Imagine a financial landscape shaped by stability, growth, and the intricate balance of risk and reward. This scene aptly describes the US corporate bond market, a crucial pillar of the country’s financial system. In recent years, the corporate bond industry has experienced significant fluctuations driven by economic shifts, interest rate changes, and the rising influence of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. The bond market is adapting, with fresh opportunities and notable challenges reshaping the industry.
This article delves into the latest statistics and trends shaping the US corporate bond market, covering everything from issuance dynamics to technological advancements in bond trading. By understanding these changes, investors, policymakers, and finance professionals can better navigate and anticipate what lies ahead in this vital sector.
Editor’s Choice
- The US corporate bond market size reached approximately $11.4 trillion in 1Q 2025, reflecting a 3.7% year-over-year increase.
- Investment-grade bonds accounted for $426 billion in gross issuance during 2Q 2025, though net issuance slowed to $32 billion.
- High-yield bond issuance declined to around $52.2 billion in Q1 2025, marking a 24% drop from the previous year.
- The impact of interest rates remains strong, with total IG issuance projected at $1.65 trillion for 2025.
- Average daily trading volume hit $59.5 billion by July 2025, up 15% year-over-year.
- ESG-related issuance remains active, with global green bond issuance projected to reach $600 billion in 2025.
- High-yield default rates stood at 4.3% as of May 2025 and are expected to ease to 4.0% by early 2026.
Major Players and Market Share
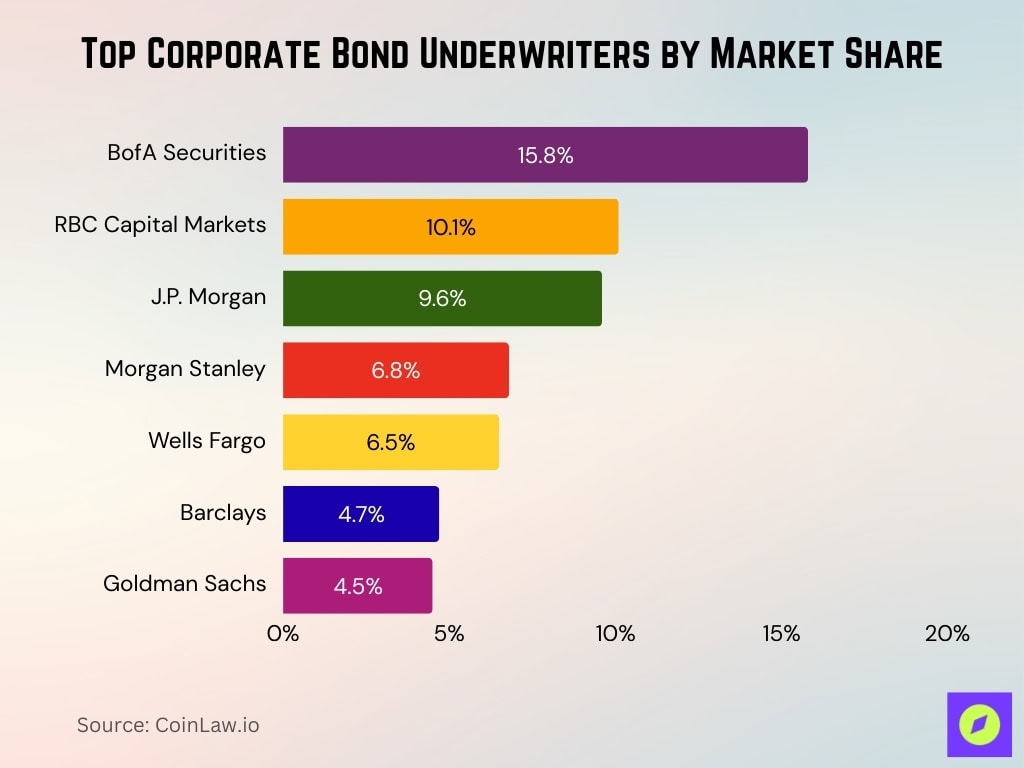
- BofA Securities led the pack in 1H 2025 with about 15.8% market share in corporate bond underwriting.
