Imagine a world where social insurance acts as a safety net for millions, securing lives against the uncertainties of health, income, and unforeseen events. Today, social insurance systems will continue to evolve, adapting to demographic shifts, economic challenges, and emerging needs. This article explores critical statistics, unveiling trends that highlight the significance of social insurance in the modern era.
Editor’s Choice
- 68.9 million Americans are enrolled in Medicare in 2025, reflecting a steady annual growth of about 2%.
- Social Security benefits reach 73.9 million recipients in 2025, with average retired worker payments around $1,999.97 per month.
- The global health insurance market is valued at $2.69 trillion in 2025, with a projected CAGR of 7.43%.
- 54% of eligible Medicare beneficiaries, or about 34.1 million people, are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans in 2025.
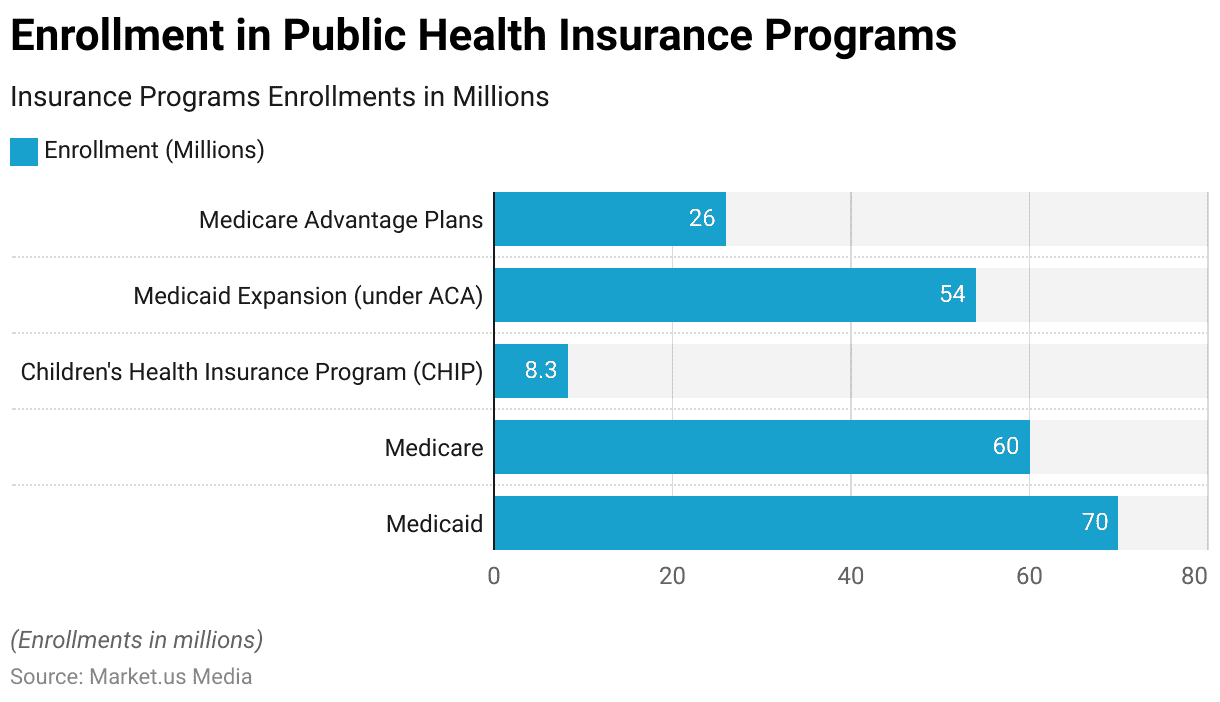
Public Health Insurance Enrollments in the US
- Medicaid leads public health coverage with 70 million enrollees, serving low-income individuals and families across all states.
- Medicare covers approximately 60 million Americans, primarily aged 65 and older, highlighting the aging population’s reliance on federal healthcare.
- Medicaid Expansion under the ACA accounts for 54 million enrollments, showing the significant impact of the Affordable Care Act reforms.
- Medicare Advantage Plans enroll 26 million participants, reflecting a growing preference for private Medicare alternatives.
- CHIP (Children’s Health Insurance Program) supports 8.3 million children, offering essential coverage for low-income families not qualifying for Medicaid.
Coverage and Enrollment Statistics
- 66.1% of Americans had private health insurance, covering 310 million people in total.
- Global public pension program enrollment is estimated at 1.4 billion individuals in 2025, marking increased reach.
- Employer‑sponsored insurance in the US covered 53.8% of the population.
