Imagine a company where every decision is transparent, every stakeholder has a say, and no single person holds all the power. Welcome to the world of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs). Over the past few years, DAOs have transformed from niche blockchain experiments to significant structures reshaping industries and governance worldwide.
With blockchain as their backbone, DAOs operate on smart contracts, allowing decentralized groups to make decisions collectively, bypassing traditional hierarchies. Let’s explore the latest statistics and trends surrounding DAOs, shedding light on their impact and the opportunities and challenges they present.
Editor’s Choice
- As of 2025, decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) collectively hold approximately $21.4 billion in liquid assets within their treasuries.
- Lido DAO’s governance structure requires that for any proposal to pass, at least 5% of the total LDO token supply must vote in favor.
- The distribution of ten major DAOs’ governance tokens reveals that less than 0.1% of all holders possess 90% of the voting power.
- Over 13,000 DAOs have been established globally, collectively managing a treasury of $24.5 billion and engaging 11.1 million governance token holders.
- More than 6,000 DAOs exhibit regular activity, engaging members in governance and operations.
Number of DAOs and Growth Trends
- There are now over 13,000 active DAOs worldwide in 2025.
- The number of DAOs grew at an estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of ~30% between 2021 and 2024, though annual growth varies by sector and activity type.
- Non-financial DAOs, particularly in gaming, media, and content, saw increased formation in 2024, with platforms like DAOhaus and Aragon reporting over a 25% increase in such DAO categories year-over-year.
- Community DAOs still dominate, making up 62% of all active DAOs globally.
- The Asia-Pacific region leads in DAO expansion, with China, South Korea, and India driving regional growth.
- Environmental-focused DAOs, such as KlimaDAO and Toucan, are expanding, with DAO research platforms estimating 500–600 sustainability-related DAOs globally by early 2025.
- Analytics platforms like DeepDAO, DAOlytics, and Tally improved tracking and visualization features by over 30% in 2024, enhancing DAO transparency and governance data accessibility.
- DAO conference attendance rose another 40% in 2025, highlighting deeper community engagement and interest.
Total Assets Held & Number of DAOs by Web3 Category
- DeFi dominates the landscape with $7.5 billion in total assets held and the highest number of DAOs (70).
- Infrastructure comes next in activity with 30 DAOs, holding a combined $0.8 billion in assets.
- Venture Capital DAOs are fewer (25 in total) but still significant, managing $0.2 billion in assets.
- The NFT sector has 20 DAOs, collectively holding $0.5 billion.
- “Other” categories also have 20 DAOs, though with smaller total assets of $0.1 billion.
- Philanthropy and Creative DAOs each have 10 DAOs, holding $0.3B and $0.1B, respectively.
- The Scientific category includes 5 DAOs, with a total asset pool of $0.2 billion.
- Gaming shows some traction with 7 DAOs and $0.3 billion in assets.
- Storage is the least represented with just 2 DAOs and $0.2 billion in assets.

Governance Token Holders and Voter Participation
- There are now over 6.5 million governance token holders worldwide in 2025.
- Voter participation in DAOs averages 17%, with leading DAOs reaching up to 28% for major proposals.
- Top DAOs like Aave and MakerDAO maintain turnout rates above 22% on critical governance votes.
- Around 78% of DAO tokens are still held by the top 20% of stakeholders, raising continued concerns about decentralization.
- Quadratic voting, a mechanism to reduce influence by token whales, has been adopted by over 100 DAOs, including Gitcoin and Optimism-based projects.
- Proposal engagement in major DAOs like Uniswap and Compound remains high for key decisions but dips on smaller governance items.
- Usage of governance tools like Snapshot and Tally surged by 45% in 2025, reflecting demand for accessible voting platforms.
- New incentive models introduced in pilot DAOs raised voter turnout by an average of 12%.
Why We Need DAOs
- DAOs enable trustless collaboration by replacing traditional intermediaries with automated, code-based systems, ensuring transparent operations and fair participation.