- RBC Capital Markets ranked second at roughly 10.1% market share in the same period.
- J.P. Morgan held approximately 9.6% market share in underwriting through mid‑2025.
- Morgan Stanley accounted for around 6.8% of underwriting volume in 1H 2025.
- Wells Fargo contributed close to 6.5% market share, underlining its role in the market.
- Goldman Sachs held a near 4.5% market share in corporate bond underwriting in early 2025.
- Barclays captured about 4.7% of the underwriting market through the first half of 2025.
Market Size and Growth Trends
- The US corporate bond market outstanding reached around $11.4 trillion in 1Q 2025, up about 3.7% year‑over‑year.
- Annual corporate bond issuance through end‑July 2025 hit $1.313 trillion, rising approximately 3.2% compared to last year.
- Corporate bonds accounted for roughly 39% of the global bond market in recent estimates, highlighting US dominance.
- In early 2025, corporates issued a record $83.4 billion in bond sales in the first week alone, the highest year‑to‑date level since 1990.
- Expected investment‑grade issuance for 2025 stands near $1.65 trillion.
- Foreign investor net purchases of US corporate bonds reached about $109 billion year‑to‑date through April, matching prior annual inflow levels.
- Average daily trading volume (ADV) for US corporate bonds climbed to $59.5 billion as of end‑July 2025, an increase of 15% year‑over‑year.
- High‑yield bonds outperformed with year‑to‑date returns near 4.0%, slightly ahead of investment‑grade at around 3.6%.
Issuance Statistics and Trends
- Total U.S. corporate bond issuance reached approximately $1.313 trillion through end‑July 2025, up 3.2% year‑over‑year.
- High‑yield issuance accounted for around $124 billion in H1 2025, roughly 9.4% of the year‑to‑date total issuance.
- Investment‑grade issuance continued to dominate with gross supply of about $426 billion in Q2 2025 and projected full‑year volumes around $1.65 trillion.
- Sector leadership remains notable, though precise 2025 breakdowns aren’t yet available; financial and energy sectors likely remain among the top issuers.
- Callable issuance specifics for 2025 remain unreported, but the financing environment suggests continued demand for such flexibility.
- Floating‑rate bond issuance data for 2025 remains sparse, though persistent interest in managing rate risk likely keeps volumes elevated.
- Corporate hybrid bond issuance figures for 2025 haven’t been released, indicating once again limited transparency in that segment.
