The auto insurance industry today is evolving rapidly, shaped by technological advancements, shifting demographics, and changes in vehicle ownership patterns. In the past decade, factors like electric vehicle adoption, changing consumer preferences, and state regulations have driven significant fluctuations in premiums and coverage options.
As we navigate the landscape of auto insurance, it’s essential to understand the key statistics shaping the industry this year. This article will provide you with comprehensive insights into market trends, premium rates, claims, and the impact of electric vehicles (EVs) on insurance costs.
Editor’s Choice
- The global EV insurance market is valued at $93.94 billion, reflecting rapid expansion alongside rising electric vehicle adoption worldwide.
- U.S. private auto insurance premiums reached $278.04 billion in Q1–Q3, highlighting the scale and revenue strength of the domestic auto insurance market.
- The Asia-Pacific car insurance market stands at $191.05 billion, supported by strong vehicle ownership growth in emerging and developed economies across the region.
- The average U.S. full-coverage auto insurance premium is $2,158, reflecting higher repair costs, inflation, and advanced vehicle features.
- North America accounts for 36% of the EV insurance market share, making it a leading region in electric vehicle coverage and policy innovation.
Recent Developments
- The global insurtech market has reached $50.03 billion, reflecting rapid digital transformation across underwriting, claims processing, and customer engagement.
- Artificial intelligence reduces claims resolution times by up to 75%, significantly improving efficiency and customer satisfaction through automation.
- AI-powered fraud detection systems now achieve 85–90% accuracy, helping insurers minimize false claims and reduce financial losses.
- The EV insurance market is expanding at a 4.6% CAGR, supported by rising electric vehicle adoption and the need for specialized coverage.
- The California Low Cost Auto (CLCA) program offers coverage as low as $244 per year, increasing affordability for eligible low-income drivers.
- Autonomous driving technology from Waymo has reduced property damage claims by 88%, highlighting the safety impact of advanced driver-assistance systems.
- The NAIC is developing telematics data usage regulations to guide how insurers collect and apply driver data for pricing and risk assessment.
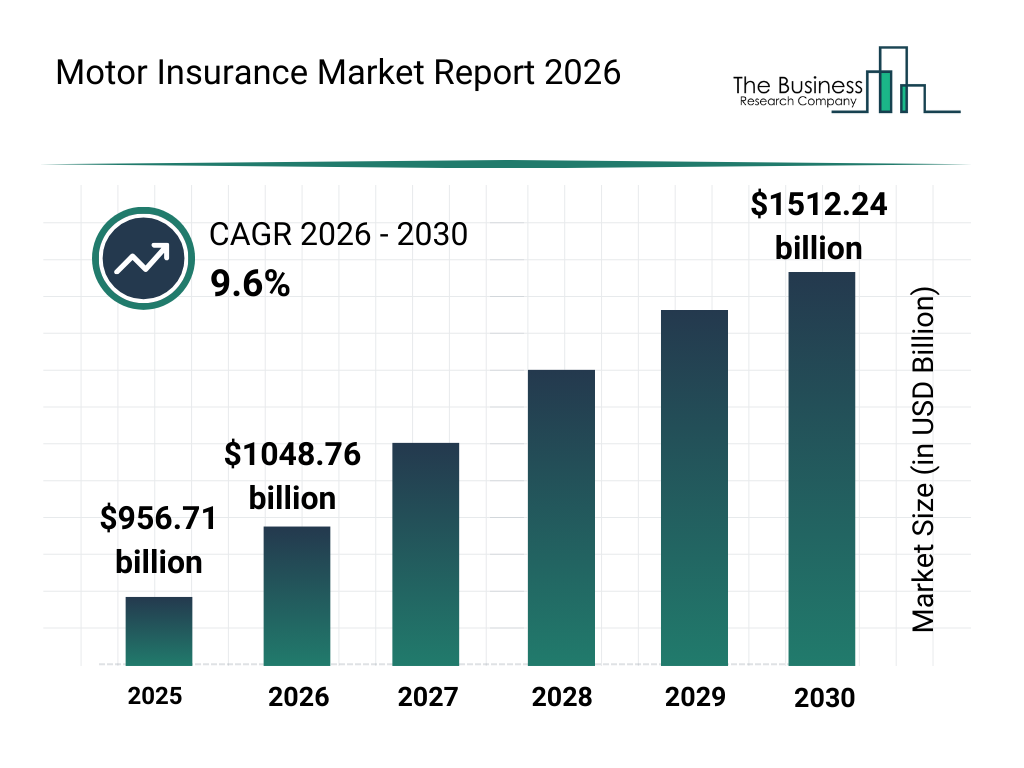
Global Motor Insurance Market Size Forecast
- The global motor insurance market reached $956.71 billion in 2025, reflecting the industry’s massive global scale.
