Imagine a world where the digital realm holds more assets than the physical one. This is our current reality, where businesses and individuals rely on a robust cyber landscape. However, with this dependency comes unprecedented risks. As cyber threats evolve, the cyber insurance industry becomes a critical player in mitigating financial fallout. Understanding key trends and statistics is vital to navigating this complex yet indispensable market.
Editor’s Choice
- Cyber claims dropped 53% in H1 compared to the prior year.
- Ransomware accounted for 76% of incurred losses in H1.
- Average ransomware insurance loss exceeded $1.18 million per claim in H1.
- Cyber insurance adoption reached 62% among firms.
- Large enterprises show 60-70% cyber insurance coverage.
- Ransomware drove 60% of large cyber insurance claims.
Cybersecurity Insurance Market Trends
- Cyber reinsurance capacity surged by $250 million in H1.
- Cyber reinsurance rates declined 5-15% amid capacity growth.
- AI adoption in insurance expanded to 17.6% in customer service.
- The parametric cyber insurance market is valued at $1.2 billion.
- Modular cyber policies enable coverage customization by incident type.
- Cloud security breaches affected 83% of organizations.
- Insurers partnered with cybersecurity firms for premium reductions.
- Cyber insurance penetration hit 62% among businesses.
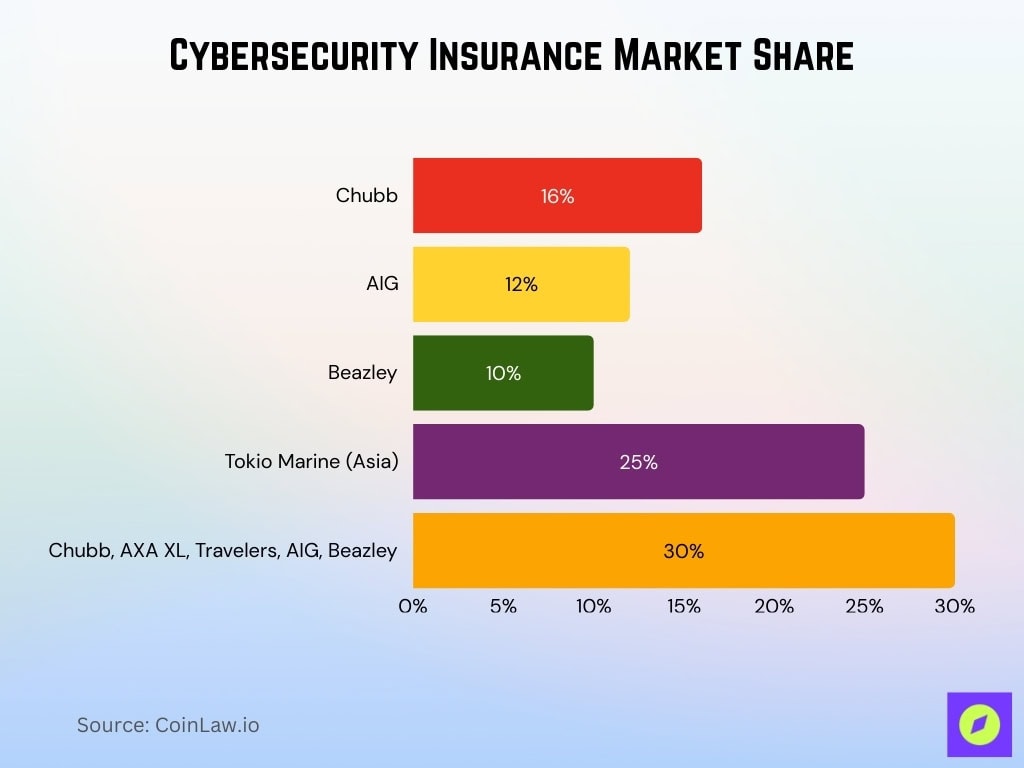
Cybersecurity Insurance Market Share
- Chubb holds 16% of the global cyber insurance market.
- AIG commands 12% global market share.
- Beazley secures 10% of the worldwide cyber insurance market.
- Tokio Marine dominates Asia with a 25% market share.
- Chubb, AXA XL, Travelers, AIG, and Beazley hold 20-30% combined.
Policy Adoption Rates
- Large US corporations show 70-80% cyber insurance adoption.
