In early 2021, a small blockchain analytics startup uncovered something alarming: a crypto wallet linked to a sanctioned Iranian exchange had just moved millions in Bitcoin. It wasn’t the first time, and it wouldn’t be the last. The stakes were high, and the U.S. Office of Foreign Assets Control (OFAC) knew it. Today, the landscape of crypto transactions under OFAC sanctions has shifted dramatically.
The intersection between decentralized finance and international regulations has become a battleground. As regulators clamp down on illicit transactions, crypto users and institutions are navigating a complex web of compliance and enforcement. This article explores the latest statistics and trends shaping OFAC sanctions and crypto transactions, helping readers understand the key developments that are reshaping this critical space.
Editor’s Choice
- $1.8 billion in crypto assets have been frozen or seized due to OFAC sanctions as of Q1 2025.
- The number of OFAC-designated crypto wallets rose by 32% year-over-year, totaling 1,245 wallets by early 2025.
- 76% of crypto exchanges operating in the U.S. reported full OFAC compliance as of March 2025.
- OFAC enforcement actions targeting crypto firms increased by 28% from 2023 to 2024.
- Approximately 45% of global ransomware payments in 2024 were linked to wallets flagged by OFAC.
- North Korean hackers stole $2.02 billion worth of digital assets through early December 2025, up 51% from a year earlier.
Overview of OFAC Sanctions on Crypto Transactions
- As of 2025, OFAC has sanctioned 57 individuals and entities specifically for illicit activities involving cryptocurrencies.
- OFAC’s first crypto-related designation occurred in 2018, and since then, there has been an annual growth rate of 18% in crypto sanctions.
- In 2024, 23% of all new sanctions designations were crypto-related, up from 17% in 2023.
- $6.9 billion in illicit crypto transactions were linked to sanctioned entities over the past 24 months.
- OFAC’s Specially Designated Nationals (SDN) List now includes over 1,200 crypto wallet addresses.
- Sanctioned entities use a variety of crypto assets, with Bitcoin (BTC) accounting for 65%, Ethereum (ETH) 18%, and stablecoins 12% of identified transactions.
- OFAC collaborates with INTERPOL and Europol to enforce cross-border compliance on crypto-related sanctions.
- In January 2025, OFAC issued its first-ever sanction against a DeFi protocol, freezing $150 million in assets.
OFAC-Listed Crypto Wallets
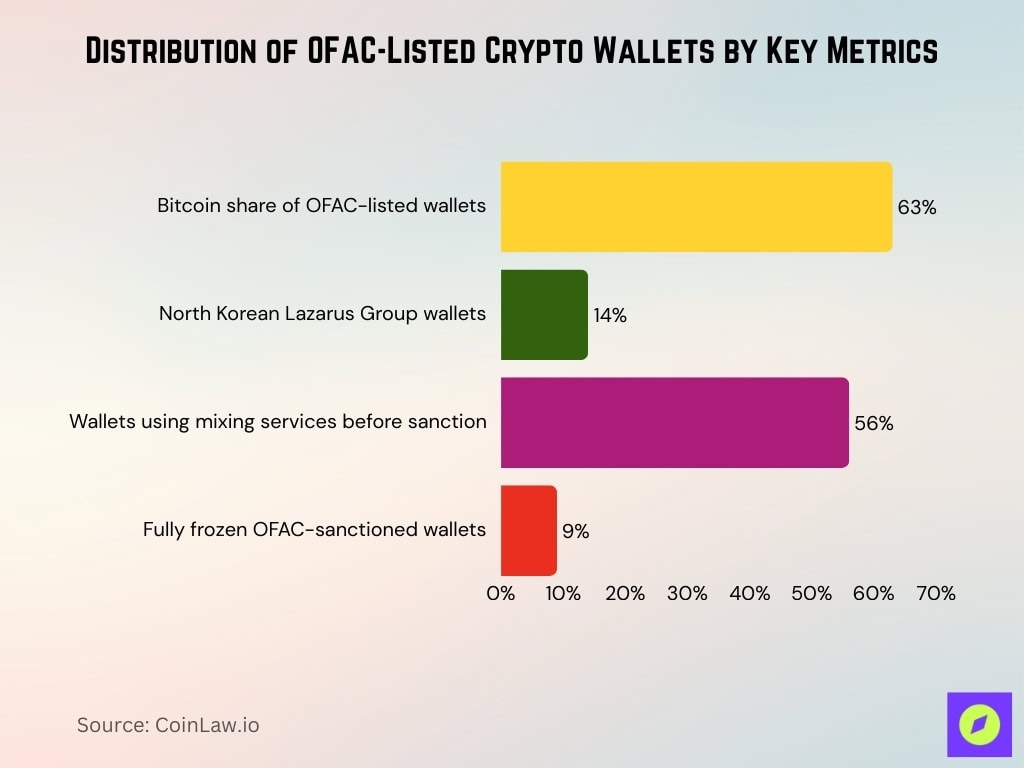
- Bitcoin addresses dominate the OFAC-listed wallets, representing 63% of all sanctioned addresses.