- The market will grow to $1,048.76 billion in 2026, surpassing the $1 trillion milestone.
- The market will expand at a 9.6% CAGR from 2026 to 2030, driven by rising vehicle ownership and premium growth.
- By 2028, the market will exceed approximately $1.25 trillion, maintaining its upward trajectory.
- In 2029, the industry will approach roughly $1.38 trillion, signaling accelerating momentum.
- By 2030, the global motor insurance market will reach $1,512.24 billion, reinforcing its position as one of the largest insurance segments worldwide.
- Overall, the market will expand by more than $555 billion between 2025 and 2030, underscoring strong long-term demand for auto coverage.
Average 6-Month Car Insurance Premiums by Age Group
- Teens aged 16–19 face the highest premiums at $5,936 per 6-month period, more than 2.5x higher than any other group.
- Drivers in their 20s pay an average of $1,989, still significantly above the national average.
- 30–39-year-olds enjoy a lower rate of $1,532, showing a notable drop as drivers gain experience.
- Rates continue to decline for 40–49-year-olds, averaging $1,474.
- The lowest average premium appears for those aged 50–59, at $1,365.
- Both the 60–69 and 70–79 age groups pay the same average rate of $1,384.
- Premiums begin to rise again for 80–85-year-olds, increasing to $1,880.
Global Share of Insurance Providers by Country
- The United States leads with the highest share of insurance providers for roughly 40%, reflecting its highly developed insurance market, broad product offerings, and strong regulatory framework.
- China ranks second, accounting for 10.1% of global insurance providers, driven by rapid economic growth and expanding demand for life and property coverage.
- Japan holds 5.0%, making it one of the largest contributors globally, supported by a mature insurance sector and high penetration rates.
- India represents 1.9% of total insurance providers worldwide, with steady growth fueled by rising financial inclusion and expanding middle-class demand.
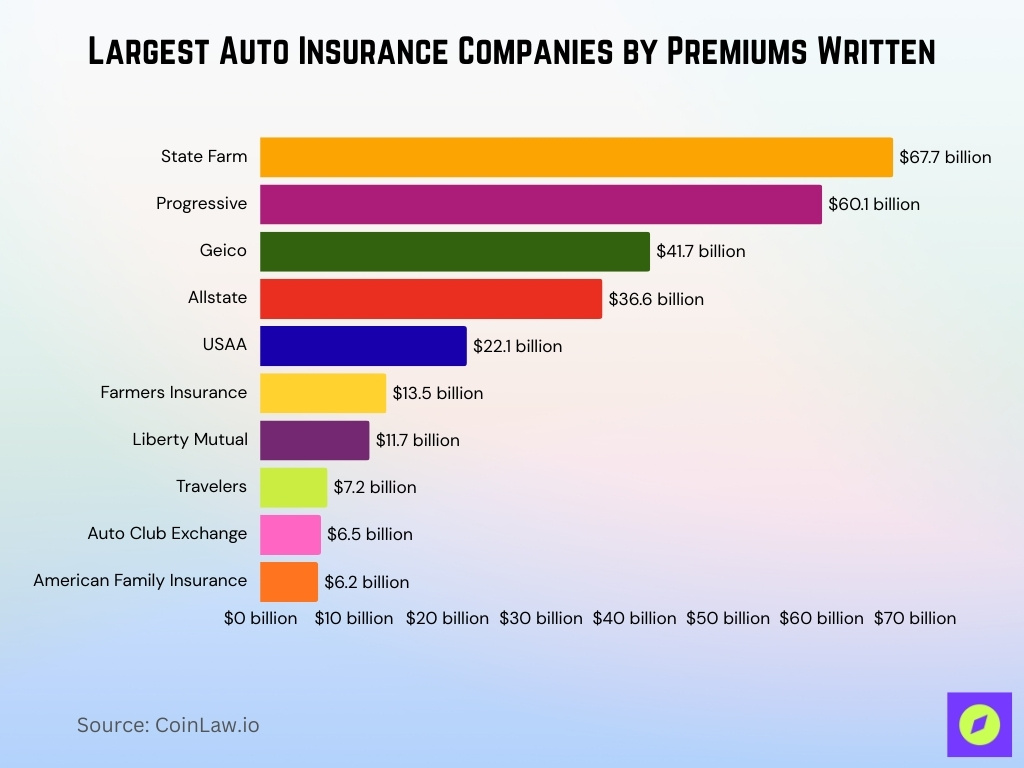
Largest Auto Insurance Companies by Premiums Written
- State Farm ranks as the largest auto insurer, generating approximately $67.7 billion in premiums written.