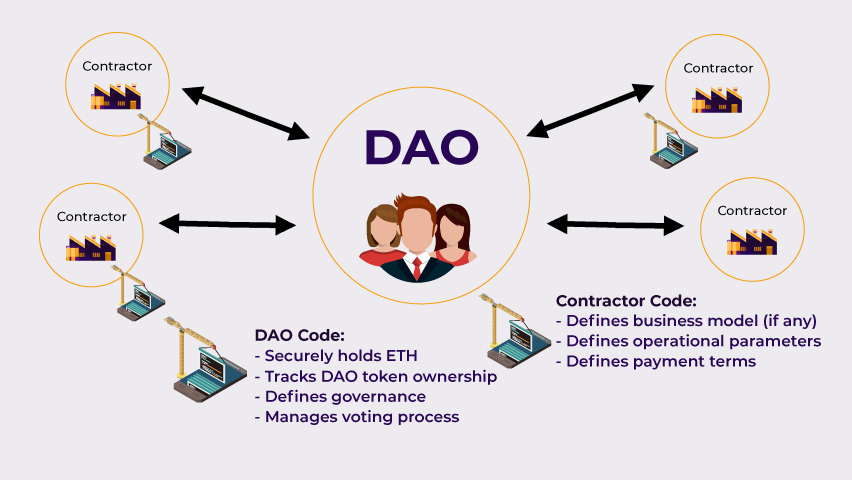
- DAO Code manages essential governance functions, including:
- Securely holding ETH and digital assets, ensuring funds are protected without relying on centralized control.
- Tracking DAO token ownership, which determines voting power and governance rights.
- Defining governance rules, outlining how decisions are proposed, debated, and approved.
- Managing the voting process through smart contracts eliminates the need for manual oversight or administrative bureaucracy.
- Contractor Code outlines clear operational guidelines, allowing contributors to:
- Understand the business model (if any), ensuring alignment with DAO goals.
- Follow defined operational parameters, providing clarity on tasks, deliverables, and expectations.
- Receive automated payments based on predefined terms, ensuring timely and transparent compensation.
Benefits of DAOs
- Transparency is one of the most significant advantages, as all financial transactions and governance decisions in a DAO are recorded on the blockchain, creating a permanent public record.
- Decentralization reduces the risk of corruption or abuse of power, as no single entity has overarching control, ensuring that decisions are made collectively by the community.
- Member-driven governance allows token holders to directly influence a DAO’s direction, fostering a strong sense of community and alignment between participants and the organization.
- Low barriers to entry enable global participation; anyone with internet access and a small investment can join and contribute to many DAOs.
- Autonomy through smart contracts reduces the need for intermediaries, enabling DAOs to execute decisions and handle resources without traditional legal or corporate structures.
- Adaptability is enhanced, as DAOs can pivot quickly in response to member input, allowing for faster responses to industry changes or member demands.
- Incentive alignment ensures members are motivated to contribute since participation and voting often lead to rewards, fostering more robust and active engagement.
- Cost efficiency is achieved by removing traditional corporate layers, which reduces overhead costs, potentially increasing funds available for projects or treasury holdings.
