In late 2022, a woman in the Bahamas used her mobile phone to purchase groceries with Sand Dollar, the country’s central bank digital currency (CBDC). She wasn’t an early adopter or a tech enthusiast, just someone benefiting from financial innovation that made everyday transactions smoother. Fast forward, and stories like hers are becoming more common, from Nigeria’s eNaira to China’s Digital Yuan.
As CBDCs move from concept to reality, regulations play an increasingly critical role. They aim to strike a balance between innovation and stability, ensuring secure, inclusive, and efficient monetary systems. This article dives into the latest CBDC regulatory statistics, giving you a clear, digestible picture of the landscape that’s reshaping how the world uses money.
Editor’s Choice
- 134 countries, representing 98% of global GDP, are exploring or developing CBDCs in 2025, up from 114 countries in 2023.
- 3 countries have fully launched a CBDC as of mid‑2025 – the Bahamas, Jamaica, and Nigeria – while China and India remain in large‑scale pilot phases.
- Retail CBDC pilots are active in 36 countries, with 12 of them targeting cross-border functionality.
- 62% of central banks cite financial inclusion as a primary motivation for CBDC development in 2025.
- 75% of jurisdictions have implemented privacy and data protection frameworks specific to CBDCs.
- 72% of global banks are collaborating with the private sector to develop CBDC-compatible infrastructure.
- 48% of surveyed governments plan to integrate CBDCs into national payment systems by 2026.
- 39% of central banks are piloting wholesale CBDCs for interbank settlements in 2025.
- 54% of emerging markets report that CBDC initiatives have improved access to digital finance by mid-2025.
The Basics of CBDC
- 64 countries have passed initial legislation enabling central banks to issue CBDCs.
- 82% of retail consumers in emerging markets are aware of CBDCs.
- 70% of policymakers express concerns over potential impacts on traditional banking models.
- 48% of central banks in developing economies prioritize financial inclusion as their main reason for exploring CBDCs.
- 87% of countries working on CBDCs are building digital currencies that support interoperability with existing payment platforms.
- 56% of central banks are conducting joint research and pilot programs with international institutions in 2025.
- 41% of governments have identified CBDC integration as a component of their national digital finance strategies.
- 38% of surveyed banks plan to adopt CBDC-based settlement systems within the next two years.

Global Overview of CBDC Regulations
- 134 countries are actively exploring CBDC regulation frameworks as of March 2025, compared to 114 countries in 2023.
- 28 countries have passed comprehensive CBDC regulatory legislation, including Japan, Sweden, and Brazil.
- 62% of countries piloting CBDCs have integrated AML and KYC regulations into their frameworks.
- The International Monetary Fund estimates that 48 countries are aligning their CBDC frameworks with FATF guidelines.
- 75% of countries with live CBDCs have introduced digital identity verification protocols as a mandatory part of transactions.
- $5.6 billion has been invested globally in CBDC-related infrastructure and regulatory compliance in 2025, a 25% increase over 2024.
- 41% of countries working on CBDCs have established dedicated regulatory bodies to oversee their development and deployment.
- 80% of advanced economies, such as Canada, Australia, and Germany, have released draft CBDC regulations focusing on privacy, security, and consumer protection.
CBDC Use Cases
- 62 countries pilot CBDCs for domestic retail payments, including South Korea and India.
- 27 countries test CBDCs for cross-border payments, such as the mBridge project involving China, Thailand, Hong Kong, and the UAE.
- 58% of governments in developing nations use CBDCs for social welfare and G2P payments.
- 46% of central banks explore CBDCs to reduce reliance on physical cash.
- 37% of countries report that CBDCs lowered transaction costs by an average of 15% compared to traditional systems.
- 29% of surveyed central banks implement CBDCs for tax collection and remittance services.
- CBDCs facilitate $42 billion in cross-border trade settlements in 2025, a 35% increase from 2024.
- 18% of central banks work on CBDCs for M2M transactions in the IoT ecosystem.
- 44% of emerging economies deploy CBDCs to enhance financial inclusion through programmable payments.
- 52% of wholesale CBDC pilots target faster interbank settlements, reducing processing times by 40%.