- Progressive holds the second position with about $60.1 billion, narrowing the gap with the market leader.
- Geico follows in third place, reporting roughly $41.7 billion in auto insurance premiums.
- Allstate secures fourth position with around $36.6 billion, maintaining a strong national presence.
- USAA recorded approximately $22.1 billion in premiums, driven largely by its military-focused customer base.
- Farmers Insurance generated about $13.5 billion, placing it among the mid-tier major insurers.
- Liberty Mutual reported roughly $11.7 billion in premiums written in the auto segment.
- Travelers produced about $7.2 billion, reflecting its smaller share in personal auto compared to commercial lines.
- Auto Club Exchange wrote approximately $6.5 billion in premiums, supported by its AAA member network.
- American Family Insurance rounds out the top ten with about $6.2 billion in auto insurance premiums.
- Collectively, the top two insurers alone account for over $127 billion in premiums, highlighting significant market concentration at the top.
Premium Rates and Consumer Demographics
- Drivers under 25 pay over 80% more than those aged 30–45, with average annual premiums around $3,450 compared to $1,820 for middle-aged drivers.
- Female drivers pay approximately 4% less than male drivers, with average annual premiums of $1,315 for females and $1,368 for males.
- Households earning under $50,000 spend about 15% of their income on auto insurance, while higher-income households allocate around 9%.
- Urban drivers face premiums that are up to 25% higher than those in rural areas, due to factors like increased traffic congestion, higher theft rates, and more frequent accidents.
- Senior drivers aged 65 and above have experienced an average premium increase of 7%, with those over 75 seeing annual increases between $200 and $380.
- Drivers with poor credit pay, on average, 105% more for full coverage car insurance than those with excellent credit.
- Married individuals often enjoy premiums that are 5–10% lower than single drivers, saving approximately $160 annually.
Vehicle-related Statistics
- Hybrid vehicle owners typically pay 7% less for insurance compared to owners of conventional gas-powered cars.
- Luxury cars carry an average annual premium of $3,500, which is 2.5 times higher than the premium for a standard sedan due to higher costs of repair and replacement.
- SUV drivers pay an average premium of $2,339 annually, reflecting the increased weight and potential for more severe accidents.
- Compact car owners enjoy the lowest premiums, averaging $1,100 per year, as these vehicles are often cheaper to repair and less likely to be involved in high-cost claims.
- Sports cars have some of the highest premiums, with owners paying $3,800 annually, reflecting their high speeds and greater accident risk.
- Pickup trucks generally have premiums of $2,439, with lower repair costs balancing the higher risk of accidents involving larger vehicles.
