Imagine transferring millions of dollars in seconds, without intermediaries or paperwork, powered purely by lines of code. This is the promise of smart contracts, the cornerstone of blockchain innovation. However, as revolutionary as they are, these digital agreements are not without flaws. The vulnerabilities of smart contracts are a growing concern. Understanding their risks and the role of security audits is crucial to unlocking their true potential today.
Editor’s Choice
- The global smart contracts market is projected to grow to $3.21 billion in 2025 at a CAGR of ~22.0%.
- Access control flaws led to financial losses totaling $953.2 million and remain a leading cause of smart contract breaches.
- Flaws in business logic within smart contracts caused losses of around $63 million due to improper token minting and flawed lending protocols.
- An estimated 61% of blockchain hacks have been attributed to North Korean hacking groups like the Lazarus Group.
- In February 2025, attackers exploited vulnerabilities in Bybit’s infrastructure, resulting in losses of approximately $1.5 billion.
- Comprehensive smart contract audits in 2025 typically range between $25,000 and $150,000, depending on complexity.
- Leading smart contract auditing firms such as Hashlock and ConsenSys Diligence have audited hundreds of projects, securing market caps exceeding $100 billion as of 2025.
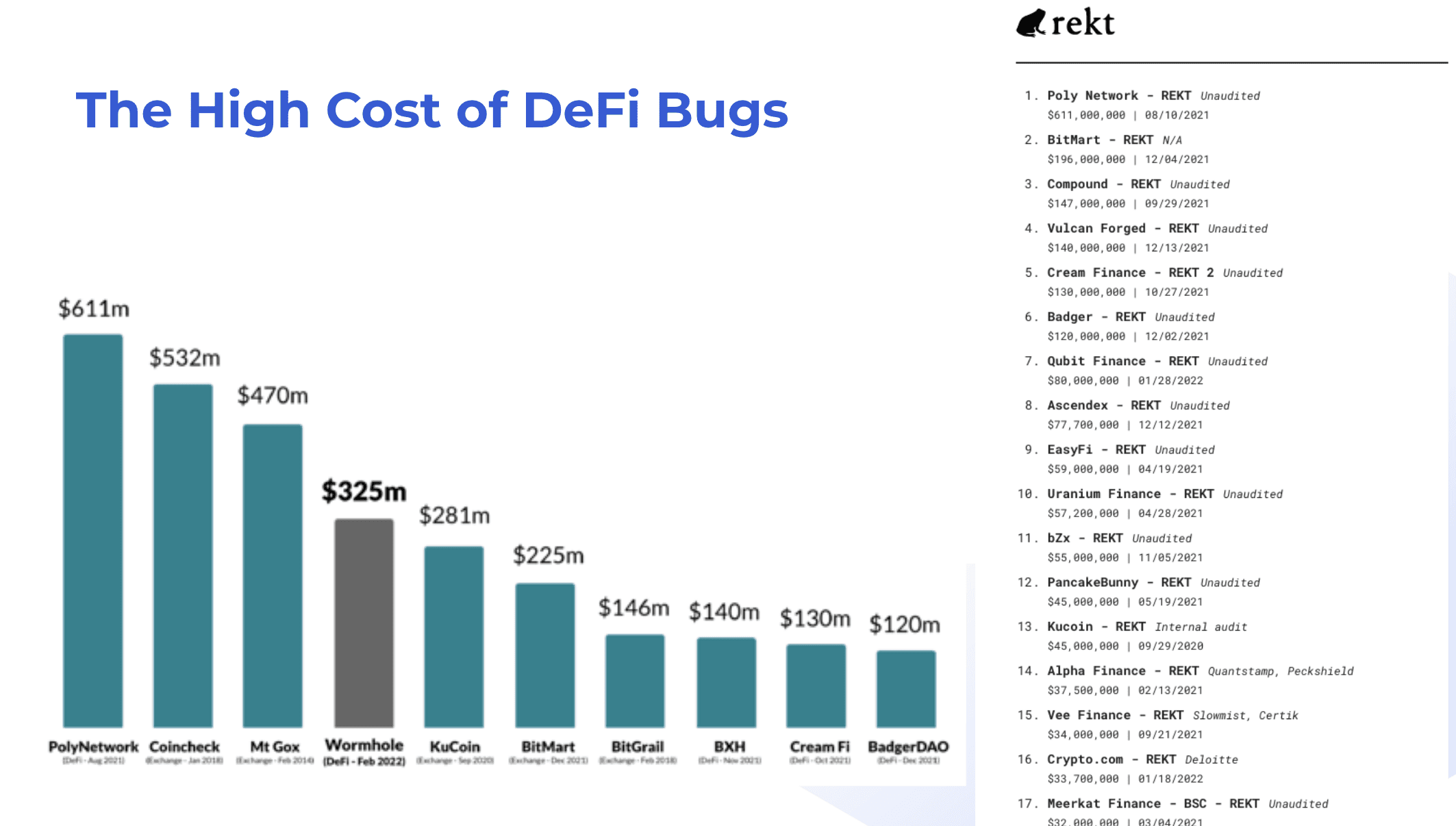
The High Cost of DeFi Bugs
- PolyNetwork suffered losses of $611 million, marking one of the largest DeFi exploits ever recorded in August 2021.