Industry Adoption and Use Cases
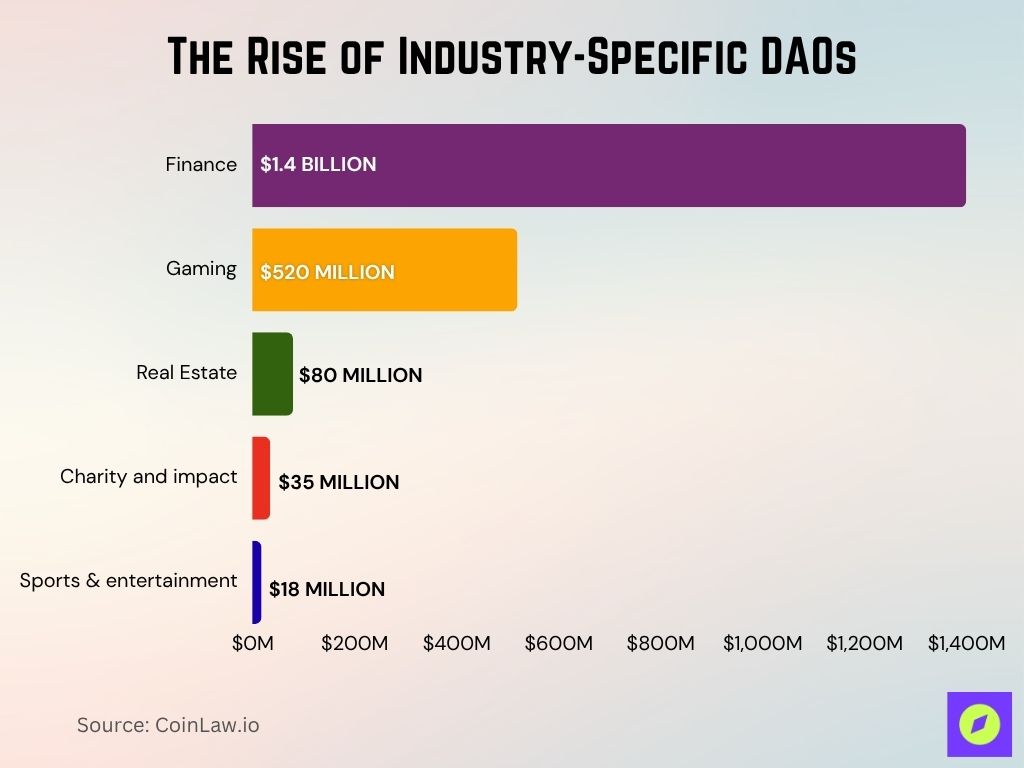
- Finance remains the top sector for DAOs, with investment DAOs now managing over $1.4 billion in diversified assets.
- Gaming DAOs like Yield Guild Games have grown to manage $520 million in digital and in-game assets.
- Media and content DAOs represent 18% of all DAOs, enabling collaborative creation and revenue sharing among members.
- Approximately $80 million in tokenized real estate assets by 2025, though broader real estate DAO assets remain unverified across platforms.
- Social media DAOs continue to rise, giving users more governance power on platforms similar to BitClout and emerging alternatives.
- Charity and impact DAOs like Giveth have distributed over $35 million globally to social and environmental causes in 2025.
- Legal DAOs such as LexDAO expanded their footprint by offering compliance tools and legal support across decentralized ecosystems.
- Sports and entertainment DAOs reached over $18 million in fan-driven assets, empowering fans in club and event decisions.
Limitations and Downsides of DAOs
- Low voter turnout remains a key issue in 2025, with most DAOs reporting participation rates below 18%, risking governance by a minority.
- Power concentration persists, with nearly 78% of governance tokens held by the top 15–20% of holders, challenging decentralization.
- Smart contract security flaws led to over $90 million in DAO-related losses in 2025 due to hacks and code vulnerabilities.
- Regulatory uncertainty continues, as most governments still lack clear DAO frameworks, keeping many projects in legal limbo.
- Consensus challenges slow down decision-making, especially in fast-moving sectors where DAOs struggle to act quickly.
- Coordination issues in large DAOs result in inefficiency, with fragmented interests complicating collective governance.
- Accountability remains weak, as decentralized structures often lack mechanisms to enforce responsibility among DAO participants.
- Member inexperience hinders progress, with many newer DAO contributors lacking the expertise to manage complex decisions.