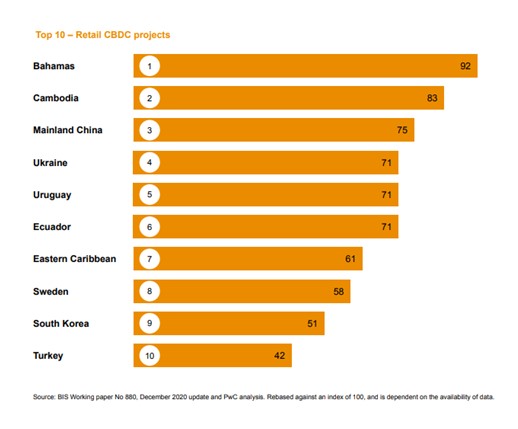
Top Retail CBDC Projects Worldwide
- Bahamas leads globally with a CBDC index score of 92, driven by early implementation of the Sand Dollar.
- Cambodia ranks second with a score of 83, showcasing strong progress through its Bakong project.
- Mainland China follows closely with 75, reflecting the rapid expansion of its digital yuan pilots.
- Ukraine, Uruguay, and Ecuador are tied at 71, indicating equal advancement in retail CBDC development.
- Eastern Caribbean achieves a score of 61, highlighting regional coordination through DCash.
- Sweden scores 58, led by the e-krona pilot aimed at modernizing cash alternatives.
- South Korea registers 51, showing steady experimentation with blockchain-based settlement.
- Turkey closes the top ten with a score of 42, marking early-stage digital lira testing.
CBDC vs. Crypto
- 89% of central banks emphasize that CBDCs aim to complement, not replace, cash and traditional bank accounts.
- 64% of surveyed citizens in Europe and North America trust CBDCs more than private cryptocurrencies for everyday transactions.
- 32% of countries that have banned or restricted cryptocurrencies are advancing CBDC pilots.
- The market cap of cryptocurrencies stands at $1.9 trillion in 2025, while CBDC circulation volumes across live projects total $213 billion.
- 75% of countries issuing CBDCs establish regulatory frameworks to prevent illicit activities, compared to 45% for cryptocurrencies.
- 56% of crypto users in emerging markets express willingness to switch to CBDCs if costs are lower and security improves.
- 100% of CBDCs operate centralized and regulated manner, whereas cryptocurrencies function predominantly decentralized manner without oversight.
- Only 3–4 countries currently grant their CBDCs full legal‑tender status, while many other jurisdictions are still debating or drafting laws on the potential legal tender status of future CBDCs.
Number of Countries Implementing CBDC Regulatory Frameworks
- 19 countries in Africa introduce CBDC regulations, focusing on financial inclusion and cross-border remittances.
- 9 out of 10 G20 nations advance regulatory frameworks for CBDCs as of Q2 2025.
- 45% of countries implementing CBDC regulations require real-time transaction monitoring to prevent fraud.
- 38% of developing nations link CBDC regulations with national digital identity programs, strengthening KYC processes.
- 28 countries legislate CBDC interoperability standards, facilitating cross-border payments and regional trade.
- 22 countries in Europe draft or implement CBDC regulations, including Sweden, France, and Germany.
- 48 countries align CBDC regulations with FATF AML/CFT standards in 2025.