- Small businesses maintain a 17% cyber insurance adoption rate.
- The healthcare sector achieves 82% policy adoption.
- SMBs report 60% viewing cybersecurity as the top concern.
- Europe’s mid-sized enterprises exceed 50% adoption via GDPR.
- Large enterprises reach 96% coverage with high revenue.
- 90% of 100-5,000 employee organizations have coverage.
- The education sector records 35% growth in adoption.
- Emerging markets like Brazil see rapid policy uptake.
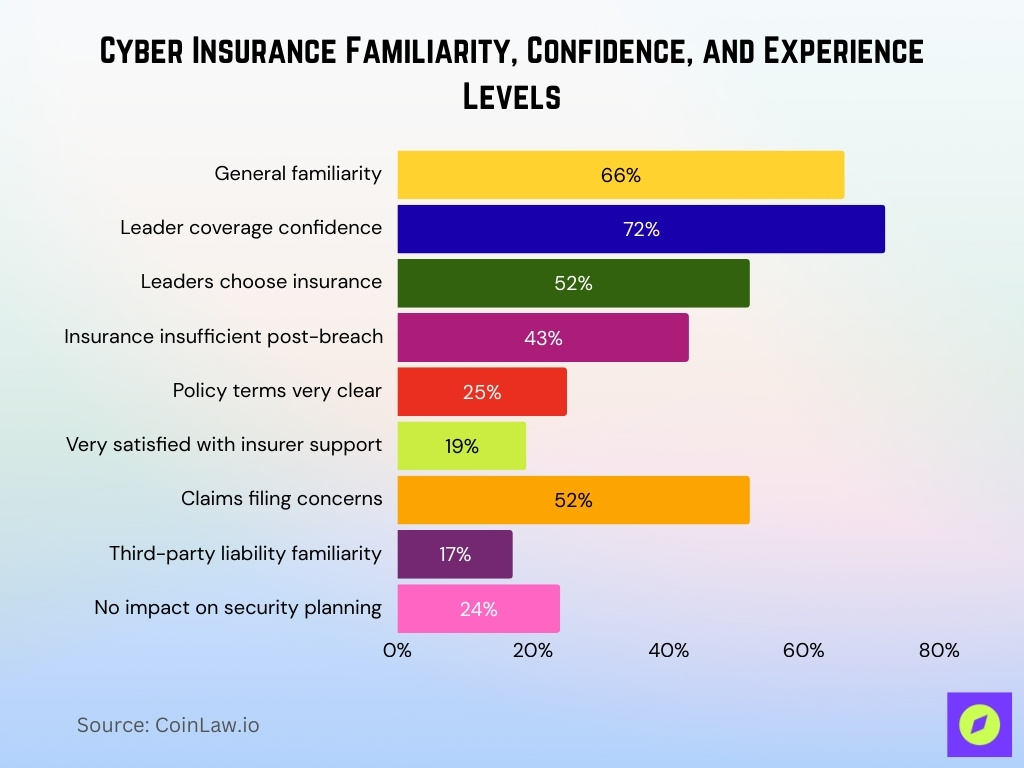
Familiarity and Experience with Cyber Insurance
- 66% of U.S. adults claim familiarity with cyber insurance.
- 72% of senior technology leaders are somewhat confident in coverage.
- 52% of senior technology leaders lead insurance selection.
- 43% of IT decision-makers found insurance insufficient post-breach.
- 25% say current policy terms are very clear.
- 19% very satisfied with insurer communication and support.
- 52% cite general concerns when filing claims.
- 17% very familiar with third-party liability coverage.
- 24% report that policy has no influence on cybersecurity planning.
Data Breach Insights
- Global average data breach cost reached $4.44 million.
- US data breach costs hit a record $10.22 million average.
- Healthcare breaches averaged $7.42 million per incident.
- Over 3,100 data compromises were reported in the US, affecting 1.35 billion individuals.
- Phishing initiated 36% of all data breaches.
- Customer PII was compromised in 53% of breaches.
- The mean time to identify a breach fell to 181 days.
- The mean time to contain a breach averaged 60 days.
- 1,732 breaches were publicly reported in H1.
Major Loss Drivers in Cyber Insurance
- Ransomware accounts for 76% of incurred losses despite 56% of claims.
- BEC and funds transfer fraud comprise 60% of all cyber claims.