DAO Participation by Age Group
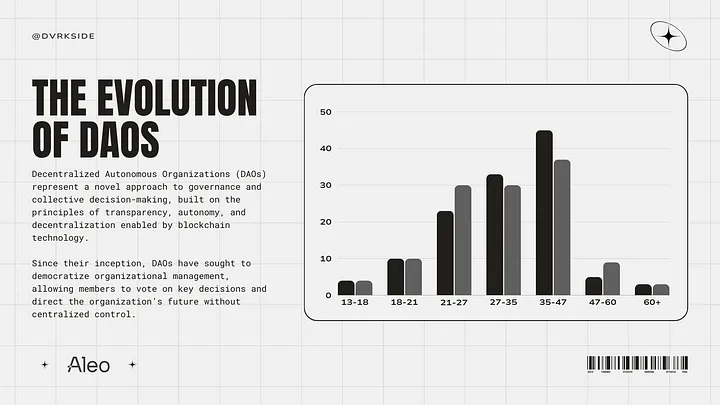
- Teenagers aged 13-18 contribute 5%, showing early adoption among the youngest demographic.
- Younger participants (ages 18-21) account for 10%, while teenagers (13-18) contribute only 5%.
- Participants in the 21-27 age range make up 25%, highlighting DAO interest among early-career individuals.
- Individuals aged 27-35 represent 30%, showing strong involvement from young professionals.
- The largest group of participants in DAOs is aged 35-47, accounting for 45% of the total.
- The second largest age group is 47-60, making up 40% of DAO participants.
- Older people aged 60+ also make up 5%, indicating limited but notable engagement from older demographics.
DAOs’ Effects on Organizations
- A flattened hierarchy is common in DAOs, transforming traditional company structures by reducing or eliminating layers of management and empowering members instead.
- Enhanced collaboration across industries is fostered, as DAOs can bring together diverse stakeholders from around the globe to work on shared goals without the need for a central office.
- Talent attraction and retention are improved by DAOs that offer decentralized governance and member influence, appealing to individuals seeking more autonomy and flexibility in their work.
- Increased focus on community has reshaped organizations, with DAOs prioritizing community-driven decision-making and open collaboration over traditional corporate profit motives.
- Borderless operations make DAOs more resilient in global markets, as they’re often open to participants from anywhere, allowing for truly international organizations.
- Operational transparency fosters trust within DAOs, as financial and decision records are available on the blockchain, contrasting sharply with closed-door boardroom meetings in traditional firms.
- Flexibility in project funding allows DAOs to raise funds quickly and allocate resources directly toward project goals without the red tape of traditional corporate budgeting.
- Cultural shifts have emerged as DAOs champion ideals of openness, innovation, and shared ownership, influencing even traditional organizations to adopt decentralized principles.
Examples of DAOs
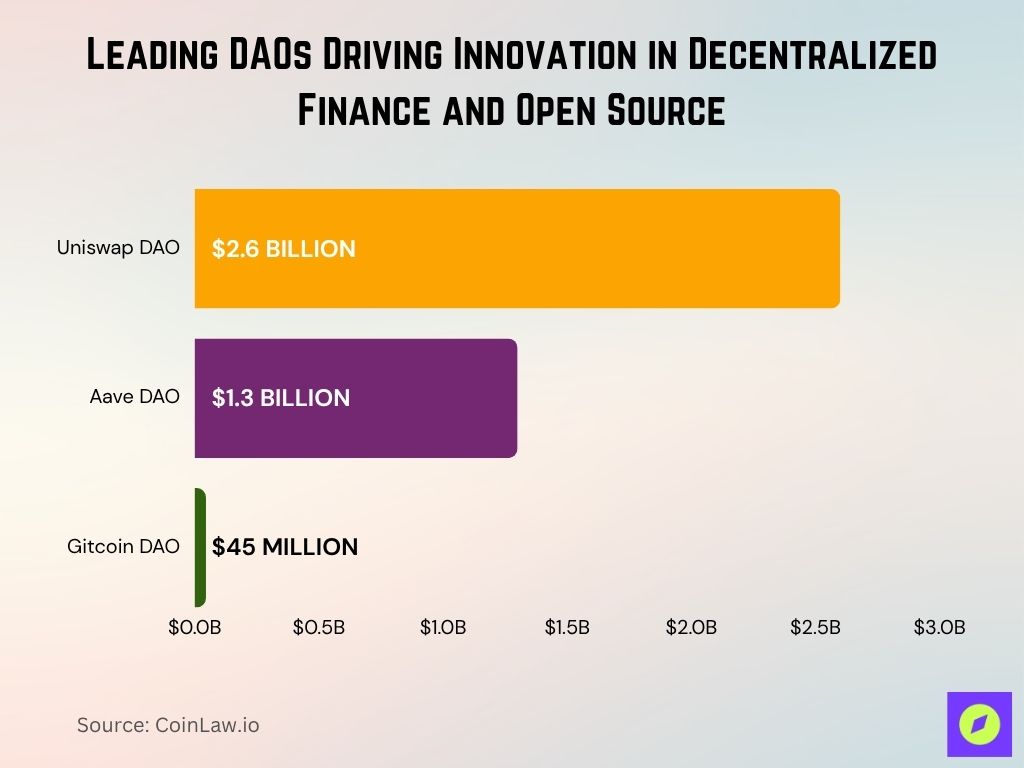
