Synthetic identity fraud has grown from a niche concern to one of the most urgent threats facing financial services, ecommerce platforms, and government benefit systems. By blending real personal data with fabricated details, fraudsters create convincing false identities that can pass verification checks and exploit systems at scale. This trend affects banks’ underwriting and lending processes, and it also undermines trust in digital interactions. In this article, we break down the latest statistics, financial impacts, and trends shaping synthetic identity fraud.
Editor’s Choice
- Estimated U.S. economic losses from synthetic identity fraud could reach $30 – $35 billion annually.
- U.S. lenders faced over $3.3 billion in exposure to synthetic identities tied to new accounts in recent data.
- Fraud rates rose for 67% of financial institutions in 2025.
- 8.3% of digital account creations were suspected fraudulent in H1 2025.
- AI/deepfake concerns were cited by 64% of industry respondents as a top fraud threat.
- Synthetic fraud’s reach is expanding beyond finance into e-commerce and public benefits sectors.
Recent Developments
- AI and generative models are now central tools for creating harder‑to‑detect synthetic identities, automating large‑scale fraud.
- Fraudsters are increasingly using deepfake IDs and synthesized documents to bypass identity checks.
- The uptick in synthetic identity fraud comes as financial institutions face higher fraud pressures overall; 67% of banks and fintechs saw fraud rates climb in 2025.
- Digital account creation fraud risks continue to rise, with 8.3% of digital onboarding attempts flagged as suspicious in early 2025.
- Firms report AI/deepfakes as a primary identity fraud concern, cited by 64% of respondents.
- Predictions for 2026 highlight stolen biometric data as a new vector for synthetic identity creation.
- Synthetic identity fraud trends increasingly overlap with broader cybercrime trends driven by AI automation.
Fraud Types by Frequency and Financial Impact
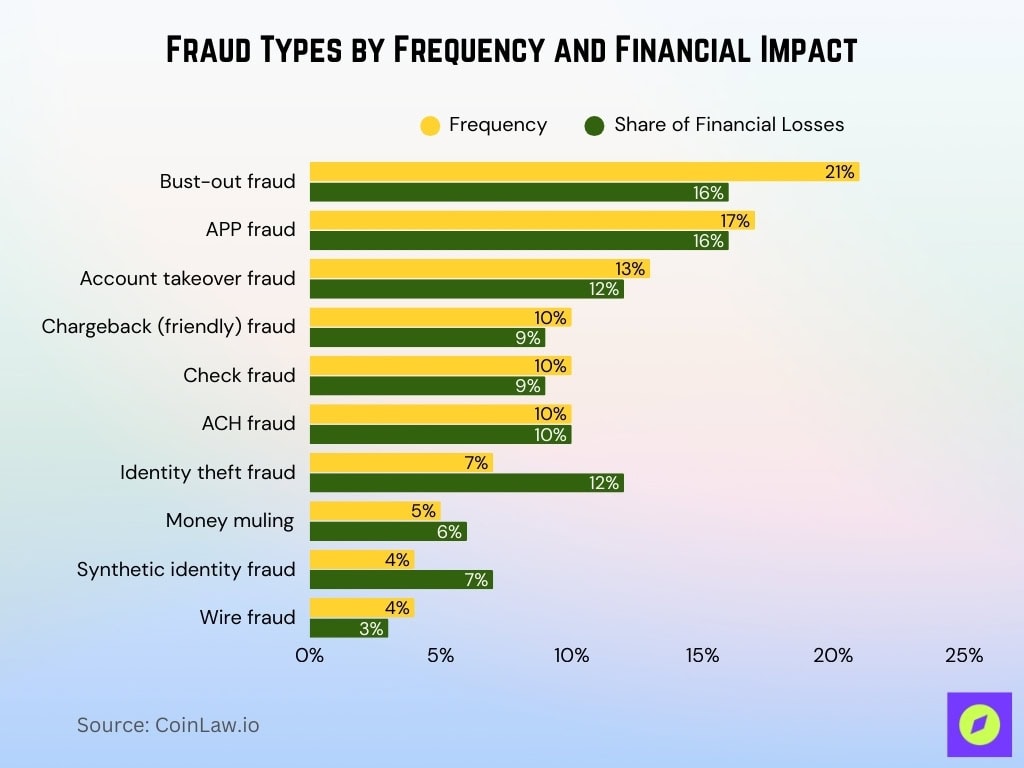
- Bust-out fraud is the most frequent fraud type, accounting for 21% of all fraud cases, while also driving 16% of total financial losses, highlighting its scale and repeat nature.
