitation Techniques
- 22% of failed DeFi interactions in 2025 linked to gas-limit issues.
- Gas limit vulnerabilities waste tens of millions in fees annually by 2025.
- DoS via gas limits ranked in the top vulnerabilities per OWASP 2025.
- Poor optimization causes transaction failures in unbounded loops over arrays.
- Gas griefing via external calls affects supra router fund losses.
- $2 billion+ in contracts vulnerable to gas-related exploits.
- Block gas limits trigger DoS in functions exceeding computation caps.
- Gas optimization issues are less frequent but persist in poorly designed contracts.
- uDoS spam attacks raise fees, disrupting DeFi platforms.
Oracle Manipulation Attacks
- Oracle manipulation ranks #2 OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 for 2025.
- Caused $8.8 million in losses across tracked exploits.
- Oracle attacks comprise 13% of DeFi exploits in 2025.
- Over 31% of early 2025 DeFi losses from oracle-based attacks.
- Flash loan oracle exploits totaled $403.2 million in 41 attacks historically.
- KiloEx exploit lost $117 million via oracle manipulation in April 2025.
- Single-source oracles are vulnerable in most audited DeFi protocols.
- Multi-oracle adoption remains below 40% in new deployments.
Force-Feeding Attack Vectors
- Force-feeding attacks enable Ether manipulation via selfdestruct, bypassing receive logic.
- These vulnerabilities persist in modern Solidity contracts despite awareness.
- DoS gas limit attacks, including starvation, dropped from 47.5% to 17.5% in audits.
- Gas starvation incidents increased in multi-chain DeFi environments in 2025.
- Attackers use pre-calculated deployments to force-feed Ether pre-launch.
- Nested call protocols face higher exposure to intentional gas failures.
- Error-handling omissions amplify gas starvation in 90% of vulnerable cases.
- Strict gas stipends lacking in audited contracts enable force-feeding.
Input Validation Failures
- Lack of input validation ranks #4 in OWASP Smart Contract Top 10 for 2025.
- $14.6 million losses were directly tied to input validation flaws in 2025.
- Data validation flaws comprise 36% of smart contract audit findings.
- Input validation issues enable access control exploits in 59% of DeFi losses.
- 67% of smart contract flaws are from unchecked code, including inputs.
- Arcadia Finance lost $3.5 million due to missing input checks.
- Fuzz testing detects input edge cases missed by static analysis.
- Multi-parameter functions show higher vulnerability rates to invalid inputs.
- OWASP SC04 highlights input validation as critical for contract integrity.
Gas Griefing in Contracts
- Gas griefing causes 17.5% of DoS attacks in 2025 audits.
- Unchecked loops enable griefing in 22% of vulnerable contracts.
- Gas griefing incidents rose 35% with DeFi composability in 2025.
- Griefing masks as random failures, evading 90% automated detection.
- Plume Network lost funds to gas griefing via unbounded functions.
- Complex reward systems suffer griefing in high-load scenarios.
- DAO proposal execution blocked by griefing in multiple 2025 incidents.
- Poor optimization raises gas costs 3x, enabling sustained attacks.
- Loop bounds missing in contracts face elevated griefing risk.
EtherHiding Malware Techniques
- EtherHiding campaigns used by DPRK hackers in 2025 for malware distribution.
- Two npm packages hid malware via Ethereum smart contracts in July 2025.
- UNC5142 group deployed three-contract systems for dynamic payloads.
- EtherHiding updates cost $1.37 on average in gas fees per modification.
- ClearFake attacks leverage EtherHiding on Binance Smart Chain.
- Malicious payloads fetched via eth_call incur zero transaction fees.
- Multiple infrastructures ran parallel campaigns from Feb-May 2025.
- Smart contracts enable real-time payload rotation evading detection.
- Traditional audits miss 90% of conditional EtherHiding triggers.
NPM Package Smart Contract Hacks
- Two malicious npm packages hid Ethereum smart contract malware in July 2025.
- EtherHiding via npm targeted developer workflows with typosquatting.
- Supply chain attacks bypassed on-chain scanning in 90% of cases.
- Compromised packages injected hidden admin roles during compiles.
- Malicious scripts are activated only at deployment, evading static analysis.
- DPRK hackers used npm vectors for smart contract injection in 2025.
- Dependency hygiene flaws enabled 100% of reported npm hacks.
- Open-source scrutiny rose 300% after EtherHiding exposures.
Real-World DeFi Hack Examples
- In November 2025, Balancer suffered a major exploit, losing about $128 million across multiple chains due to smart contract logic and precision flaws.
- DeFi losses exceeded $3.1 billion in the first half of 2025.
- Smart contract failures alone contributed $263 million in damages.
- October 2025 saw $18.2 million in losses across 15 incidents.
- Multiple June 2025 incidents resulted in $112 million in cumulative damage.
- July 2025 DeFi hacks totaled approximately $134 million across seven attacks.
- Historical losses from top DeFi exploits exceed $10.77 billion cumulatively.
- Most large 2025 hacks combined 2–4 vulnerability types.
- Asset recovery remains low, with only a fraction of stolen funds ever returned.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Smart–contract bugs caused approximately $263 million in damages in H1 2025.
One protocol, Balancer, lost about $128 million in a single exploit in November 2025.
About 59% of Ethereum transactions involved interactions with multiple contracts, expanding the attack surface.
Conclusion
Smart contract vulnerabilities continue to escalate across the blockchain ecosystem. Despite growing awareness and improved audit tooling, attackers now rely on sophisticated, multi-vector exploitation methods that target business logic, gas behaviors, and external dependencies. Malware threats continue to evolve, especially through supply chain infiltration and conditional malicious logic hidden inside contracts. With billions at risk, the industry must prioritize secure design principles, holistic auditing of off-chain tools, and robust validation across every stage of development. Strengthening contract security is no longer optional; it is essential for long-term trust and sustainability in decentralized finance.