Nvidia’s stock dropped after reports surfaced that Google is in talks with Meta to sell its custom AI chips, potentially shifting billions in future business away from Nvidia.
Key Takeaways
- Google is negotiating with Meta to supply tensor processing units (TPUs) for Meta’s data centers beginning in 2027, marking a shift from its current in-house chip usage.
- The deal could redirect billions of dollars away from Nvidia, whose GPUs currently dominate the AI data center market.
- Google’s pitch to other cloud customers signals broader ambitions, with potential to capture up to 10% of Nvidia’s annual revenue.
- Nvidia shares dropped as much as 6.5%, while rival chipmakers like AMD also faced losses, reflecting fears of rising competition in the AI chip space.
What Happened?
Nvidia shares fell sharply after a report from The Information revealed that Google is in discussions with Meta Platforms to supply its custom-designed TPUs, which are typically reserved for internal use. If the deal materializes, it could mark one of the first times Google sells these chips to another major cloud player, potentially reducing Nvidia’s dominance in the AI accelerator market.
BREAKING: Nvidia responds to news of Meta using Google’s TPUs, sending $NVDA stock -6% lower:
— The Kobeissi Letter (@KobeissiLetter) November 25, 2025
Nvidia says they are “delighted by Google’s success” and they “continue to supply Google.”
They also say, “Nvidia is a generation ahead of the industry” and “offers greater… pic.twitter.com/uTbbaQHLgx
Google’s TPU Strategy Gains Momentum
Google has long developed its own tensor processing units for AI and machine learning workloads. These chips, designed with a focus on speed and efficiency, are typically made available to developers through Google Cloud. However, this model may change soon. According to the report, Google is not only targeting Meta but is also actively pitching TPUs to other cloud customers, a move that could challenge Nvidia’s market share directly.
- Google’s TPU business could seize up to 10% of Nvidia’s yearly revenue, according to estimates in The Information’s report.
- The chips are already gaining traction, with Anthropic agreeing earlier this year to a deal involving up to 1 million TPUs.
- Bloomberg Intelligence analysts noted Meta’s interest in TPUs reflects a broader trend, as large AI developers seek alternatives to Nvidia’s GPUs.
Meta Eyes Chip Diversification
Meta’s interest in Google TPUs is part of a larger strategy to reduce reliance on Nvidia for its AI workloads. The company reportedly plans to use TPUs in its data centers starting in 2027 and could even begin renting the chips through Google Cloud as early as next year.
- Analysts estimate Meta could spend $40 billion to $50 billion on AI inference chips in 2026, making this potential deal a significant win for Google.
- The partnership would also give Meta more control over infrastructure and pricing, which is crucial as AI operations expand.
Industry Reactions and Stock Market Impact
The news triggered a notable market response. Nvidia’s stock fell up to 6.5% in early trading before recovering slightly, while Alphabet shares gained up to 3%. Advanced Micro Devices, another Nvidia rival, also saw an 8% drop, underscoring broader investor concern over AI chip competition.
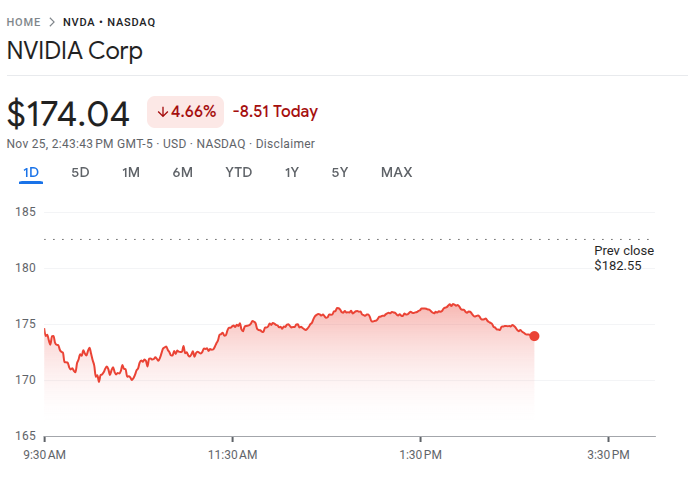
Meanwhile, Nvidia continues to innovate rapidly, releasing new GPU models every one to two years. Despite the competitive threats, demand for AI hardware is expected to grow significantly, supporting Nvidia’s long-term outlook.
CoinLaw’s Takeaway
I found this news to be a clear signal that the AI chip race is heating up in ways that will reshape the competitive landscape. In my experience, when major players like Meta and Google explore multi-billion-dollar shifts in supply chains, it’s rarely just exploratory. Nvidia has enjoyed a long lead in AI processing, but these moves by Google could seriously chip away at that edge over time. Still, Nvidia’s pace of innovation and entrenched ecosystem keep it relevant. I wouldn’t call this the beginning of the end for Nvidia, but it’s definitely the beginning of a new chapter in AI hardware competition.