- About 17.6% of Americans relied on Medicaid, with the rest depending on other public programs, including CHIP, for under 35.5% public coverage overall.
- Public health insurance (Medicaid, Medicare, etc) participation among children under 19 was 34.2% and among adults 19‑64 was 25.5%.
- US Disability Insurance had 8.113 million beneficiaries in August 2025 with an average monthly benefit of $1,445.72.
- Over 24 million people enrolled through the Affordable Care Act marketplaces in 2025, with over 90% receiving federal tax credits.
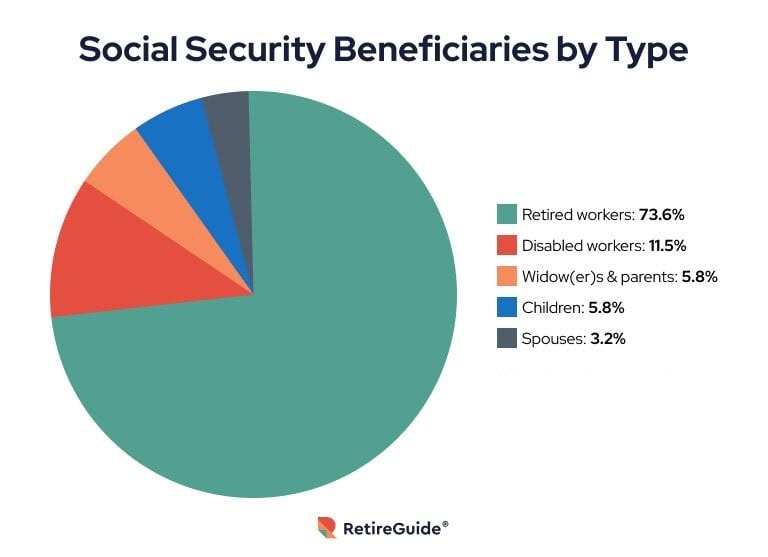
Social Security Beneficiaries by Type
- Retired workers represent the largest share of Social Security recipients at 73.6%, reflecting the core retirement purpose of the program.
- Disabled workers account for 11.5% of beneficiaries, highlighting Social Security’s critical role in supporting those unable to work.
- Widows and parents make up 5.8%, receiving survivor benefits after the death of a covered worker.
- Children also comprise 5.8% of the total, typically receiving benefits through survivor or disability claims.
- Spouses represent 3.2%, often receiving spousal or survivor benefits tied to their partner’s work history.
Financial Performance and Sustainability
- Combined Social Security Trust Fund reserves held in special‑issue Treasury securities are $2.72 trillion at the beginning of 2025, declining toward projected depletion in 2034.
- U.S. health spending is expected to grow by 7.1% in 2025, reflecting continued strong growth in medical costs.
- Under intermediate assumptions, Medicare’s Hospital Insurance Trust Fund is projected to deplete by 2033, after which only about 89% of scheduled Part A benefits would be payable.
- Assets held in 401(k) plans reached $8.7 trillion in Q1 2025, with total defined contribution plan assets at $12.2 trillion.
- The COLA for Social Security benefits in 2025 is projected to be around 3.2%, reflecting recent inflation levels.
- Pension funds in OECD countries now manage approximately $42 trillion in combined assets as of 2025, reflecting steady growth.
- Public social insurance spending in the EU is estimated to represent about 29.5% of GDP in 2025.