- Social engineering attacks represent 42% of incurred claims.
- Business interruption now dominates 44% of cyber claims.
- Average ransomware claim exceeds $1.18 million per incident.
- Vendor-related ransomware drives 91% of total incurred losses.
- Legal costs from class actions exceed $5 million in major cases.
- Denied claims often cite 14% vendor breach exclusions.
- Manufacturing suffers 23.1% of all ransomware claims.
Cybersecurity Insurance Global Market Growth Highlights
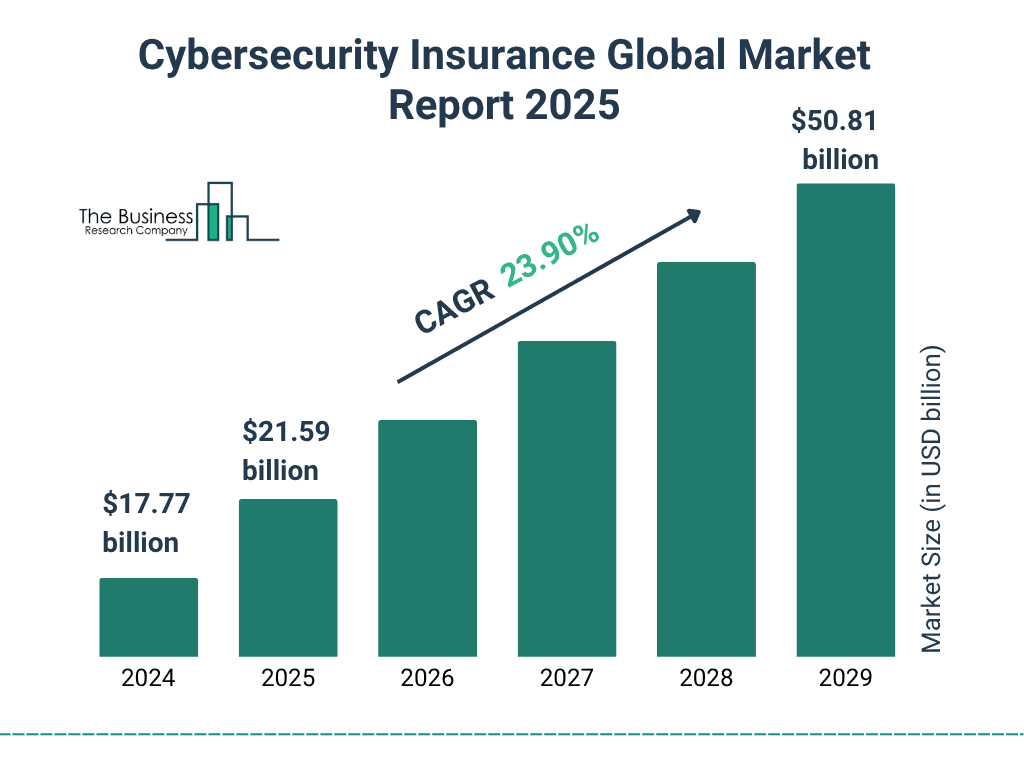
- The global cybersecurity insurance market expands from $17.77 billion in 2024 to $50.81 billion by 2029, reflecting rapid sector maturation.
- Market size rises to $21.59 billion in 2025, showing accelerating enterprise adoption of cyber risk transfer.
- Continued growth lifts the market to approximately $26.8 billion in 2026 and $32.9 billion in 2027, driven by higher breach frequency and regulatory pressure.
- By 2028, the market will surpass $40.1 billion, underscoring increasing reliance on cyber insurance for financial resilience.
- The industry posts a strong 23.9% CAGR, positioning cyber insurance among the fastest-growing segments within the global insurance market.
Premium Pricing Trends
- Global cyber premiums stabilized with 6% rate decline in Q3.
- Premiums expected to grow 15-20% annually through 2026.
- Healthcare faces double-digit premium increases due to poor controls.
- SMBs pay $1,000-$7,500 annually for typical coverage.
- Bundled cyber policies yield 5-15% multi-policy discounts.
- Robust cybersecurity earns 10-30% premium discounts.
- High-risk sectors see flat or rising rates despite market softening.
- Market softening driven by increased reinsurance capacity.
