The life insurance sector continues to grapple with significant policy lapse rates that influence insurers’ financial stability and consumers’ long-term protection. These lapse rates matter because they indicate the proportion of policies that end prematurely, often due to nonpayment or voluntary surrender, rather than fulfilling their full term or paying out a claim. Real-world consequences show up when families lose out on death benefits, or insurers adjust pricing and reserves in response to unpredictable policy retention behavior. Read on to explore key numbers and understand how lapse rate calculations shape industry behavior and consumer outcomes.
Editor’s Choice
- 7.0%, the overall individual life insurance lapse ratio for U.S. insurers in 2024.
- 5.1%, the same lapse ratio in 2023, before the increase.
- 86.9%, renewal premium persistency in 2023.
- 87.6%, renewal premium persistency in 2024 across U.S. individual life insurers.
- $169,000, average in force policy size in 2023.
- $189,000, average in force policy size in 2024.
- 24%, share of the U.S. individual life insurance market represented by Indexed Universal Life new premiums in 2024.
Recent Developments
- The lapse ratio for U.S. individual life insurers increased from 5.1% in 2023 to 7.0% in 2024, indicating a notable shift in policy retention.
- Renewal premium persistency improved slightly from 86.9% in 2023 to 87.6% in 2024, suggesting that while more policies lapsed, those that remained tended to renew.
- The average face amount of active, in-force policies rose from $169,000 in 2023 to $189,000 in 2024.
- In 2024, the new premium for Indexed Universal Life reached a record high, reflecting continued growth and shifting consumer preferences.
- New premiums for Whole Life policies declined 4% in 2024 compared with 2023, even as some rebound occurred in the fourth quarter.
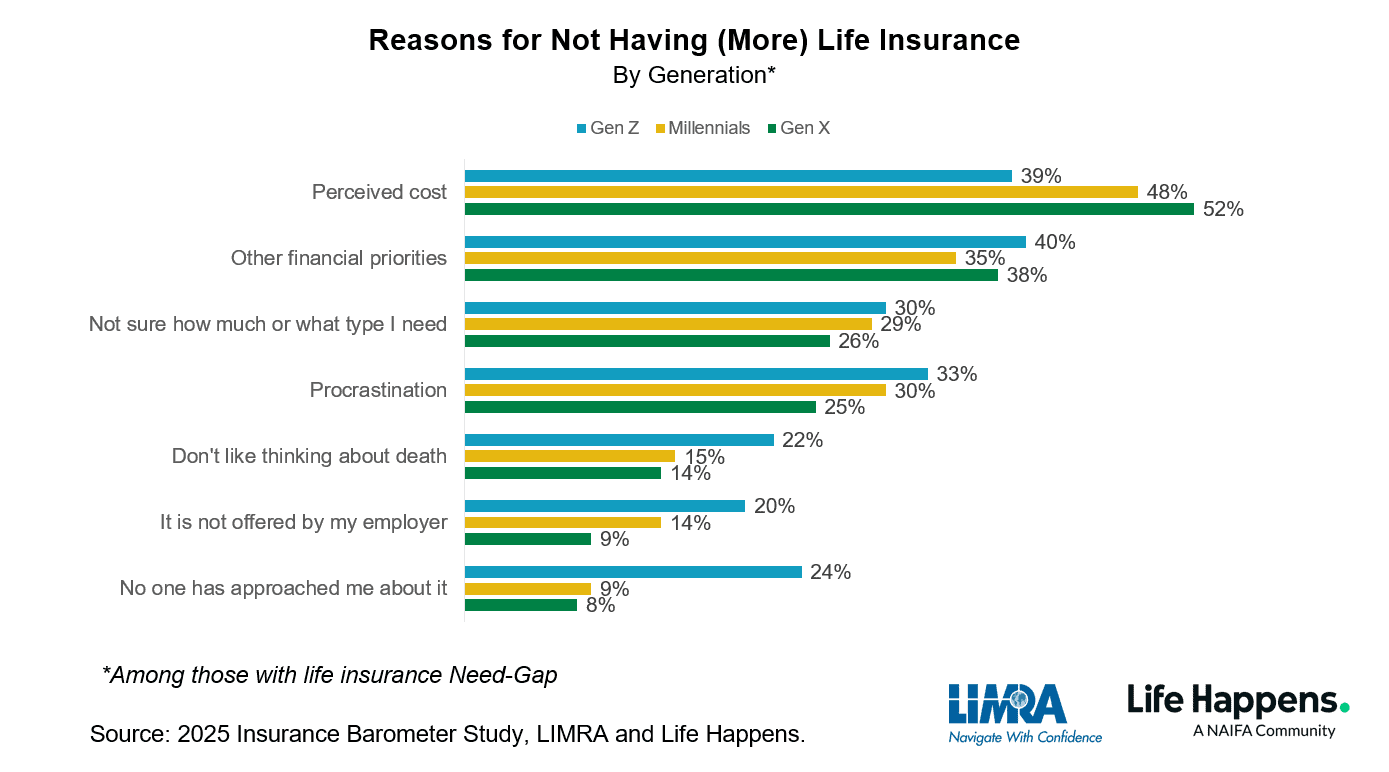
Top Reasons for Not Having Life Insurance by Generation
- 52% of Gen X say perceived cost is the main barrier to buying more life insurance, the highest among all generations.