Benefit Distribution and Utilization
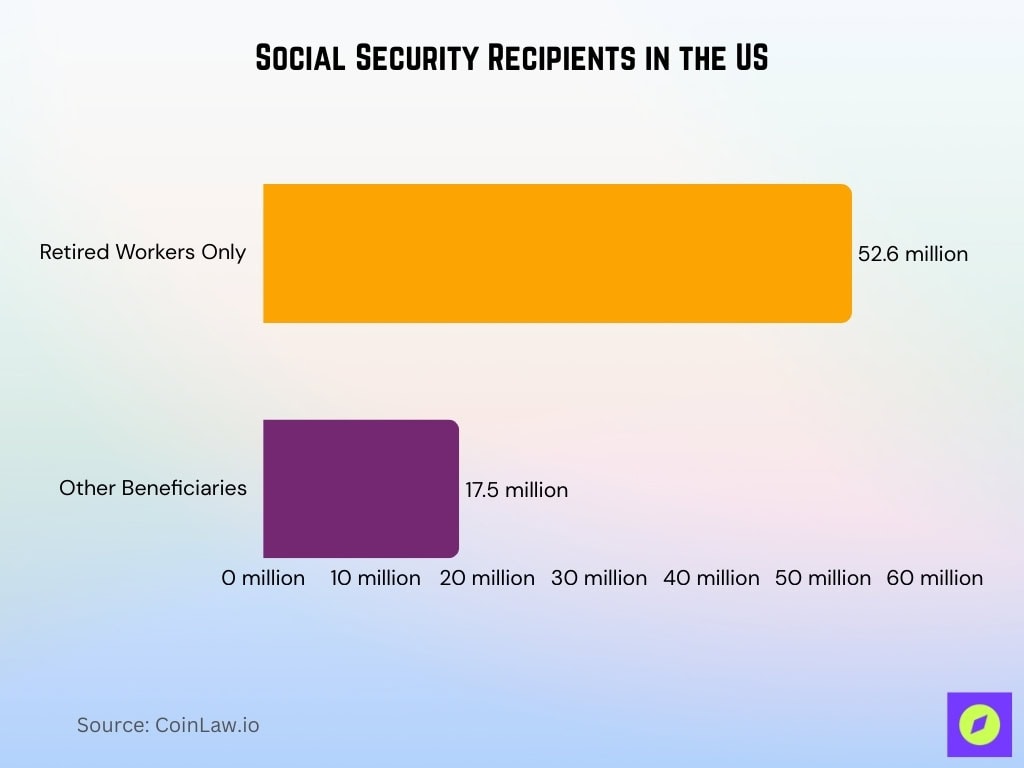
- 70.1 million Americans receive Social Security benefits in 2025, with 52.6 million retired workers forming the largest group.
- Medicare Advantage plans cover about 30 million beneficiaries in 2025, representing roughly 45% of all Medicare enrollments.
- Supplemental Security Income assists about 7.4 million Americans in 2025 with maximum federal payments of $967 per person and $1,450 per couple per month.
- Unemployment insurance payments in 2025 totaled approximately $40 billion, reflecting modest recoveries after workforce adjustments.
- The average monthly Social Security benefit for retirees is now $2,008 in mid‑2025.
- Social insurance utilization by individuals with disabilities reached 8.1 million beneficiaries in mid‑2025.
- Global health insurance claim volumes in 2025 rose by about 10% year-over-year, aided by improved automation.
Benefits, Costs, and Coverage
- The annual cost of family health insurance in the US is about $35,119 in 2025.
- The average cost of individual health insurance is around $6,468 per year in 2025.
- Retirement benefits continue to make up the majority of Social Security payouts, with an estimated share near 65%.
- Private health insurers in the US paid over $550 billion in claims in 2025, showing moderate growth.
- Canada’s public healthcare spending is projected to exceed $340 billion in 2025, covering over 38 million citizens.
- India’s social insurance schemes provided health coverage to more than 500 million people in 2025.
- Life insurance penetration across Africa rose to approximately 4.4% in 2025, with strong growth in several key markets.
- US government contributions to public pension funds reached nearly $190 billion in 2025, supporting long-term solvency.
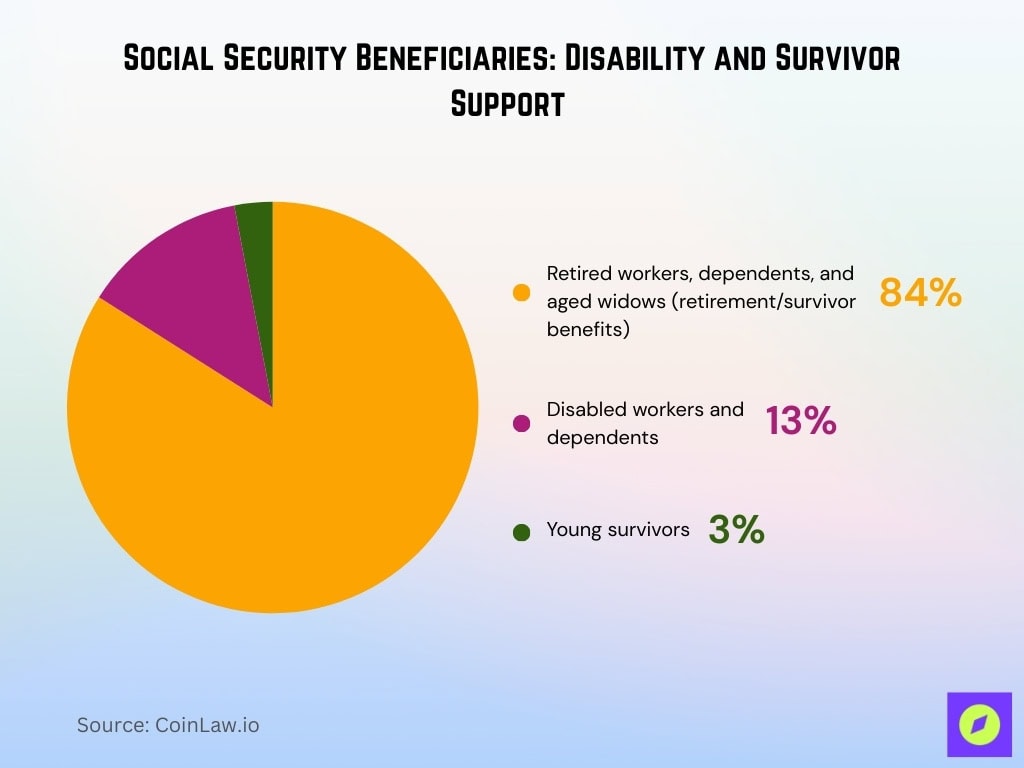
Social Security Beneficiaries: Disability and Survivor Support
- 84% of Social Security beneficiaries are retired workers, aged widows, and their dependents, receiving retirement or survivors benefits.