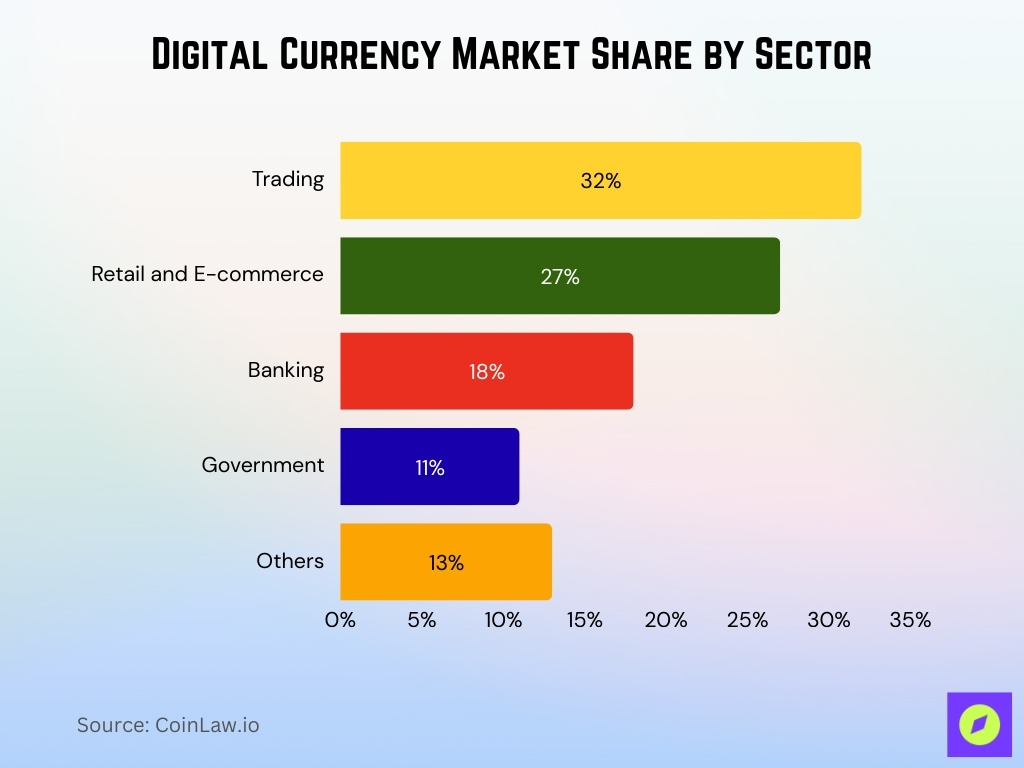
Digital Currency Market Share by Sector
- Trading dominates the digital currency landscape with a 32% share, reflecting its core use in crypto exchanges and asset speculation.
- Retail and E-commerce hold a significant 27%, indicating rapid adoption of digital currencies for online payments.
- Banking accounts for 18%, showing integration into financial services and settlements.
- Government applications, including CBDCs and welfare disbursement, represent 11% of the market.
- Other sectors like remittances, gaming, and donations make up the remaining 13%.
Regional Distribution of CBDC Regulations
- Europe leads with 22 countries drafting or implementing CBDC regulations, including Sweden, France, and Germany.
- Asia-Pacific follows with 19 countries, including China, India, Singapore, and Japan, adopting advanced CBDC legal frameworks.
- Latin America sees 14 countries, including Brazil, Argentina, and Colombia, actively working on CBDC regulations.
- Africa reports 19 countries drafting CBDC laws, driven by financial inclusion and mobile payments ecosystems.
- North America includes the United States and Canada, both in advanced CBDC pilot stages with regulatory consultation papers under review.
- 72% of European CBDC regulations address privacy protections, aligning with GDPR compliance.
- 58% of Asian countries implementing CBDC frameworks prioritize interoperability with private digital payment systems like Alipay and Paytm.
- 35% of African nations adopting CBDCs include cross-border remittance regulations to lower transaction costs.
- 100% of Caribbean countries with CBDCs mandate anti-money laundering (AML) protocols.
Compliance Rates with International CBDC Regulatory Standards
- 48 countries align their CBDC regulations with FATF AML/CFT standards.
- 57% of jurisdictions adopting CBDCs comply with IMF and World Bank guidelines on digital currency issuance.
- 42 countries follow ISO 20022 messaging standards for CBDC transactions, facilitating international interoperability.
- 71% of central banks developing CBDCs engage in regulatory sandbox testing to ensure compliance requirements.
- 65% of countries implement privacy-by-design principles in CBDC frameworks, meeting OECD data governance standards.
- 22% of CBDC pilot projects globally participate in international cross-border payment trials like BIS mBridge.
- 30 central banks regularly share CBDC regulatory practices through BIS CPMI.
- 89% of countries with CBDC initiatives update cybersecurity regulations to meet international resilience benchmarks.
- 45% of central banks adopt ISO 20022 fully in RTGS systems for CBDC compatibility by mid-2025.
Key Regulatory Challenges in CBDC Implementation
- 68% of central banks cite data privacy as their biggest concern in CBDC implementation.
- 53% of regulators express concerns over potential bank disintermediation due to CBDC adoption.
- 46% of jurisdictions report legal ambiguity regarding the legal tender status of CBDCs, delaying deployment.
- 31% of central banks face challenges with cross-border CBDC interoperability due to inconsistent regulatory standards.