- Green bond issuance numbers for 2025 are not yet clear, but were a significant growth area prior to this year.
U.S. Treasury Securities Breakdown
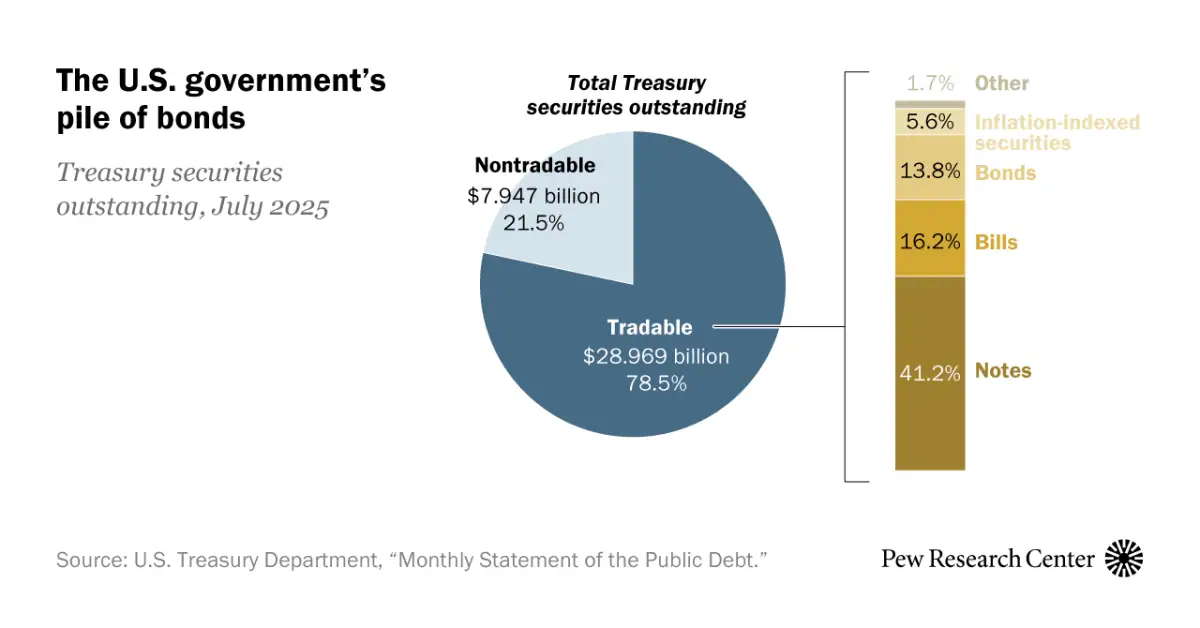
- $28.969 trillion (78.5%) of U.S. Treasury securities are tradable, making them the dominant portion of outstanding debt.
- $7.947 trillion (21.5%) are nontradable securities, held mostly by government accounts and special funds.
- Treasury notes lead the market at 41.2% of total outstanding securities.
- Treasury bills account for 16.2%, reflecting their short-term financing role.
- Treasury bonds make up 13.8%, representing longer-term borrowing instruments.
- Inflation-indexed securities represent 5.6%, providing protection against inflation pressures.
- Other securities contribute just 1.7%, highlighting their minimal role in overall debt composition.
Investment Grade vs. High Yield Analysis
- Investment‑grade bonds continue to dominate with approximately $1.5 trillion in issuance expected for 2025.
- High‑yield bonds contributed around $302 billion and remain a stable portion of the market in 2025.
- High‑yield default rates are forecasted in the range of 2.8% to 3.4% for 2025.
- Yield spreads for high‑yield bonds narrowed to about 2.9%, reflecting reduced investor risk premiums.
- Effective yields stand at around 7.5% for high‑yield bonds and 5.33% for investment‑grade bonds.
- The average duration for high‑yield bonds is shorter at approximately 3.3 years, compared to 6.8 years for investment‑grade.
- High‑yield bonds returned about 4.0% year‑to‑date, slightly outperforming investment‑grade bonds at 3.6%.
- Upgrades from high‑yield to investment‑grade remain moderate, supported by improving corporate fundamentals.
Corporate Bond Trading Volume
- Total corporate bond trading volume approached $1 trillion in Q2 2025, setting a new record for the sector.
- Average daily trading volume reached approximately $49 billion in June 2025, reflecting continued liquidity.
- Electronic trading gained momentum with portfolio trading rising to 18% of total electronic volume in early 2025.
- Daily notional volume remained steady at around $50 billion per day, consistent with last year’s levels.
- High-grade credit electronic trading averaged $7.8 billion in ADV, with total credit ADV at $16.8 billion in Q2 2025.
- Algorithmic and automated trades accounted for nearly 28% of all US corporate bond executions.