- Coincheck experienced a massive $532 million loss in January 2018, caused by stolen NEM tokens from its exchange wallets.
- The infamous Mt. Gox hack resulted in $470 million in Bitcoin losses back in February 2014, a defining early crypto security breach.
- Wormhole, a cross-chain bridge, lost $325 million in February 2022 due to a vulnerability in its smart contract verification process.
- KuCoin faced losses of $281 million after private keys were compromised during the September 2020 incident.
- BitMart was hacked for $225 million in December 2021, with attackers exploiting stolen exchange wallets.
- BitGrail, an Italian exchange, lost $146 million worth of Nano coins in February 2018, leading to its collapse.
- BXH saw $140 million drained in November 2021 through a suspected private key leak in its DeFi platform.
- Cream Finance was hit with a $130 million exploit in October 2021, due to a flash loan vulnerability.
- BadgerDAO lost $120 million in December 2021, when hackers injected malicious scripts into its website interface.
Background on Ethereum and the Ethereum Virtual Machine
- As of 2025, Ethereum hosts over 4,983 active dApps, making it still among the most prominent smart contract platforms.
- A study has shown that about 70% of smart contracts on Ethereum are inactive or vulnerable, posing latent security threats.
- The Ethereum Merge transitioned the network to Proof of Stake, cutting energy use by over 99%, while also introducing new attack vectors in staking and validator layers.
- The introduction of Layer 2 solutions like Optimism, Arbitrum, and Base has improved scalability but added complexity to smart contract interactions.
- Ethereum’s gas fee model, designed to deter spam attacks, has been exploited in the past and has cost users millions in wasted fees.
- By 2025, it is estimated that about 60% of blockchain developers globally will focus on Ethereum-based smart contracts, reflecting Ethereum’s central role.
Common Vulnerabilities in Smart Contracts
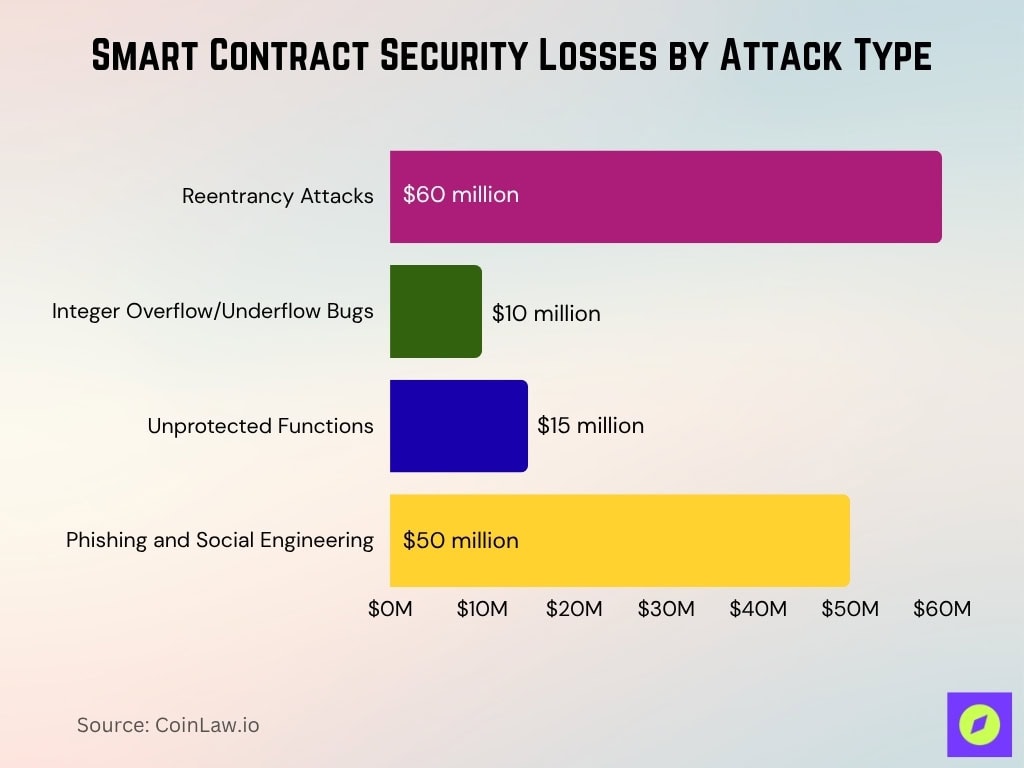
- Reentrancy attacks (e.g. DAO exploit in 2016) historically caused $60 million losses and remain a core risk in 2025.