- 13% of recipients are disabled workers and their dependents, highlighting Social Security’s role in providing financial support for those unable to work due to disability.
- 3% of beneficiaries are young survivors, typically children or young dependents of deceased workers who qualify for survivor benefits.
International Labor Standards on Social Security
- About 60% of global workers had access to at least one form of social insurance in 2025.
- India’s social security coverage rose to 64.3% of its population in 2025, covering approximately 940 million people.
- Over 110 countries have ratified ILO Convention No.102 as of mid‑2025, maintaining a long‑standing global agreement on minimum social security standards.
- Nearly 90 nations operated universal healthcare systems in 2025, providing broad coverage to most citizens and residents.
- Workplace injury compensation schemes now protect around 450 million workers globally in 2025.
- Informal worker access to social insurance in South Asia and Sub‑Saharan Africa increased by about 20% over the past few years through 2025.
- Women workers globally now enroll in social insurance systems at a rate of about 70% in 2025, approaching gender parity in many regions.
Comparative International Analysis
- Japan’s old‑age dependency ratio is among the highest in OECD, with over 50 persons aged 65+ per 100 working‑age people as of recent years.
- Germany maintains contributions from ~40 million active workers supporting ~24 million retirees in its pension system.
- Brazil’s coverage of informal workers in pension systems has expanded modestly and now includes about 55‑60% of that population.
- Australia’s superannuation assets are estimated at AUD 4.4 trillion in 2025, benefiting around 16 million participants.
- Canada spends approximately 11‑12% of GDP on healthcare insurance in recent years, compared to the US at about 16‑17%.
- South Korea’s employment‑linked insurance programs support about 20 million people, including gig and freelance workers, as of 2025.
Recent Developments
- The SECURE 2.0 Act requires 401(k) and 403(b) plans to include part-time workers with two consecutive years of 500+ hours starting in 2025.
- Ghana’s universal healthcare program aims to reach 21.08 million members in 2025, expanding access across the country.
- The Affordable Care Act marketplaces reached a record 24.3 million enrollees in 2025 during open enrollment.
- The European Union continues implementing a €2 billion modernization fund to upgrade social insurance infrastructure across member states.
- India’s e-Shram digital platform surpassed 300 million registered informal workers, improving access to social insurance benefits.
- Estonia’s blockchain-based public pension pilot cut administrative costs by 10% and reduced fraud in benefit management.
- The World Bank pledged $5 billion to help low-income countries strengthen their social insurance systems through 2025.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
74.52 million people were receiving Social Security or SSI (or both) benefits.
About 93% of workers in paid employment and self‑employment are covered by OASDI in 2025.
There were 73.9 million beneficiaries, and the average retired worker benefit was about $1,999.97/month.
The shortfall is projected at about $25.1 trillion over 75 years and represents about 3.82 percentage points of taxable payroll.
Conclusion
Social insurance remains an indispensable pillar for economic and social stability, touching lives across generations and geographies. As populations age and economic uncertainties persist, the need for innovative, efficient, and inclusive social insurance systems is greater than ever. From technological advancements to policy reforms, these systems are evolving to meet the challenges of the modern world. By addressing coverage gaps, demographic changes, and global disparities, social insurance holds the potential to ensure equity, security, and prosperity for all.



































