- Authorized Push Payment (APP) fraud represents 17% of fraud incidents and contributes 16% of overall losses, making it one of the costliest fraud categories per incident.
- Account takeover fraud makes up 13% of fraud occurrences and 12% of financial losses, reflecting its continued dominance in digital and credential-based attacks.
- ACH fraud shows a balanced impact, responsible for 10% of fraud frequency and 10% of total losses, indicating consistent monetary damage per case.
- Chargeback (friendly) fraud accounts for 10% of fraud cases but only 9% of losses, suggesting high volume but lower average loss values.
- Check fraud also represents 10% of fraud activity and 9% of losses, reinforcing its persistence despite declining check usage.
- Identity theft fraud stands out for its outsized financial impact, generating 12% of total losses from just 7% of cases, pointing to higher loss severity per incident.
- Money muling contributes 5% of fraud incidents and 6% of financial losses, reflecting its role as an enabler in broader fraud networks.
- Synthetic identity fraud accounts for only 4% of fraud frequency yet drives 7% of financial losses, underscoring its high cost and long-duration nature.
- Wire fraud remains relatively limited, representing 4% of fraud cases and just 3% of financial losses, compared with more scalable digital fraud schemes.
What Is Synthetic Identity Fraud?
- Synthetic identity fraud involves creating a new fake identity by combining real personal data with fabricated details to open credit lines or other accounts.
- Synthetic identity fraud accounts for up to 80% of new account fraud cases.
- Businesses lose an estimated $20–$40 billion globally to synthetic identity fraud each year, with U.S. losses alone projected to exceed $23 billion by 2030.
- US lenders faced $3.3 billion exposure from synthetic identities in H1 2025.
- 44% of organizations rank synthetic identity fraud as the top-tracked fraud type.
- Synthetic identities were used in 21% of first-party frauds detected in 2025.
- AI-enabled fraud losses projected to $40 billion by 2027 from $12.3 billion in 2023.
- The life insurance sector links synthetic fraud to $30 billion yearly losses.
- 0.08% synthetic government benefit transactions expose $283 million annual risk.
Financial Losses From Synthetic Identity Fraud
- Some estimates suggest that synthetic identity fraud has cost the U.S. economy between $30 billion and $35 billion annually.
- Conservative projections put U.S. losses at $23 billion by 2030 due to synthetic fraud alone.
- U.S. lenders saw $3.3 billion in exposure to suspected synthetic identities tied to new accounts.