- Integer overflow/underflow bugs exposed $10 million in tokens and are still routinely flagged in audits.
- Unprotected functions allowed attackers to drain funds or manipulate data and caused $15 million in losses in recent years.
- Phishing and social engineering targeting smart contract teams led to $50 million in losses globally in recent years.
- Front-running, where attackers exploit transaction ordering, impacted about 20% of DeFi protocols and remains a vector in 2025.
- Unchecked external calls accounted for 18% of total vulnerabilities reported in blockchain audits and continue to be a common flaw.
Types of Smart Contract Security Audits
- Automated Audits use tools to scan for common vulnerabilities, speeding up reviews but often missing nuanced logic errors, and in 2025 still catch ~70-80% of low-level flaws.
- Manual Audits executed by expert developers tackle complex vulnerabilities, often taking weeks in 2025 and costing up to $150,000 for critical contracts.
- Formal Verification applies mathematical proofs to ensure correctness and is used in 2025 for high-value contracts (e.g., core token bridges) with costs often exceeding $200,000.
- Static Analysis Tools like MythX and Slither in 2024–2025 could detect roughly 92% of known vulnerabilities in the test environments, but still miss edge-case logic issues.
- Real-time Monitoring Audits post-deployment prevented over $100 million in potential losses on decentralized platforms in 2023 and remain critical in 2025 defense.
- Bug Bounty Programs (e.g., Immunefi) rewarded around $65 million to ethical hackers in 2023, and in 2025, median payouts approach $2,000, with average rewards around $52,800.
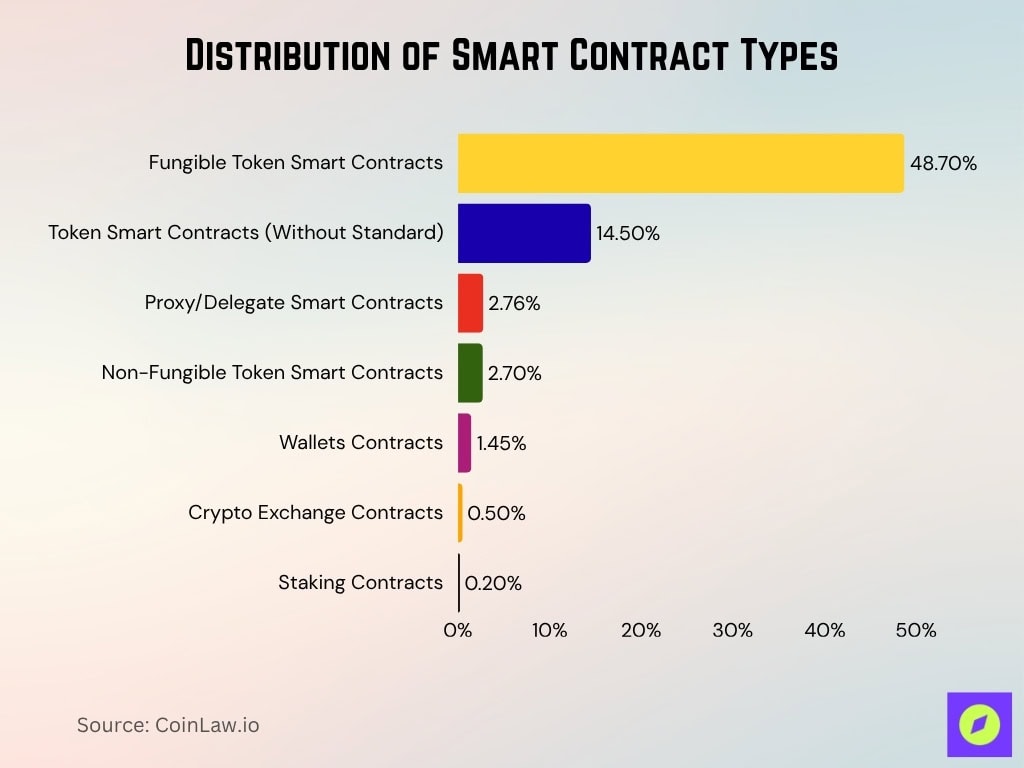
Distribution of Smart Contract Types
- Fungible Token Smart Contracts dominate the ecosystem, accounting for 48.7% of all deployed contracts.