- North Korean Lazarus Group wallets account for 14% of all wallets designated by OFAC as of 2025.
- 56% of OFAC-sanctioned wallets showed signs of using mixing services prior to being blocklisted.
- Only 9% of blocklisted wallets have been completely frozen; the rest remain active but under heavy monitoring.
- By February 2025, the SDN List contains 1,245 unique crypto wallet addresses.
- In 2024, OFAC flagged 120 wallets associated with Iranian ransomware groups.
- The average transaction volume per OFAC-listed wallet in 2024 was $1.2 million.
Most Sanctioned Countries in Crypto-Related OFAC Actions
- North Korea accounts for 40% of OFAC’s crypto-related sanctions through Lazarus Group activities.
- Russia represents 28% of crypto sanctions linked to ransomware and evasion networks.
- Iran comprises 20% of enforcement actions involving terrorism financing via USDT.
- OFAC designated 65 new entities in Russia and Belarus for crypto evasion.
- Venezuela holds 9% of crypto-related designations tied to state actors.
- China entities account for 5% of sanctions focused on laundering schemes.
- North Korea stole $2.02 billion in crypto, prompting expanded OFAC blocks.
- Iran shadow networks facilitated $100 million in crypto oil sales frozen by OFAC.
- Russia-based Garantex processed over $100 million in sanctioned illicit transactions.
- OFAC crypto wallets rose 32% to 1,245, with North Korea at 14%.
Impact of OFAC Sanctions on Global Crypto Transactions
- OFAC sanctions froze or seized $1.8 billion in crypto assets as of Q1.
- Crypto transaction volume linked to sanctioned entities decreased by 18%.
- The number of OFAC-designated crypto wallets rose 32% to 1,245.
- 76% of U.S. crypto exchanges reported full OFAC compliance.
- OFAC issued its first DeFi protocol sanction, freezing $150 million in January.
- OFAC penalties on crypto businesses totaled $430 million.
- 56% of sanctioned wallets used mixing services prior to blocklisting.
- 33% of illicit crypto funds are funneled through DeFi platforms.
- Interoperable blocklists across DeFi protocols froze $600 million.
- Tether froze $450 million in assets linked to sanctioned Iranian entities.