Bond Market Sector Breakdown
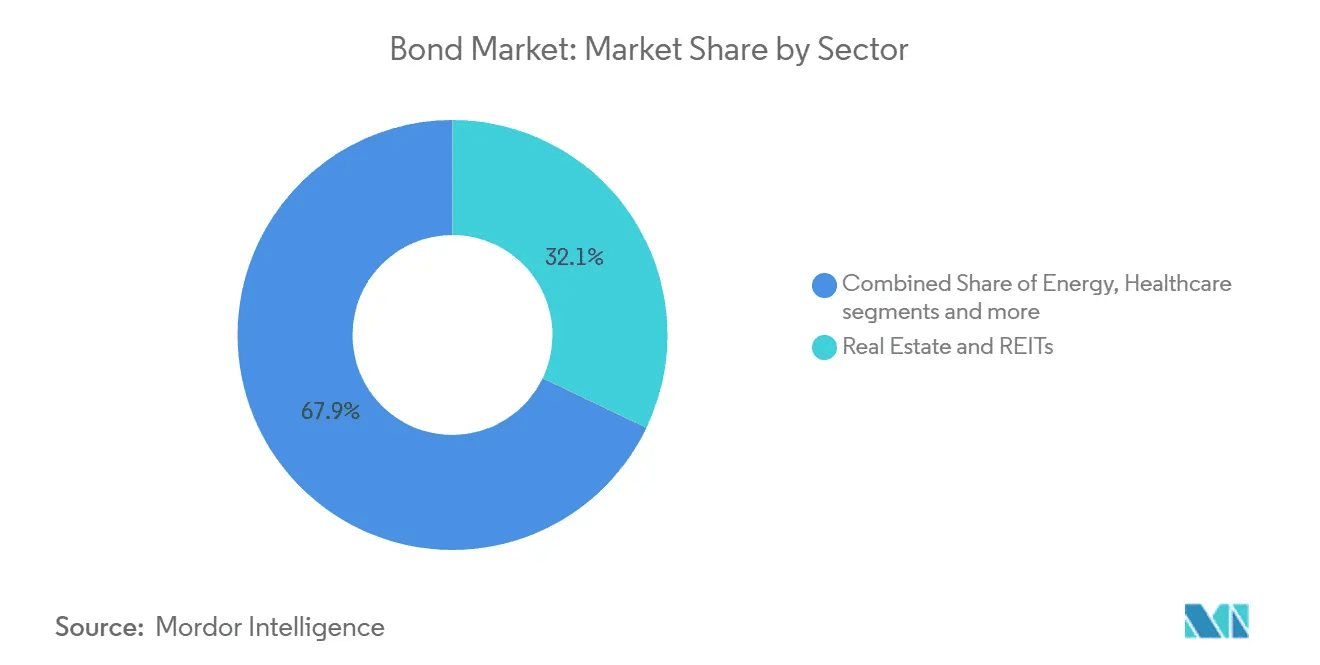
- Combined share of Energy, Healthcare, and other sectors holds 67.9%, making it the dominant portion of the bond market.
- Real Estate and REITs account for 32.1%, highlighting their significant role in market financing.
Interest Rate Impact on Corporate Bond Issuance
- Higher borrowing costs in early 2025 contributed to issuance pull‑forwards, with corporates opening the year by issuing a record $83.4 billion in the first week alone.
- Investment‑grade issuance for 2025 is projected at around $1.65 trillion, indicating sustained demand despite rate pressures.
- High‑yield bonds continue to face cost sensitivity with elevated default risk, while overall default rates remain above 4 %, consistent through May 2025.
- Corporate spreads widened in 2025 to approximately 120 basis points for investment‑grade and 461 basis points for high‑yield bonds.
- Floating‑rate note issuance trends remain visible through Treasury metrics rather than corporate specifics, with FRNs now comprising 2.35 % of total marketable U.S. Treasury debt as of June 2025.
Investment Review and Outlook
- The corporate bond market’s average yield rose to approximately 5% in early 2025, providing stronger income for investors.
- High-yield bonds delivered total returns near 4.0% year-to-date, maintaining appeal for income-focused strategies.
- Investment-grade bonds returned around 3.6% year-to-date, offering reliable income for conservative portfolios.
- High-yield yields stand near 7.5%, compared to 5.3% for investment-grade, reflecting a meaningful income gap.
- Fixed-income indices posted returns between 4.0% and 7.3% in H1 2025, supported by stronger coupon structures.
- Risk appetite is improving, with fund managers optimistic on high-yield credit amid solid corporate fundamentals.