- Token Smart Contracts (Without Standard) make up 14.5%, showing continued experimentation outside established ERC standards.
- Proxy/Delegate Smart Contracts represent 2.76%, often used for contract upgrades and modular architectures.
- Non-Fungible Token (NFT) Smart Contracts account for 2.7%, reflecting sustained NFT market activity.
- Wallet Contracts comprise 1.45%, supporting personal and custodial crypto storage solutions.
- Crypto Exchange Contracts contribute only 0.5%, due to most exchanges using centralized infrastructure.
- Staking Contracts are minimal at 0.2%, indicating limited use compared to token-related deployments.
Challenges and Countermeasures in Smart Contract Security
- Rapid Development Cycles projects often deploy without sufficient testing, and encouraging test net deployments has mitigated this by ~30%.
- Evolving Threat Vectors attack techniques change faster than security protocols, prompting greater investment in adaptive ML-driven tools.
- Cross-chain Risks bridges remain high risk, with cross-chain solutions accounting for nearly 40% of Web3 exploits in 2025.
- High Costs of Audits: Comprehensive audits in 2025 can cost $20,000 to $500,000, pushing smaller projects to crowd-fund solutions.
- Skill Shortages: Only 2,000 security specialists globally focus on blockchain, increasing reliance on automated tools.
- Delayed Vulnerability Patching post-deployment updates with multi-signature governance reduced patch delays by ~40%.
- Lack of Standards, absence of a universal audit framework, persists, though efforts like CERT and OWASP for blockchain are gaining traction.
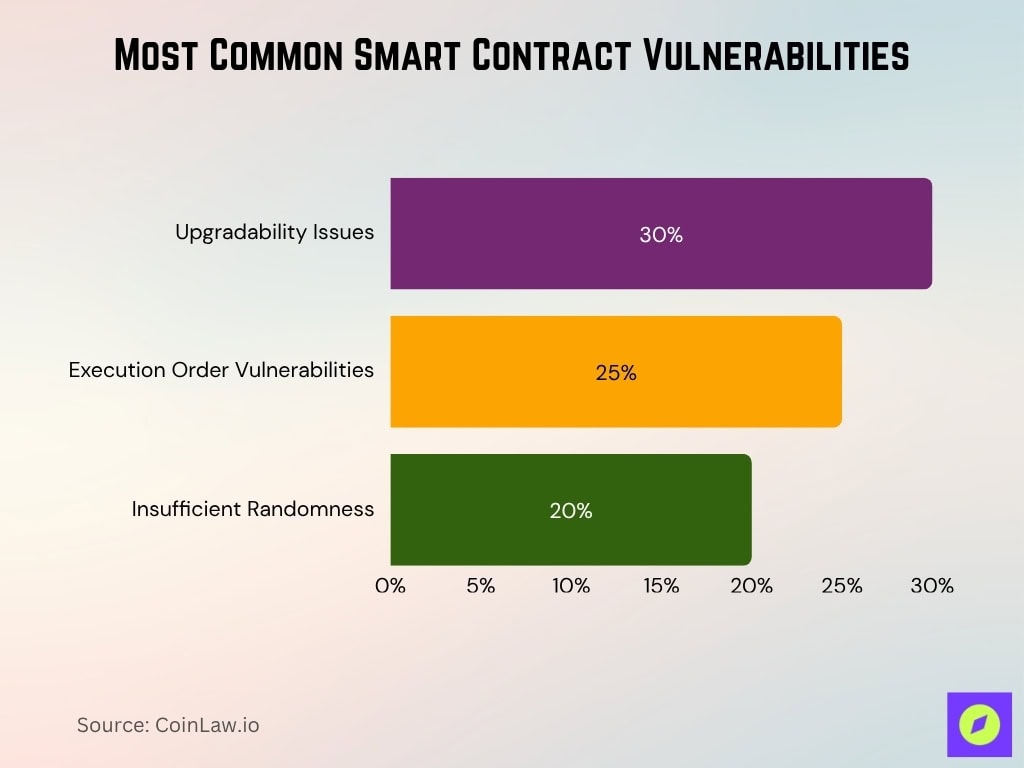
Technical Risks of Smart Contracts
- Upgradability Issues: Rigid contracts are unable to patch vulnerabilities, affecting about 30% of audited projects in past audits and still present risks in 2025.