Trends in Crypto Wallet Freezing and Blocklisting
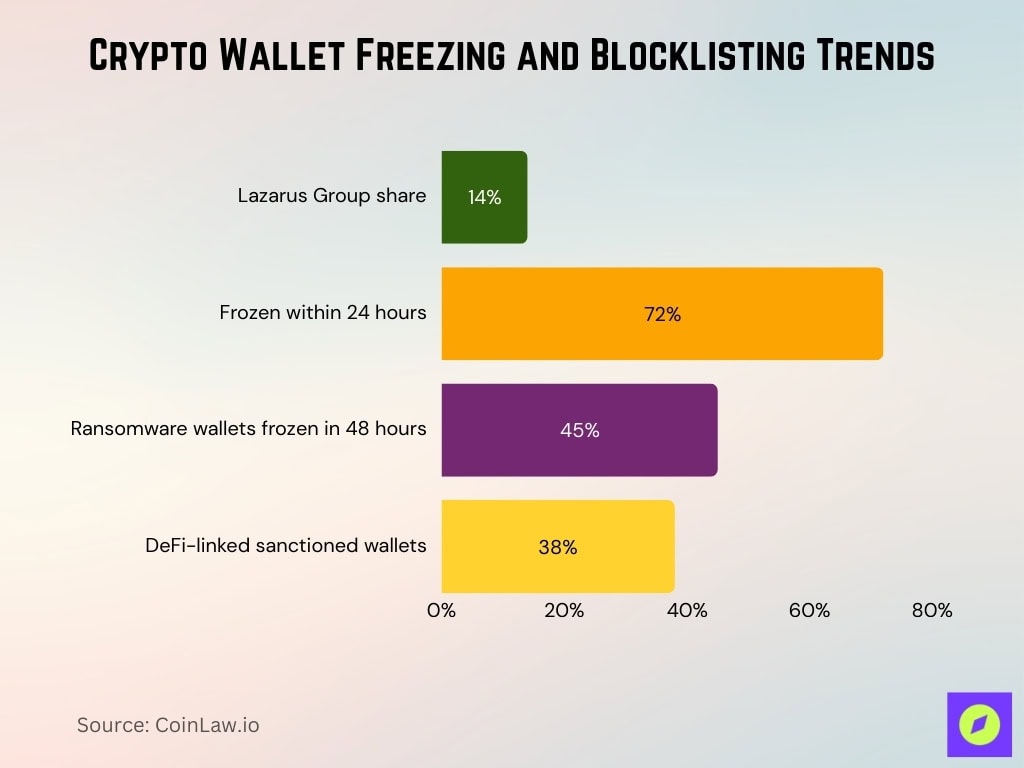
- North Korean Lazarus Group wallets comprise 14% of all OFAC designations.
- 72% of flagged wallets are frozen within 24 hours of designation.
- 45% of ransomware payment wallets are frozen within 48 hours.
- Elliptic identified 420 newly sanctioned wallets, 38% DeFi-linked.
- The number of OFAC-designated crypto wallets reached 1,245, up 32% year-over-year.
- OFAC added 280 wallets linked to Russian darknet markets.
- Tether froze $450 million in assets linked to sanctioned Iranian entities.
- SDN list covers crypto addresses across 17 blockchains.
- OFAC sanctioned the first AI trading bot that laundered $60 million.
Compliance Rates Among Crypto Exchanges and Platforms
- 83% of top-tier centralized crypto exchanges claim full compliance with OFAC regulations.
- 76% of US-based exchanges implemented automated OFAC wallet screening by late 2024.
- 45% of non-US exchanges had formal compliance programs for OFAC sanctions by Q1.
- Coinbase, Kraken, and Gemini scored 98% on OFAC compliance audits.
- Binance introduced mandatory OFAC compliance training for all 5,000 employees.
- 28% of smaller crypto exchanges in Southeast Asia remained noncompliant as of Q4.
- 61% of DeFi protocols reviewed by OFAC lacked sufficient sanctions screening.
- Only 30% of DeFi platforms implemented sanctions compliance controls by January.
- Bitfinex reported a 99% sanctions compliance success rate with OFAC analytics.
Evasion Tactics Used to Circumvent OFAC Sanctions
- Chain-hopping accounts for 37% of sanctioned funds moving across multiple blockchains.
- Privacy coins like Monero usage rose 21% among sanctioned entities evading detection.
- Layer 2 solutions on Ethereum are exploited in 18% of sanctions evasion attempts.
- Flash loans are utilized in 11% of laundering cases tied to sanctioned addresses.
- Cross-chain bridges comprised 25% of total evasion methods employed.