- Uniswap DAO manages one of the largest DEXs, with community-driven governance and assets now exceeding $2.6 billion.
- MakerDAO governs the DAI stablecoin, letting token holders adjust parameters that maintain DAI’s stability and $1 peg.
- Aave DAO oversees DeFi lending with governance over new asset listings and a treasury now worth over $1.3 billion.
- PleasrDAO acquires iconic cultural assets and NFTs, with shared ownership and governance among community members.
- Gitcoin DAO has distributed over $45 million in grants to open-source developers building impact-driven blockchain projects.
- Friends With Benefits (FWB) is a social DAO blending exclusive access and community governance for creative initiatives.
- Decentraland DAO allows members to vote on virtual real estate rules, partnerships, and in-world policy changes.
- Bankless DAO leads in DeFi education, enabling members to produce content, run events, and vote on outreach efforts.
- LexDAO delivers decentralized legal expertise, expanding tools for blockchain compliance and accessible legal services.
- Aragon DAO powers DAO creation globally, supporting over 3,000 DAOs with governance frameworks and toolkits.
Technological Developments and Innovations
- Smart contract innovations in 2025 introduced Solidity v0.9 and expanded Rust and Move support, boosting DAO security and performance.
- Cross-chain DAOs now operate across multiple blockchains, with growing adoption of Polkadot, Cosmos, and zk-powered bridges.
- DAO tooling platforms like Snapshot, Tally, and Aragon saw a 40% increase in usage, streamlining governance workflows.
- AI-powered tools are integrated into DAOs, enhancing treasury management, proposal analysis, and member engagement scoring.
- Decentralized identity (DID) systems are now used in over 200 DAOs, verifying voters while preserving anonymity and trust.
- Ethereum Layer-2s such as Optimism, Arbitrum, and Base cut DAO gas fees by up to 90%, making participation more accessible.
- Quadratic voting adoption rose by 30%, helping DAOs balance influence and reduce token whale dominance in decision-making.
- Tokenized reputation systems track and reward long-term contributions, becoming critical for voting power and DAO governance weight.
- On-chain analytics platforms provide real-time dashboards for treasury health, voting trends, and governance transparency.