- 48% of Millennials and 39% of Gen Z also cite cost concerns as their top reason.
- 40% of Gen Z prioritize other financial obligations, slightly more than 38% of Gen X, and 35% of Millennials.
- Uncertainty about coverage needs affects 30% of Gen Z, 29% of Millennials, and 26% of Gen X.
- Procrastination is common, reported by 33% of Gen Z, 30% of Millennials, and 25% of Gen X.
- 22% of Gen Z avoid the topic because they don’t like thinking about death, compared to 15% of Millennials and 14% of Gen X.
- 20% of Gen Z say lack of employer offering is a barrier, while only 14% of Millennials and 9% of Gen X agree.
- 24% of Gen Z have never been approached about life insurance, unlike 9% of Millennials and 8% of Gen X.
What Is an Insurance Policy Lapse Rate?
- The average lapse rate for life insurance policies ranges from 5% to 20% annually.
- About 30% of term life insurance policies lapse before the end of their term.
- Nearly 15% of whole life insurance policies experience lapse within the first five years.
- Policyholders aged 25-34 have a lapse rate exceeding 18%, higher than older age groups.
- Nonpayment of premiums accounts for around 70% of policy lapses.
- Voluntary surrenders make up roughly 25% of lapses in permanent life insurance.
- High lapse rates can reduce insurers’ active policies by up to 10% in a given year.
- Persistency rates improve by 5-7% when insurers offer flexible premium payment options.
- Insurers use lapse rate data to forecast liabilities with an accuracy margin of ±3%.
- Product-specific lapse rates vary widely, with annuities showing as low as 2-5% annual lapses, compared to term policies.
How Lapse Rates Are Calculated in Insurance
- Lapse rate equals (lapsed policies ÷ average in force policies) × 100 for the period.
- Annual lapse ratios typically range from 5% to 20% across life insurance products.
- Renewal premium persistency rates average about 80-90% annually.
- Lapse rates vary by policy duration, with first-year lapses often exceeding 20%.
- Machine learning models improve lapse timing forecasts by reducing error margins to less than 5%.
- Whole life policies show persistency rates above 85% after 10 years.
- Term policies often have higher lapse rates, averaging around 25% in early years.
- Actuarial models include variables like issue age and payment mode, influencing lapse estimations by up to 10%.