- Decentralized mixers like Sinbad processed $350 million in illicit transactions.
- NFT marketplaces laundered $45 million, up 33% from the previous year.
- P2P platforms facilitated $620 million involving OFAC-sanctioned wallets.
- Social engineering via OTC brokers moved $200 million of sanctioned funds.
US Crypto Enforcement Penalties Overview
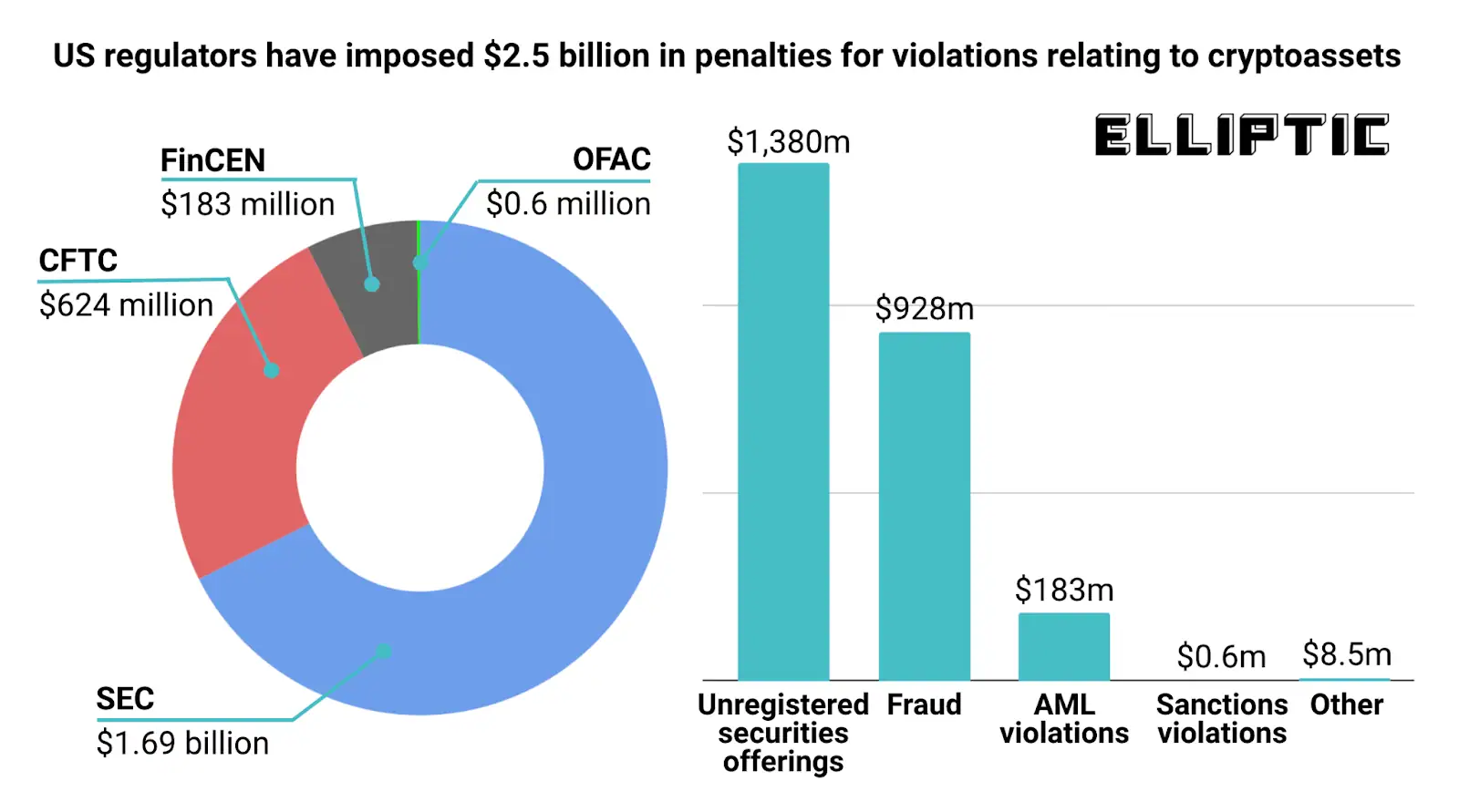
- $2.5 billion in total penalties have been imposed by US regulators for cryptoasset-related violations.