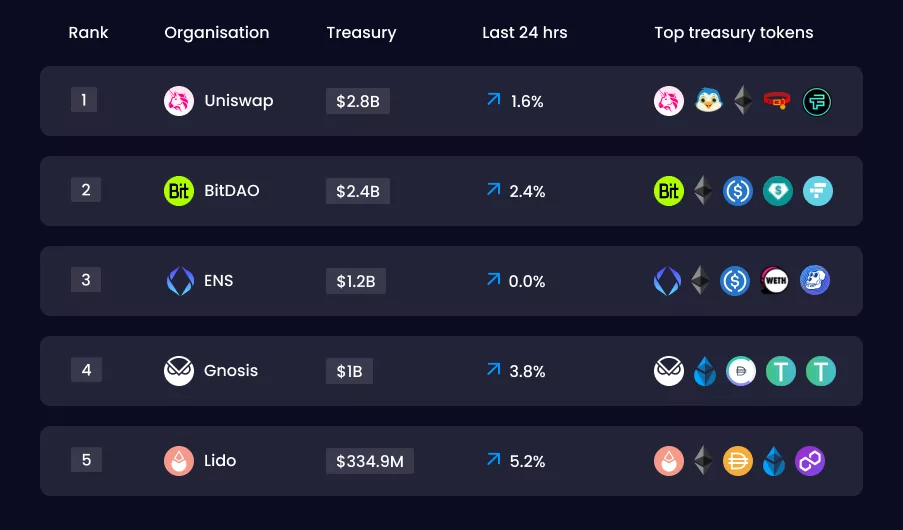
Top DAOs and Their Treasuries
- Uniswap leads the DAO space with a massive treasury of $2.8 billion, cementing its dominance as the largest DAO by funds under management.
- BitDAO, holding $2.4 billion in treasury, highlights its focus on investment and funding initiatives to support decentralized projects.
- ENS (Ethereum Name Service) manages $1.2 billion, reflecting strong community support and the growing importance of blockchain-based domain services.
- Gnosis, with a $1 billion treasury, shows an emphasis on decentralized prediction markets and governance tools, maintaining steady growth.
- Lido, with a treasury of $334.9 million, has shown the highest 24-hour growth rate at 5.2%, underscoring its rising role in liquid staking solutions within DeFi.
Challenges and Regulatory Considerations
- Regulatory uncertainty persists in 2025 as countries like the United States, China, and India still lack clear DAO governance laws.
- Legal liability risks for DAO members remain high, with no uniform frameworks to determine accountability for hacks or losses.
- Tax treatment of governance tokens varies widely, with some jurisdictions treating them as securities and others as digital property.
- DAO hacks in 2025 resulted in over $310 million in losses, underscoring the need for stronger smart contract security.
- Lack of standardized governance models across DAOs leads to inconsistencies in voting systems and quorum requirements.
- Decentralization challenges continue as over 75% of voting power is often held by top token holders, limiting true community control.
- AML compliance pressure increased in 2025, with regulators pushing DAOs to implement identity checks and transaction monitoring.
- Insurance coverage for DAOs remains rare, as most providers avoid covering decentralized assets due to perceived risk.
- Cross-border legal complexity raises DAO operational costs, with compliance burdens rising in globally distributed teams.