Cyber Insurance Market Share by Organization Size
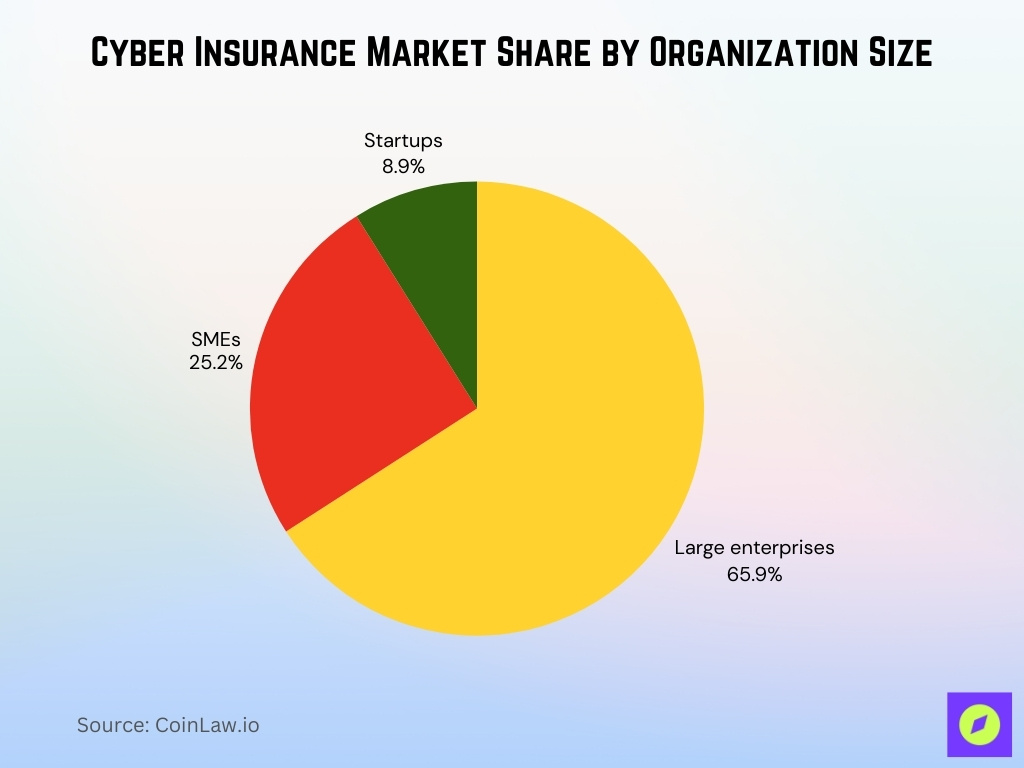
- Large enterprises dominate the cyber insurance market with a 65.9% share, reflecting higher exposure to complex cyber risks and stricter compliance needs.
- Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) account for 25.2% of market demand, driven by rising ransomware attacks and growing regulatory awareness.
- Startups hold just 8.9%, highlighting lower penetration due to budget constraints and limited risk maturity.
- Market concentration shows cyber insurance adoption is heavily skewed toward larger organizations with higher digital asset values.
- The data underscores a significant growth opportunity in SMEs and startups as cyber threats and insurance awareness continue to rise.
Recent Developments
- Cyber reinsurance capacity expanded by $250 million in H1.
- AI underwriting reduced processing times from 3 days to 3 minutes.
- CIRCIA mandates cyber incident reporting for critical infrastructure.
- NIS2 Directive expands cybersecurity requirements to 15 sectors.
- Insurers introduced affirmative AI coverage endorsements.
- Usage-based pricing ties premiums to real-time risk metrics.
- Hybrid cyber-liability products gained market traction.
- Risk prevention services are bundled into premium packages.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Roughly 62% of organizations report having a cyber insurance policy in place.
The cyber insurance market has nearly tripled in size over the last five years.
Business cyber insurance accounts for about 75% of total cyber insurance premiums.
Cyber insurance represents less than 1% of global property and casualty premium volume.
Conclusion
The cyber insurance industry today stands at the crossroads of exponential growth and evolving challenges. With premium pricing trends reflecting the heightened risk landscape, insurers are innovating to meet the demands of an increasingly connected world. From tailored policies for large corporations to expanding coverage for small businesses, the industry is adapting to bridge gaps in security and preparedness. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, robust insurance policies remain critical for financial resilience, ensuring businesses can weather the storm of potential digital disruptions.