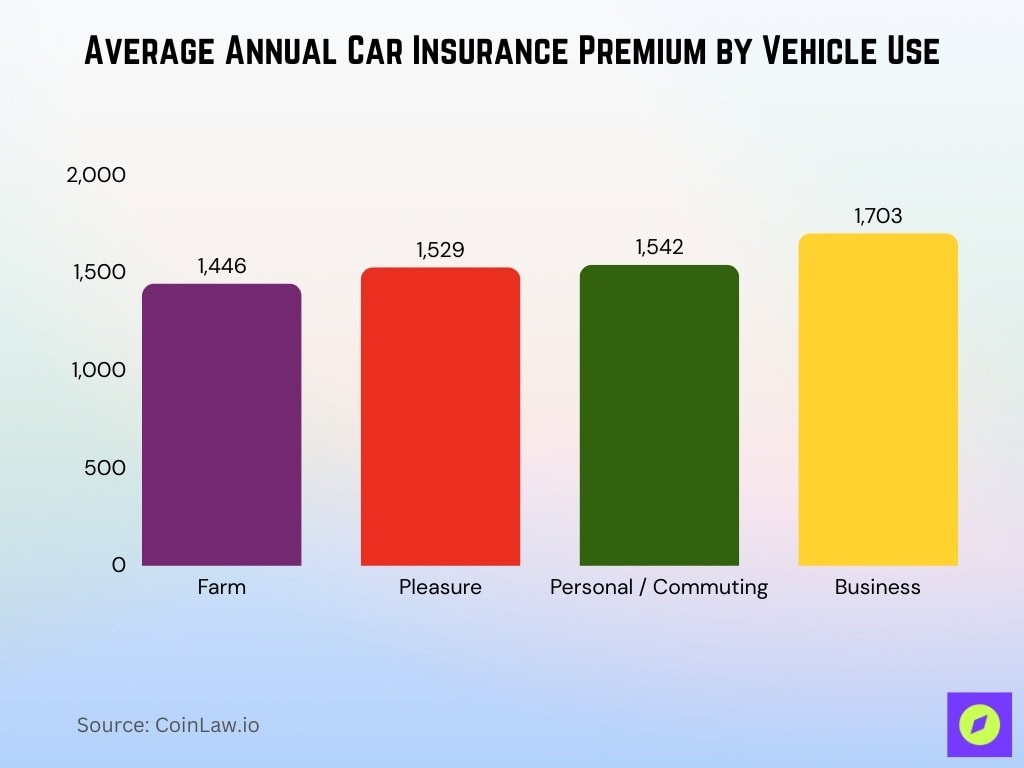
Average Car Insurance Rates by Vehicle Use
- Farm vehicles have the lowest average annual premium at $1,446, largely because they are driven less frequently and mainly used on private property or rural roads.
- Vehicles used for Pleasure driving are insured at an average of $1,529, as insurers view occasional, non-daily driving as lower risk compared to commuting or commercial use.
- Personal/Commuting use carries a slightly higher average premium of $1,542, reflecting increased exposure to traffic congestion, peak-hour driving, and accident risk.
- Business use has the highest average rate at $1,703, since commercial driving often involves longer distances, more time on the road, and higher liability exposure.
Auto Insurance Premium Trends
- Telematics-based policies grew by 25%, enabling safer drivers to reduce premiums by up to 30%.
- Usage-based insurance (UBI) adoption increased by 25%, particularly among urban drivers who drive less frequently.
- Bundling discounts for combining auto and home insurance offer savings up to 30%, with more consumers opting for package deals.
- Pay-per-mile insurance gained traction, allowing low-mileage drivers to save an average of $500 annually compared to traditional policies.
- Premiums for rideshare drivers (Uber, Lyft) increased by 28% due to the added risk of commercial use.
- Climate-related risks led to a 6% rise in premiums for drivers in flood-prone or wildfire-affected areas.
- Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) contributed to premium reductions averaging 5–10%, as these technologies lower accident likelihood.
Impact of Electric Vehicles on Insurance Costs
- Electric vehicles (EVs) typically have 49% higher premiums than gas-powered vehicles due to their higher repair costs and expensive battery systems.
- Repairing an EV battery can cost up to $16,000, significantly raising claim costs when these components are damaged.
- The increasing number of EV repair shops has the potential to lower repair costs over time, but the market is still catching up with demand.
- Tesla continues to dominate the EV insurance market, with average premiums of $4,058 annually for EVs.
- EV theft rates are lower than those of conventional vehicles, contributing to lower comprehensive coverage costs for certain models.
- The growing popularity of EV-specific insurance policies has allowed for more tailored coverage options, offering benefits like charging station access or roadside assistance specifically for EVs.