- The SEC accounts for the largest share, issuing $1.69 billion in fines, driven largely by unregistered securities offerings.
- The CFTC follows with $624 million in penalties, reflecting heightened oversight of crypto derivatives and market misconduct.
- FinCEN imposed $183 million in penalties, primarily tied to AML compliance failures.
- OFAC sanctions violations resulted in just $0.6 million, highlighting enforcement focus on broader compliance gaps rather than sanctions breaches alone.
- By violation type, unregistered securities offerings dominate with $1.38 billion in penalties, underscoring regulatory pressure on token issuances.
- Fraud-related cases contributed $928 million, reinforcing ongoing concerns around investor protection.
- AML violations accounted for $183 million, showing persistent weaknesses in transaction monitoring and reporting.
- Other violations made up a relatively small $8.5 million, indicating concentrated enforcement priorities.
Emerging Technologies Aiding OFAC Sanctions Enforcement
- AI blockchain analytics identified $2.1 billion in illicit transactions tied to sanctioned addresses.
- Zero-knowledge proof monitoring detected 16% of transactions masking sanctioned origins.
- Smart contract protocols froze $280 million in assets linked to sanctioned users.
- Predictive AI models reduced illicit flows by 22% through evasion forecasting.
- On-chain KYC wallets boosted sanctioned entity detection by 38%.
- Interoperable blocklists across 18 DeFi protocols froze $750 million.
- Real-time compliance APIs enabled instant blocking by 58% of exchanges.
- DAO voting sanctions lists cut illicit exposure by 25%.
- Machine learning caught 45% of complex evasion strategies missed by humans.
Challenges in Tracking and Regulating Sanctioned Crypto Transactions
- 71% of decentralized protocols without KYC fail to screen for OFAC sanctions.
- Privacy coins limit traceability in 30% of sanctioned fund tracking attempts.
- Cross-chain bridges enabled $550 million in untraceable transfers, complicating enforcement.
- 43% of non-US jurisdictions refuse to enforce OFAC sanctions.
- 20% of smaller exchanges lack resources for OFAC compliance monitoring.
- Regulatory gaps allow 27% of DAO proposals to bypass sanction policies.
- False positives affected 15% of wallet screenings requiring manual reviews.
- Lightning Network routed $100 million in illicit payments undetected by OFAC.
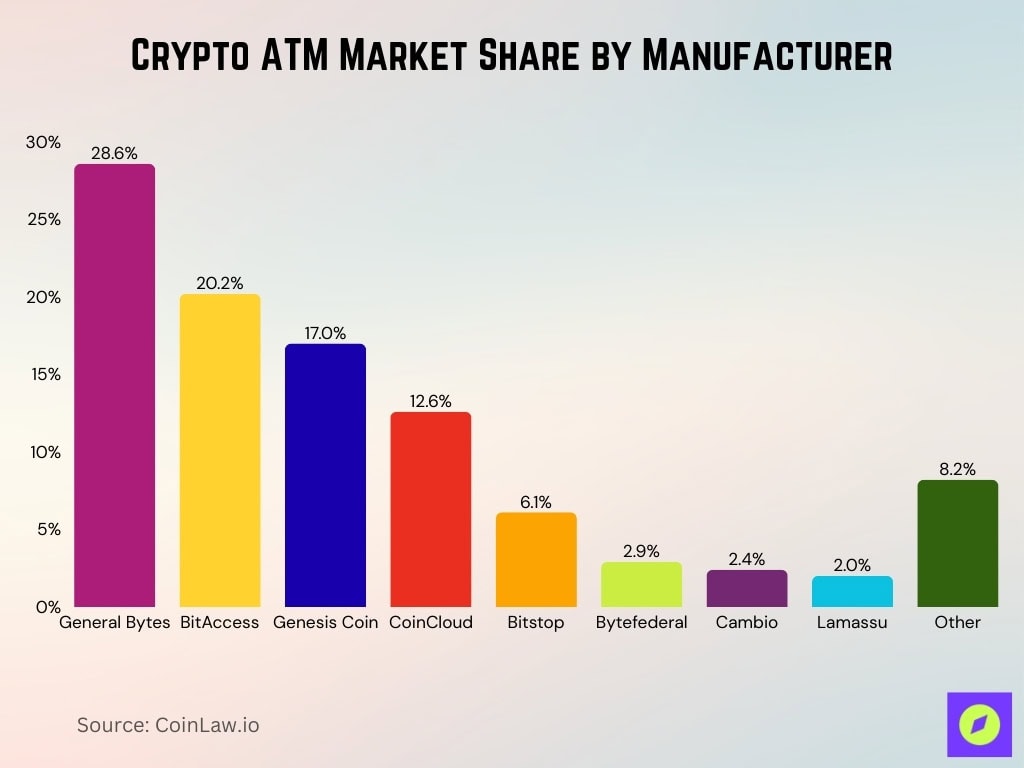
Crypto ATM Market Share by Manufacturer
- General Bytes leads the global crypto ATM market with a 28.6% share, making it the dominant hardware provider worldwide.