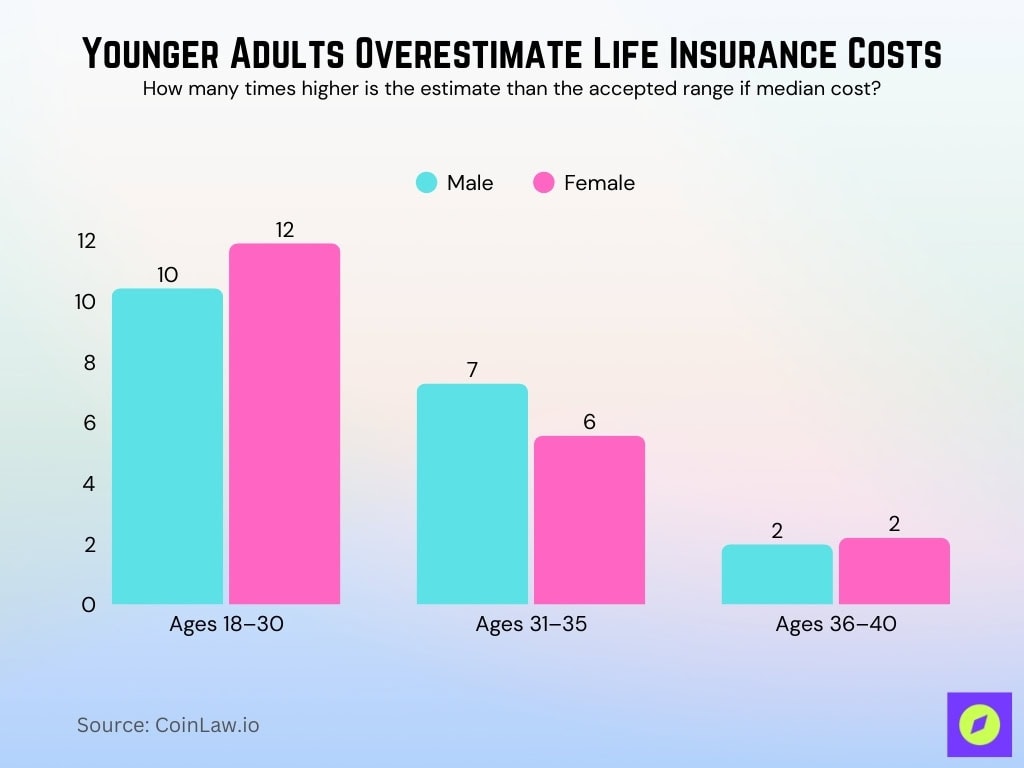
Younger Adults Overestimate Life Insurance Costs
- Women aged 18–30 overestimated the cost of life insurance by 11.9×, the highest among all groups.
- Men aged 18–30 estimated costs at 10.42× higher than the actual median, also significantly inflated.
- Among those aged 31–35, men overestimated by 7.28×, while women estimated 5.56× higher.
- Overestimation drops notably for older groups: ages 36–40 saw men at 1.98× and women at 2.19×.
- These findings show that younger adults, especially those under 30, have the greatest misconceptions about life insurance affordability.
Term Life Insurance Lapse Rate Statistics
- Overall individual life lapse ratio for U.S. insurers reached 7.0% in 2024, up from 5.1% in 2023.
- Term life showed unusually high lapse or nonrenewal patterns at early durations, especially 10 to 20-year terms, following the COVID period.
- Exposure data for 2023 showed rising term life lapse and surrender events compared with 2022.
- Shock lapse rates for 20-year term policies spiked to 83.5% in 2023, up from pre-COVID levels near 76%.
- Term life accounted for about 19% of U.S. life insurance market premiums in 2024.
- Despite higher lapse rates, term life remains attractive for consumers seeking affordable coverage.
- Rising lapse rates in term products can pressure insurer pricing assumptions.
Universal Life Insurance Lapse Rate Statistics
- UL lapse rates decreased by 15% from 2015 to 2021 compared to prior years.
- Larger UL policies show lapse rates up to 25% higher than smaller face amounts.
- UL policies with secondary guarantees have surrender rates 3 times higher than standard UL at older ages.
- UL and VUL surrender rates were around 12% in 2023, higher than whole life rates of 5%.
- Interest rate spikes in 2024 may increase UL surrender risk by up to 10%.
- UL policies with premium flexibility see lapse rates rise by 8-10% during policyholder life changes.
- Insurers report UL persistency rates around 75% at year 10.
- Market volatility in 2024 could boost UL lapse risk by up to 7%.
- UL lapse modeling accuracy improved by 20% with advanced actuarial techniques.