- Fraud cost trends show an increase in fraud‑related revenue loss for businesses, with U.S. firms losing 9.8% of revenue to fraud on average.
- Identity fraud costs overall climbed to $27.2 billion in consumer losses in 2024, up 19% year over year.
- FBI identity fraud complaints in 2025 reflected more than $262 million in losses across various schemes.
- Cybercrime costs, including identity and synthetic fraud, are projected to rise to $10.5 trillion annually by 2025.
- Fraudsters often exploit seasonal spending peaks, increasing average losses tied to identity fraud events.
Economic Impact of Identity Fraud by Loss Size
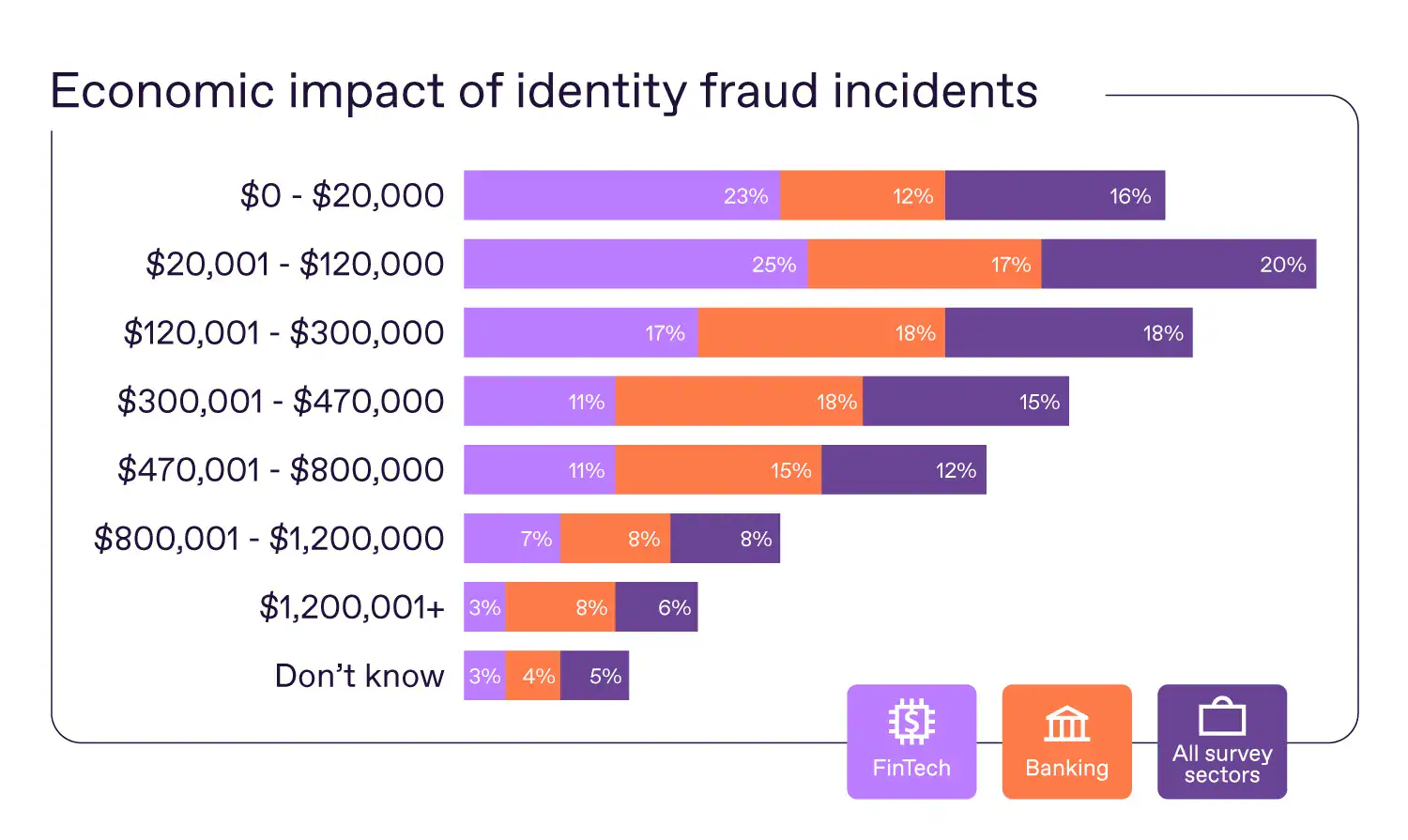
- Lower-value identity fraud dominates in FinTech, with 23% of incidents resulting in losses of $0–$20,000 and 25% falling in the $20,001–$120,000 range, showing that most FinTech cases involve smaller but frequent losses.
- Banking-sector identity fraud skews toward higher losses, with 18% of incidents in both the $120,001–$300,000 and $300,001–$470,000 brackets, highlighting greater exposure to mid-six-figure fraud events.
- Across all surveyed sectors, the most common loss range is $20,001–$120,000, accounting for 20% of identity fraud incidents, making it the single largest loss bracket overall.
- Severe identity fraud losses above $300,000 represent a meaningful share of cases, totaling 27% in banking when combining the $300,001–$470,000 and $470,001–$800,000 ranges.
- High-value fraud exceeding $800,000 remains less frequent but impactful, accounting for 8% of banking incidents and 6% across all sectors, reinforcing the outsized damage of large-scale identity fraud.
- FinTech firms report fewer extreme losses, with only 3% of cases exceeding $1.2 million, compared with 8% in banking, suggesting differences in account limits, transaction controls, and customer profiles.
- A small but notable share of respondents reported uncertain loss amounts, with 5% across all sectors selecting “Don’t know”, pointing to measurement and reporting gaps in identity fraud assessments.
Synthetic Identity Fraud In Banking And Lending
- Fraudulent activity in financial services rose about 21% between 2024 and 2025, driven by identity and synthetic schemes. Many banks now flag 1 in every 20 verification attempts as potentially fraudulent.
- 62% of banks say digital onboarding is the highest risk point for synthetic identity fraud exposures.
- Reported identity and related fraud losses in financial services reached $12.5 billion in 2024, up 25% over 2023, with synthetic identities a growing driver.
- Large banks reported fraud losses roughly four times the industry average, highlighting the magnitude of synthetic and related threats.