- 25% of emerging markets highlight high implementation costs as a barrier to CBDC launch.
- 59% of countries developing CBDCs deal with cybersecurity threats, driving stronger compliance frameworks.
- 40% of regulators worry about centralized control risks, particularly in authoritarian regimes.
- 18% of pilot CBDCs encounter technical glitches due to infrastructure standardization.
- 41% of central banks prioritize privacy protection as the top design characteristic for CBDCs.

Impact of CBDC Regulations on Financial Inclusion
- 78% of countries exploring CBDCs cite financial inclusion as a primary motivation.
- 43% of live CBDC projects result in increased access to digital financial services among unbanked populations.
- Nigeria’s eNaira has onboarded 13 million new users in rural areas since 2023, expanding financial access.
- 48% of surveyed citizens in Latin America report that CBDCs have lower transaction costs, enabling micro-payments and peer-to-peer lending.
- 24% of countries implementing CBDCs include offline payment capabilities, benefiting limited internet regions.
- $6.4 billion in G2P payments disbursed via CBDCs in 2025, targeting social welfare recipients.
- 32% of central banks provide zero-fee CBDC wallets as part of financial inclusion strategies.
- 67% of countries deploying CBDCs integrate them with mobile banking solutions, increasing underserved area reach.
- 33% of eNaira users in Nigeria previously lacked access to traditional banking systems.
Legal Status and Enforcement Statistics of CBDCs
- 89% of CBDC-issuing countries introduce legal frameworks addressing dispute resolution mechanisms for CBDC transactions.
- 46 countries classify CBDC holdings as public liabilities, backed by central banks, unlike commercial bank deposits.
- 38% of CBDC regulations include explicit consumer rights, such as refund guarantees and error rectification protocols.
- 27 countries legislate penalties for misuse or fraudulent use of CBDCs, including fines and criminal charges.
- 60% of countries harmonize CBDC legal frameworks with existing payment laws, reducing regulatory fragmentation.
- 19 countries establish CBDC dispute resolution tribunals or ombudsman services to handle user complaints.
- 81% of jurisdictions with live CBDCs enforce real-time compliance monitoring systems for transaction legal integrity.
Recent Developments
- ECB finalizes Digital Euro regulatory framework in March 2025, rolling out pilots in Germany, France, and Italy, involving 3 countries.
- Japan passed the Digital Currency Act in 2025, defining consumer protection, privacy safeguards, and legal tender status for its Digital Yen for over 125 million residents.
- United States Federal Reserve releases an updated white paper on its FedNow CBDC pilot in 2025, inviting more than 300 million citizens to provide consultation feedback.
- Brazil launches its DREX CBDC in January 2025, targeting financial inclusion for over 200 million citizens and interoperability with 2 major national payment schemes.
- India’s Reserve Bank expands its Digital Rupee pilot in 2025 to include offline payments, aiming to reach over 600,000 villages with limited internet connectivity.
- Sweden’s Riksbank plans to shift e-Krona from pilot phase to full deployment in early 2026, after more than 5 years of testing and legal review.
- Australia initiates cross-border eAUD CBDC trials in 2025, collaborating with 2 partner countries, Singapore and New Zealand, for cross-jurisdictional payments.
- China’s Digital Yuan adds programmable payments in 2025, allowing millions of businesses to automate conditional payments and smart contract functions across 31 provinces.
- UAE announces new CBDC licensing regulations in 2025, setting up a streamlined approval process for more than 50 prospective fintech and digital wallet providers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
134 countries, representing 98% of global GDP, are exploring or developing CBDCs and related regulatory frameworks in 2025.
28 countries have passed comprehensive CBDC regulatory laws, while global investment in CBDC-related infrastructure and regulatory compliance reached $5.6 billion in 2025.
62% of countries piloting CBDCs have integrated AML and KYC regulations into their CBDC frameworks in 2025.
Conclusion
The CBDC regulatory landscape has transformed rapidly, driven by technological advances, global collaboration, and an urgent need to modernize monetary systems. Central banks are now working to balance innovation with privacy, security, and financial stability. The private sector’s involvement, cross-border cooperation, and evolving privacy laws signal a maturing market that promises greater financial inclusion, lower transaction costs, and a more resilient global payments infrastructure.