Whole Life Insurance Lapse Rate Statistics
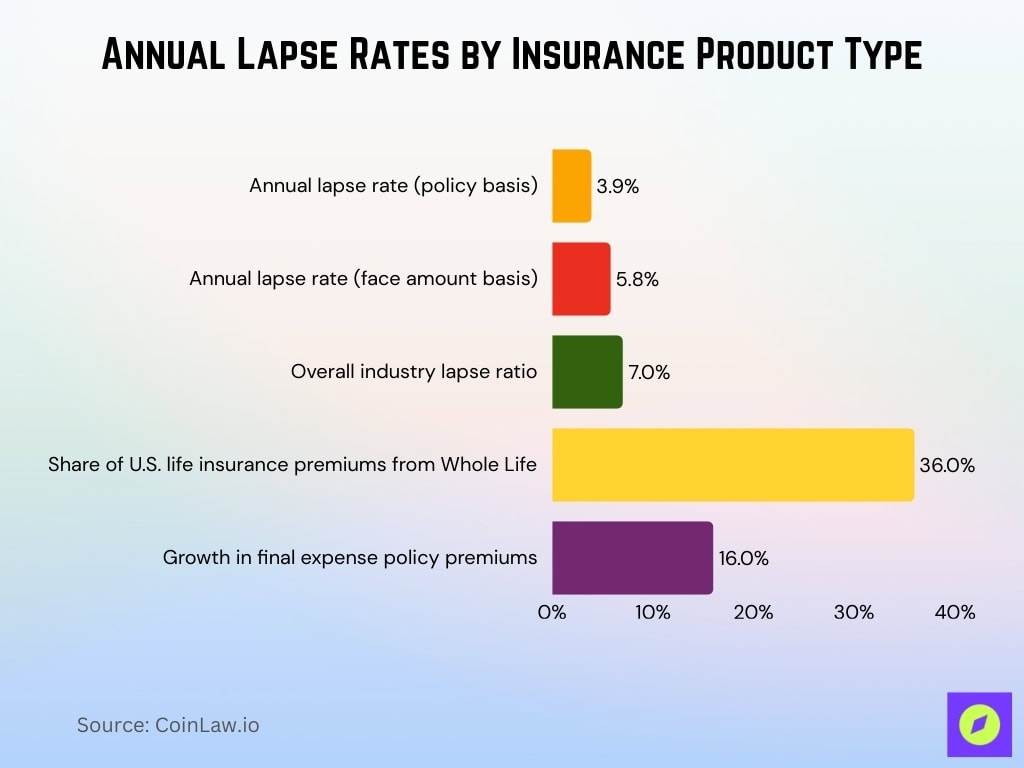
- Annual lapse rates for whole life policies have historically been low, around 3.9% on a policy basis and 5.8% on a face amount basis.
- Whole life contributes less to aggregate lapse ratios than term or universal life, but overall lapse ratios rising to 7.0% suggest some indirect impact.
- Whole life accounted for about 36% of total U.S. premiums.
- Final expense policies, often structured as whole life, saw a 16% rise in new annualized premiums.
- Stable whole life persistency helps insurers maintain long-term reserves and predictable underwriting risk.
Variable Life and VUL Lapse Rate Statistics
- The U.S. variable life market was valued at $138.4 billion in 2025, up from $130.97 billion in 2024.
- VUL lapse rates averaged 15-18% annually, higher than whole life rates around 5-7%.
- Surrender rates for VUL increased by 3% in the 2023 post-COVID era lows.
- Market volatility in 2024 raised VUL surrender likelihood by up to 12%.
- VUL and UL policies account for about 30-35% of the life insurance market share.
- Some insurers reported double-digit premium growth of over 10% for VUL in 2024.
- VUL lapse rates spike by 20% during market downturns.
- VUL contributes to 30% higher reserve uncertainties for insurers compared to whole life.
- Persistency rates for VUL declined by 5% between 2022 and 2024.
- VUL lapse variability causes actuarial liability projections to vary by ±8% annually.
Lapse Rates by Face Amount and Policy Count
- Universal life lapse rates rise by 12-15% in higher face amount bands.
- Whole life lapse by count was 3.9%, while lapse by face amount was 5.8%.