- U.S. lenders faced $3.3 billion in exposure to synthetic identities tied to newly opened accounts through 2024.
- Financial institutions increasingly rely on behavioral and public data signals to fight synthetic fraud before credit is extended.
- Traditional KYC and static identity checks struggle to keep pace with fraud sophistication powered by AI‑generated identity data.
- Customer trust in identity verification remains low, with only 13% of consumers feeling fully secure opening new accounts.
Credit Cards And Consumer Finance
- Synthetic account fraud attempts grew 153% from late 2023 to early 2024, reflecting the rising use of fictitious identities to open credit cards and lines of credit.
- Overall identity fraud cases, including credit card fraud, rose significantly, with 323,459 credit card fraud reports in H1 2025, up about 51% year over year.
- New account fraud represents approximately 90% of all credit card fraud, often tied to synthetic identities.
- Identity‑related financial fraud accounts increased 12% annually since 2020, a trend expected to continue.
- Americans aged 30‑39 reported the highest identity fraud reports, often related to credit card and loan fraud.
- Cross‑border and digital banking fraud channels contribute to rising fraud volumes in consumer finance.
- Advanced AI tools help fraudsters refine credit‑application documents, challenging traditional prevention methods.
- Consumer confidence in credit safety remains weak, with rising fraud alerts impacting financial behavior.
Share of Fraud Attributed to Synthetic Identities
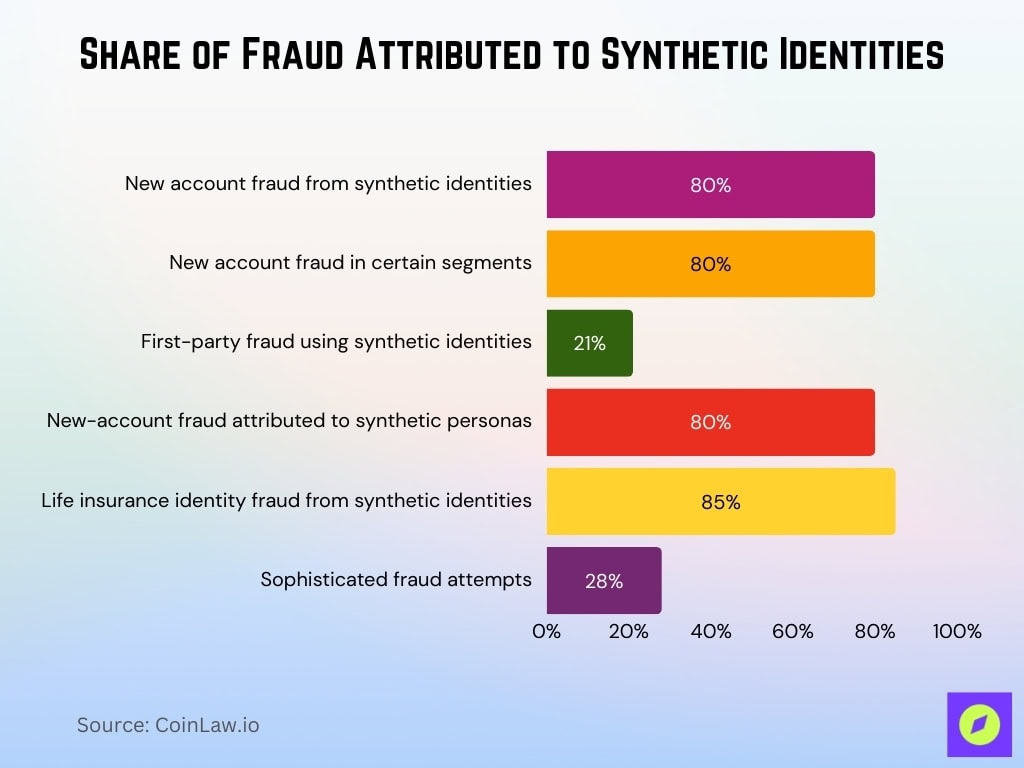
- Synthetic identities account for over 80% of new account fraud.
- Synthetic accounts represent 80% of all new account fraud in certain segments.
- 21% of first-party frauds detected in 2025 used synthetic identities.
- Over 80% of new-account fraud is attributed to synthetic personas.
- Synthetic identity fraud accounts for up to 85% of life insurance identity fraud.
- Sophisticated fraud nearly tripled to 28% of attempts in 2025.
Government Benefits And Public Sector
- 0.08% of government benefit transactions involve synthetic identities, exposing $283 million annual risk.