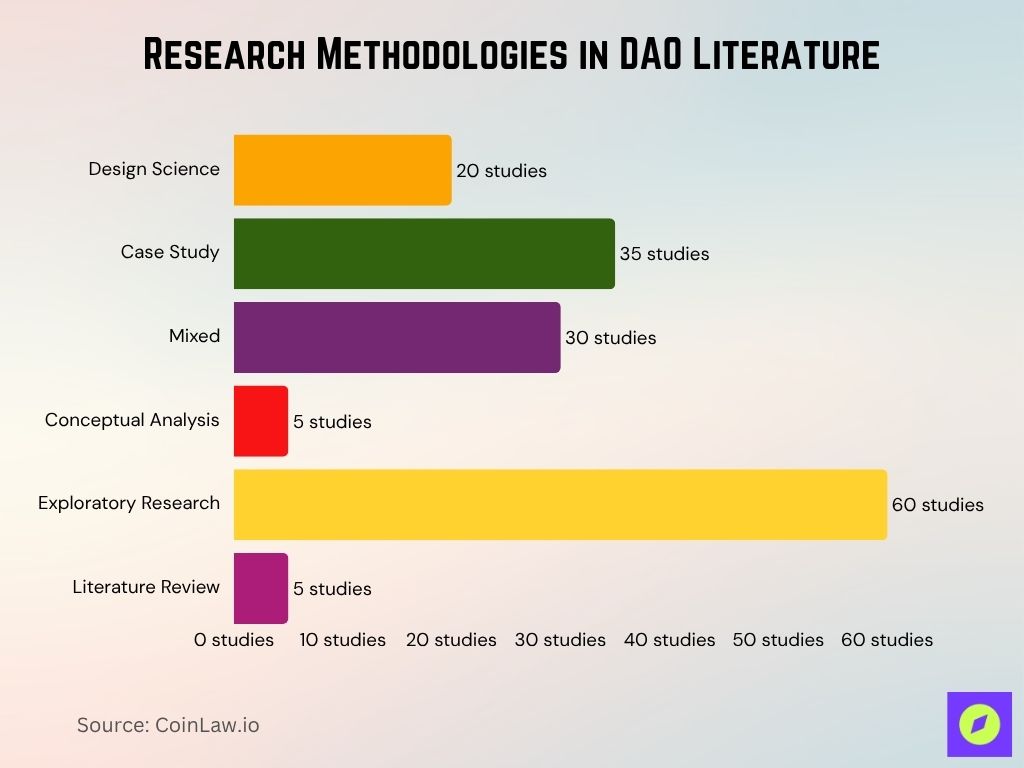
Research Methodologies in DAO Literature: Key Insights
- A systematic literature review on Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) reveals the dominant research methodologies used in this emerging field.
- Exploratory research is the most prevalent method, appearing in 60 studies, indicating the nascent and evolving nature of DAO-related research.
- Case studies are the second most common approach, featured in 35 studies, suggesting a strong interest in examining real-world DAO implementations.
Mixed methods were used in 30 studies, reflecting an effort to combine quantitative and qualitative perspectives. - Design science appears in 20 studies, highlighting the development of practical frameworks and tools for DAOs.
- Conceptual analysis and literature reviews are the least utilized, each found in only 5 studies, showing limited focus on theoretical synthesis or consolidation of existing knowledge.
Recent Developments
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): DAOs are increasingly incorporating AI to enhance decision-making processes and automate complex tasks, leading to more efficient and responsive governance structures.
- Enhanced Security Measures: In response to vulnerabilities, DAOs are adopting advanced security protocols, including multi-signature wallets and formal verification methods, to safeguard assets and maintain trust within their ecosystems.
- Legal Recognition and Frameworks: Jurisdictions like Wyoming have enacted legislation recognizing DAOs as legal entities, providing a clearer regulatory environment and encouraging broader adoption of decentralized governance models.
- DAOs are exploring use cases beyond finance, with early projects emerging in healthcare (VitaDAO), education (EduDAO), and supply chain (OriginTrail), though adoption in these sectors remains limited.
- Improved Governance Mechanisms: The implementation of delegation mechanisms within DAOs has emerged to increase community decision-making efficiency and improve user convenience in exercising their rights.
Conclusion
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations are evolving from experimental concepts into influential entities with real-world impact. DAOs offer a bold new way for communities to govern themselves, backed by transparency, security, and smart contract technology. However, as DAOs continue to expand across industries and borders, they face complex challenges such as regulatory hurdles, security concerns, and voting power imbalances.
The developments today suggest a bright future, with advances in technology, increased community engagement, and growing support from both the corporate and public sectors. As DAOs navigate these challenges, they are likely to reshape the way we think about organizational structures, empowering individuals worldwide to participate in collective decision-making and ownership. With continued innovation and adaptation, DAOs are set to become an enduring fixture in the global digital economy.



































