- The average U.S. individual life policy size increased to $189,000 in 2024, up from $169,000 in 2023.
- High-value policy lapses can understate financial impact by up to 30% in aggregate ratios.
- Insurers track face amount persistency with an accuracy of ±5% for risk control.
- Growth in average policy size has increased reserve risk exposure by 20% in recent years.
- Value-weighted lapse rates diverge from count-based lapse rates by as much as 2 percentage points.
- Larger policies exhibit lapse rates up to 50% higher than small policies on a weighted basis.
Cover Type and Benefit Category
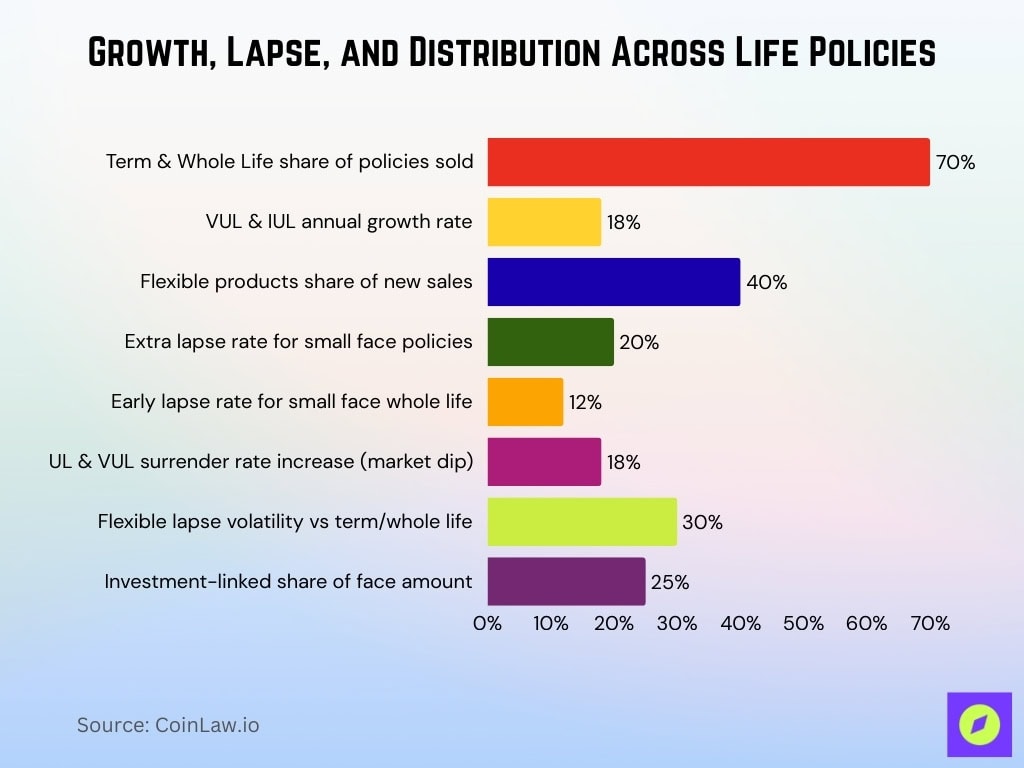
- Term and whole life products represent well over 70% of policies sold and a majority of individual life premiums, with UL/IUL/VUL making up the balance depending on the market and distribution mix.
- VUL and IUL policies grew by 18% annually over the past five years.
- Flexible products account for 40% of all new life insurance sales.
- Smaller face amount policies lapse at rates up to 20% higher in early durations.
- Whole life small face amount policies had early lapse rates around 12%.
- UL and VUL surrender rates rise by 15-18% during adverse market conditions.
- Flexible product lapse volatility is 30% higher than term or whole life.
- Investment-linked products represent 25% of total life insurance face amounts.
Distribution Channel and Advice Model
- Digital platforms increased term and VUL sales by 15% annually from 2022 to 2025.
- VUL sales through nontraditional channels grew by 20% in 2024.
- Independent channels see surrender rates 10-12% higher for UL and VUL products.
- Traditional advice-driven channels report whole life lapse rates around 4%, lower than digital channels.