- Synthetic identities targeted government programs like unemployment and welfare during pandemic payouts.
- Medicare lost $60 billion to various fraud types, including synthetic identities, in 2017.
- Synthetic fraud was used to intercept tax returns and benefits, with federal False Claims Act recoveries at $3.7 billion in 2017.
- Government benefit programs are vulnerable to synthetic ID claims, diverting funds from legitimate recipients.
- Synthetic identity fraud exploits public sector systems for tax fraud and entitlement programs.
- 0.08% synthetic rate in government identity verifications highlights persistent public sector risk.
- Fraudsters use children’s SSNs for synthetic IDs in benefits, undetected for years.
E-commerce and Digital Payments
- Global e-commerce and online payment fraud is projected at $48 billion annually.
- 40% of global ecommerce fraud attacks originate from the U.S.
- Online merchants lose 2.9% of revenue on average to fraud.
- Fraud management costs average 10% of revenue for e-commerce merchants.
- E-commerce marketplaces hit 19.2% net fraud rate, nearly five times the global average.
- Synthetic identity document fraud surged 311% in North America in Q1 2025.
- Financial services net fraud rate exceeds 5.5% of online identity verifications.
- Payment method fraud rate reaches 6.6%, surpassing ID document fraud.
- Digitally presented media is 300% more likely to be AI-generated or altered.
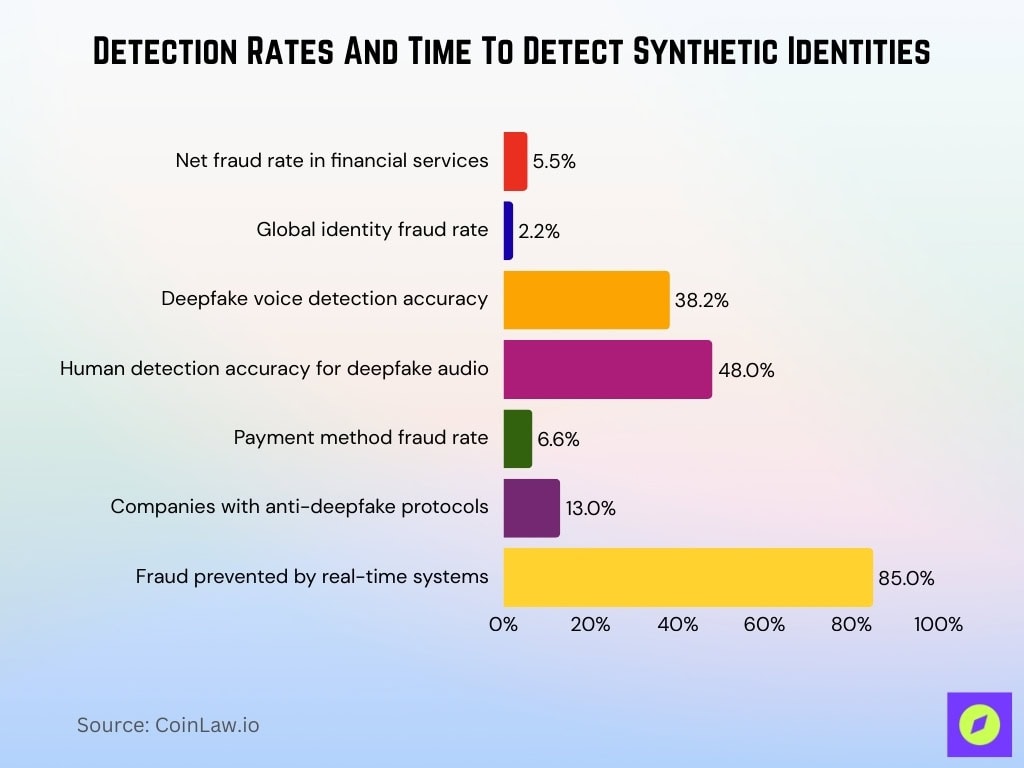
Detection Rates And Time To Detect Synthetic Identities
- Net fraud rate in financial services exceeds 5.5% of verifications.
- Global identity fraud rate stands at 2.2%.
- Deepfake voice detection accuracy is as low as 38.2%.
- Human detection of deepfake audio at 48% accuracy.
- Payment method fraud rate reaches 6.6%.
- 13% of companies have anti-deepfake protocols.
- Real-time systems prevent 85% more fraudulent transactions.
- Deepfake files projected at 8 million.