- BitAccess ranks second, controlling 20.2% of installed crypto ATMs and maintaining a strong presence in North America.
- Genesis Coin holds 17.0% market share, reinforcing its position as a major legacy manufacturer.
- CoinCloud accounts for 12.6% of crypto ATMs, reflecting its expansion through retail-focused deployments.
- Bitstop represents 6.1% of the market, specializing in compliance-driven ATM networks.
- Smaller manufacturers remain fragmented, with Bytefederal at 2.9%, Cambio at 2.4%, and Lamassu at 2.0%.
- The “Other” category makes up 8.2%, indicating a long tail of niche and regional ATM providers.
- Combined, the top three manufacturers control 65.8% of the crypto ATM market, highlighting strong industry concentration.
Recent Developments in OFAC Crypto Sanctions
- In January 2025, OFAC expanded sanction criteria to include DAOs and decentralized protocols without formal governance.
- OFAC launched Crypto Compliance Guidance 2025, mandating real-time monitoring for US-based exchanges.
- Three new wallet screening technologies were endorsed by OFAC in March 2025, focusing on DeFi platforms.
- OFAC sanctioned the first AI-powered autonomous trading bot, laundering $60 million in February 2025.
- Lazarus Group linked to $200 million stolen via sanctioned DeFi protocols in Q1.
- OFAC’s collaboration with Interpol and Europol led to six international raids on crypto infrastructure hubs.
- OFAC and FATF released a joint directive in April 2025, enhancing global crypto sanctions coordination.
- Tether required to freeze $450 million in assets linked to sanctioned Iranian entities in March.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
OFAC-linked actions have frozen or seized about $1.8 billion in crypto assets as of Q1 2025.
The OFAC SDN list contains around 1,245 unique crypto wallet addresses in early 2025.
Bitcoin addresses account for roughly 63–65% of all OFAC‑sanctioned crypto wallets.
By 2025, OFAC has sanctioned approximately 57 individuals and entities specifically for illicit activities involving cryptocurrencies.
Conclusion
As we progress, OFAC sanctions have reshaped the global crypto landscape. The growing sophistication of blockchain analytics, AI-driven enforcement, and inter-agency cooperation has strengthened efforts to combat illicit crypto activity. Yet, the rise of decentralized systems and anonymity tools poses enduring challenges. Crypto exchanges, DeFi protocols, and regulators are engaged in a high-stakes race, one balancing innovation, privacy, and global security. Understanding these evolving statistics and trends is essential for anyone involved in the future of digital finance.