- Online self-directed buyers have lapse rates up to 18%, nearly double traditional buyers.
- Distribution mix can cause insurer persistency volatility fluctuations of ±7%.
- Flexible product sales via digital channels rose by 25% in 2023-2025.
- Lapse management’s importance grew by 30% with digital and flexible product growth.
- Advice-driven sales showed 85% persistency rates, digital channels closer to 70%.
- Nontraditional distribution channels contributed to 40% of VUL sales in 2024.
Lapse Rates by Insurer and Market Share
- The top 10 U.S. life insurers accounted for roughly 45–50% of total individual life premiums in 2024, highlighting how concentrated the market remains at the top.
- Total direct individual life premiums written by leading U.S. life insurers were around $180 billion in 2024, reflecting a large and relatively concentrated market.
- Northwestern Mutual reported a 3.5% lapse ratio and 94.1% persistency in 2023.
- State Farm Life reported roughly 5.4% lapse and 93.5% persistency.
- Pacific Life reported a 16.3% lapse ratio, highlighting wide variation among carriers.
- Product design, underwriting, and retention strategy drive differences in lapse performance.
- Smaller or flexible product heavy insurers face greater surrender risk.
- Diversified insurers with traditional protection portfolios benefit from stable persistency.
Economic Conditions and Policy Lapse Behavior
- Rising interest rates increased insurer investment returns by 7-10% in 2024.
- Insurer-managed assets grew to $4.5 trillion in 2024.
- Policyholders experiencing financial or health changes have a 15% higher lapse rate.
- Economic shocks increase lapse rates by up to 20% during downturns.
- Lapse rates show a long-term structural trend of 5% annually plus cyclical spikes.
- Low interest rates reduce surrender incentives by 10-12% on older guaranteed policies.
- High-interest-rate environments increase surrender incentives by up to 15%.
- Use of alternative assets raised insurer volatility by 8%, affecting policyholder confidence.
- Economic conditions account for about 60% of lapse rate fluctuations.
Persistency Ratios vs Lapse Rates in Insurance
- U.S. individual life insurers had a persistency ratio of 86.9% in 2023.
- Top insurers achieved persistency rates above 94%.
- Persistency can remain steady while lapse rates spike in select product segments by up to 10%.
- Face amount lapse rates averaged 5.3% annually during certain study periods.
- High value lapse rates can increase reserve risks by 20% or more.
- Active engagement improves persistence by up to 7% annually.
- Disciplined product design reduces lapse rates by 5-8% across portfolios.
Strategies to Reduce Insurance Policy Lapse Rates
- Longer guarantee periods reduce lapse rates by up to 12%.
- Flexible payment options lower lapse rates by 8-10% during financial hardship.
- Customer education programs improve persistency by 15% on average.
- Persistency bonuses increase policy retention rates by 6-9%.
- Regular policy reviews reduce lapse rates by 5-7%.
- Hybrid products with surrender penalties lower lapse rates by up to 10%.
- Predictive modeling improves early lapse risk identification accuracy by 20%.
- Targeted outreach based on modeling increases retention by 12%.
- Transparent value communication decreases short-term surrenders by 7%.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Historically, whole life policies have shown typical annual lapse rates of about 3.5–4.0% on a policy‑count basis, reflecting their strong long‑term persistency relative to other products.
Flexible premium UL and VUL generally experience higher lapse and surrender activity than whole life, with overall lapse rates often in the 5–9% range versus roughly 3–4% for whole life, especially at later durations.
In 2024, about 51% of American adults reported owning some form of life insurance coverage, leaving a sizeable protection gap across many demographic groups.
Conclusion
The data underscore that lapse rates remain a core concern for the life insurance sector, influenced by product mix, economic conditions, insurer practices, and policyholder behavior. While core products like term and whole life continue to offer relative stability, growing consumer demand for flexible and investment-linked policies, UL, VUL, and IUL, raises the stakes for lapse management. Insurers that combine prudent product design, active persistency efforts, and robust communication stand a better chance at reducing lapse risk and maintaining a solid in-force base. For consumers and insurers alike, understanding these dynamics matters and offers a roadmap toward more sustainable protection and reliable coverage.