- Synthetic identities develop undetected for months.
Victim Demographics And Vulnerable Populations
- Millennials comprise 42% of identity theft reports.
- 30-39 age group accounts for 21% of all claims.
- Generation Z represents 21% of reports.
- Adults 60+ suffer 41.46% of total financial losses.
- People 20-29 are most likely (44%) to report fraud losses.
- 24.6% of victims were victimized three times.
- 63% of cybersecurity leaders are concerned about deepfakes.
- 60% of organizations are unprepared for deepfake threats.
- 71% globally unaware of deepfakes.
Data Breaches Fueling Synthetic Identity Fraud
- Global net fraud rate exceeds 4% of online identity verifications for the third year.
- Digitally presented media is 300% more likely to be AI-generated or altered.
- E-commerce marketplaces hit with 19.2% net fraud rate.
- Financial services net fraud rate surpasses 5.5% of verifications.
- Crypto/lending platforms see 38% YoY fraud increase.
- Impersonation fraud accounts for over 85% of attacks.
- Synthetic identities are used in 21% of first-party frauds.
- 44% of firms rank synthetic identity fraud as the top-tracked type.
- Digital forgeries comprise 35% of document fraud.
- Synthetic identity fraud causes 80% of credit card fraud losses.
Synthetic Identities And AI / Deepfake‑Driven Fraud
- Deepfake‑powered fraud has surged dramatically; files created with deepfake technology grew from ~500,000 in 2023 to ~8 million in 2025.
- Fraud attempts leveraging deepfake content have climbed more than 2,000% over the last three years, illustrating rapid criminal adoption.
- In some sectors, deepfakes now account for roughly 6.5% of all fraud attacks, reflecting the scale of AI misuse.
- Deepfake fraud tied to credential phishing and social engineering has jumped over 3,000%, driven by automated spear phishing and AI‑generated content.
- Traditional deepfake detection remains challenging: human detection rates are under 25% for high‑quality video manipulations.
- Around one in every five biometric fraud attempts involves deepfakes, where attackers employ face swaps and animated selfie manipulation to defeat verification systems.
- A large industry survey found 64% of fraud professionals cite deepfakes as a top fraud concern, second only to broader identity misuse issues.
Synthetic Identity Fraud Attack Methods And Tactics
- First-party synthetic identity fraud accounts for 21% of detections.
- Impersonation fraud comprises over 85% of online attacks.
- 2% of fake documents are generated by AI tools like ChatGPT.
- AI-enabled fraud is projected to reach $40 billion by 2027.
- Synthetic identities are used in 1 in 5 first-party frauds.
- Multi-step fraud attacks rose 180% YoY.
- 1 in 10 adults encountered AI voice cloning scams.
- 77% of AI voice scam victims reported financial losses.
- Deepfake injection bypasses basic verification checks at scale.
- Credential stuffing employs human-like variability via AI.
Technology Solutions For Detecting Synthetic Identities
- Behavioral biometrics achieves 98.7% accuracy against synthetic fraud.
- Universal deepfake detector reaches 98% accuracy.
- AI-powered fraud detection reduces false positives by 75-90%.
- Behavioral biometrics detects with <220ms latency.
- 2% of fake documents generated by AI tools were detected.
- Real-time ML prevents 85% more fraudulent transactions.
- Liveness detection combined with AI improves accuracy to 99.1% on real IDs.
- AI analyzes thousands of security features per document.
- Federated learning preserves privacy in ML models.
- Networks cover 180 billion compromised identities.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Up to 80% of all new account fraud is estimated to be driven by synthetic identity fraud.
Synthetic identity fraud could generate $23 billion in losses in the U.S. by 2030.
U.S. businesses reported losing 9.8% of annual revenue to fraud in 2025.
16% of merchants reported synthetic identity fraud as their most common source of fraud losses.
Conclusion
Synthetic identity fraud stands as a core threat across finance, ecommerce, and public services, driven by data breaches, AI‑driven deepfakes, and evolving fraud tactics. Losses continue to escalate, and synthetic schemes now outpace traditional identity theft in sophistication and scale. While detection challenges persist, advances in behavioral analytics, layered authentication, and AI‑powered identification tools promise stronger defenses, but only if organizations adopt them proactively.
As fraud tactics evolve faster than ever, the gap between attack innovation and defense readiness will determine how tightly systems can resist synthetic abuse. Continuous investment in detection technology and cross‑industry collaboration will be essential to curbing these threats.