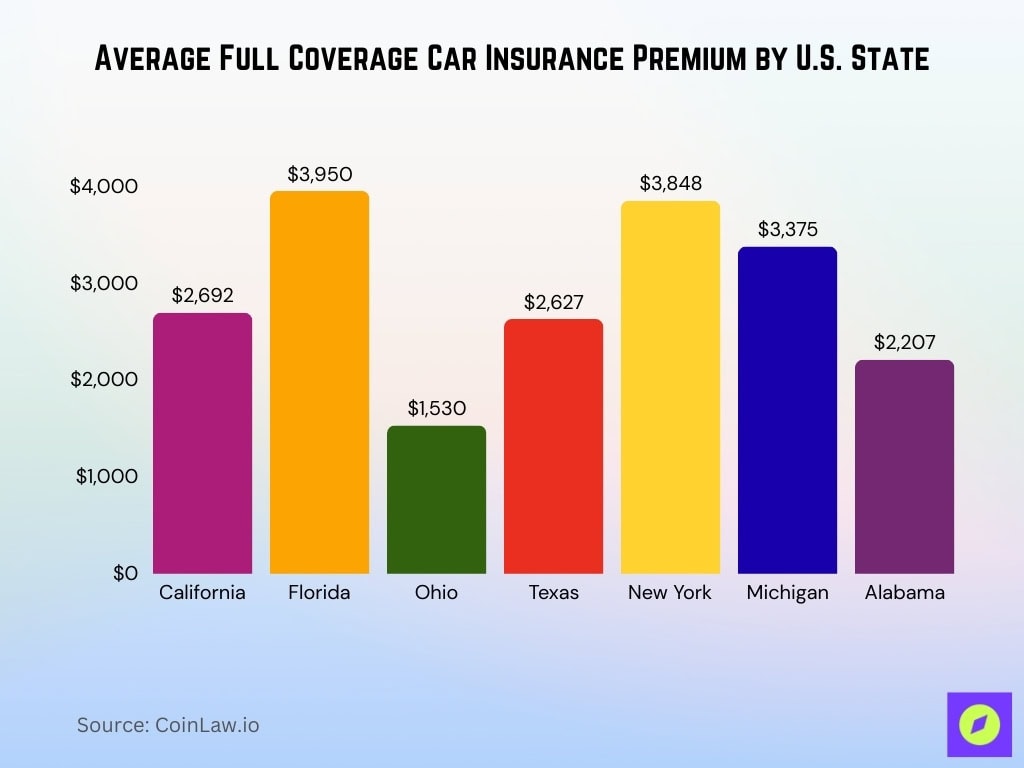
Car Insurance Statistics by State
- The average annual premium for full coverage car insurance in California is $2,692, primarily due to high vehicle densities and traffic-related incidents.
- Florida‘s average premium stands at $3,950, driven by a large number of uninsured drivers and frequent weather-related claims.
- Ohio maintains one of the lowest premiums in the U.S., averaging $1,530 annually, attributed to lower accident rates and favorable state regulations.
- In Texas, the average car insurance premium has risen to $2,627, influenced by the state’s high accident frequency and weather impacts.
- New York car insurance premiums have reached an average of $3,848, reflecting the state’s no-fault insurance laws and dense urban areas.
- Michigan, previously known for its high premiums, now averages $3,375; recent reforms in the state’s no-fault insurance laws have contributed to this adjustment.
- Alabama experienced a rise in auto insurance premiums, averaging $2,207, due to an uptick in severe weather events and claims.
Auto Insurance Affordability
- 32% of U.S. consumers now find auto insurance unaffordable, especially in states like California and Florida, where premiums are highest.
- On average, Americans spend 2.44% of their annual income on auto insurance, with low-income households paying as much as 15%.
- Telematics-based insurance has helped reduce costs for safe drivers, offering potential savings of up to 30%.
- State-regulated insurance programs in high-risk areas, such as Louisiana, have seen premiums rise by 7% due to increased claims from natural disasters.
- Low-income drivers in urban areas often struggle with higher premiums, paying up to 50% more than rural drivers with similar risk profiles.
- Subsidized insurance programs in some states are helping low-income drivers obtain basic coverage, reducing the risk of driving uninsured.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The industry combined ratio is forecast to reach 99% by 2026.
The automobile insurance carriers market is forecasted to grow to $1,149.38 billion in 2026.
The average U.S. auto insurance annual premium is projected at $2,256 in 2026.
The U.S. personal auto insurance combined ratio was 95.3 in 2026, indicating underwriting profitability (below 100).
Conclusion
The auto insurance industry is undergoing significant transformations, driven by the rise of electric vehicles, advanced technologies, and evolving consumer behaviors. While challenges like rising repair costs, climate change risks, and the increase in uninsured drivers put pressure on profitability, innovations such as telematics and AI are helping insurers navigate this complex landscape.
As the market continues to grow and evolve, particularly with the adoption of EV-specific policies and insurtech solutions, companies that embrace digital transformation and customer-centric products will thrive. The future of auto insurance will undoubtedly be shaped by advancements in autonomous driving, blockchain technology, and data-driven policies, promising a dynamic and rapidly changing environment for both insurers and consumers.



































