- Execution Order Vulnerabilities, exploits like front-running, have impacted nearly 25% of DEX transactions in recent years and remain a key risk.
- Insufficient Randomness: Predictable random number generators were exploited in ~20% of gaming dApps, leading to fraudulent wins.
- Gas Limit Constraints, poor optimization in contract code, can cause transactions to fail, and by 2025, waste tens of millions annually in fees.
- Dependency on Third-party Oracles, a misconfigured oracle caused $34 million in losses (e.g., Compound 2022), and similar incidents continue.
- Imprecise Smart Contract Logic errors resulted in over $1.1 billion in lost assets in prior years and remain a top contributor to exploit losses.
- Immutable Bugs deploying faulty contracts permanently locked $500 million in user funds (e.g,. past incidents), and such irreversible risks persist.
Smart Contract Immutability and Associated Risks
- Permanent Bugs in deployed contracts permanently locked $500 million in user funds on Ethereum, and similar irreversible losses still occur.
- No Reversibility, irrevocable transactions resulted in $1.6 billion in accidental losses due to user errors, and such risks remain in 2025.
- Compliance Challenges immutability conflicts with laws like GDPR, which require data to be modifiable or deletable, raising legal tension.
- Hacker Exploits of immutable contracts give attackers unlimited time to exploit flaws, as seen in the $60 million DAO attack and other enduring exploits.
- Loss of Investor Trust unrectified bugs led to an 18% drop in investor confidence in affected projects, and distrust remains a serious consequence.
Key Benefits of Smart Contract Auditing
- Prevention of Exploits audited contracts saw 98% fewer hacks than unaudited ones.
- Investor Confidence projects with thorough audits raised 37% more capital than those without.
- Regulatory Compliance, complying with new regulations in the US and EU, demands stringent security measures.
- Cost-effectiveness fixing vulnerabilities post-deployment costs 10× more than addressing them pre-launch.
- Improved Transparency audits provide stakeholders with detailed security reports, fostering trust.
- Enhanced Scalability by detecting bottlenecks, audits improve contract capacity to handle increased traffic.
- Community Trust open-source audits let the broader blockchain community verify a project’s security.
Recent Developments
- OWASP’s Updated Top 10 Smart Contract Vulnerabilities in February 2025 introduced key entries like Price Oracle Manipulation and Lack of Input Validation in its SC01–SC10 list.
- Advancements in Automated Auditing Tools such as Slither and Mythril in 2025 have boosted scan speed and caught roughly 90%+ of low-level vulnerabilities in early passes.
- Increased Complexity in On-Chain Attacks in 2025 sees attackers favoring zero-day exploits and multi-vector chains instead of simple bugs.
- Significant Financial Losses from Smart Contract Exploits in 2024 exceeded $3.5 billion, underscoring the need for robust auditing and defenses.
- High-profile exchange Hacks like the $1.5 billion Bybit breach in February 2025 exposed critical gaps in key management and contract infrastructure protections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
$2.17 billion was stolen YTD 2025, led by the $1.5 billion Bybit breach.
The 2025 market is about $2.69 billion, up from $2.14 billion in 2024.
Simple ERC-20 audits often cost $8,000 to $20,000, while advanced cross-chain or complex DeFi audits run $75,000 to $150,000+.
There were 344 incidents with $2.29 billion in net losses after recoveries.
Conclusion
Smart contracts hold immense promise for transforming industries, but their risks cannot be ignored. As blockchain adoption grows, prioritizing robust security measures, advanced auditing, and continuous innovation will determine its success. The evolution of tools, regulations, and developer practices suggests a brighter future for secure and trustworthy smart contracts. By addressing vulnerabilities head-on, the blockchain community can ensure that smart contracts remain the bedrock of decentralized ecosystems for years to come.



































