- Spreads on high-yield bonds narrowed to approximately 309 basis points, reflecting stronger investor confidence.
- Investor sentiment continues to strengthen, as credit spreads approach their lowest levels since 2021.
Bond Market Composition by Instrument
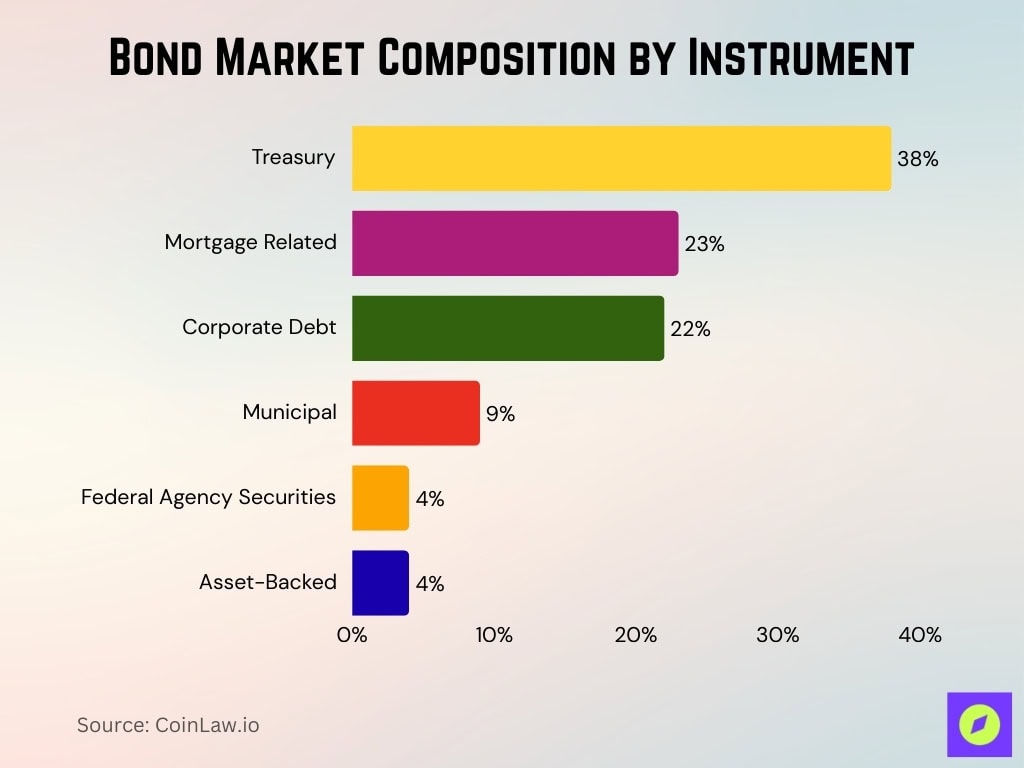
- Treasury securities lead with 38%, making them the largest component of the bond market.
- Mortgage-related debt holds 23%, showing strong demand in the housing finance sector.
- Corporate debt represents 22%, underlining the role of companies in capital raising.
- Municipal bonds account for 9%, supporting state and local government financing.
- Federal agency securities make up 4%, reflecting their smaller but stable presence.
- Asset-backed securities contribute 4%, tied to loans, receivables, and other structured finance products.
Role of ESG and Green Bonds
- Global green bond issuance is projected to reach $600 billion in 2025, underlining continued investor demand.
- Labeled sustainable bond issuance, including green, social, and sustainability bonds, was around €247 billion (~$287B) in early 2025, a slowdown from projected growth levels.
- In the U.S., corporate sustainable bond issuance has nearly stopped; only two labeled bonds (a $350 million green bond and a $500 million sustainability bond) were issued in Q1 2025.
- The aligned green bond market surpassed $671 billion globally, as defined by the Climate Bonds Initiative’s taxonomy and certification criteria.
- High interest in catastrophe bonds, a form of climate-linked bond, also surged, with issuance reaching $18.1 billion so far in 2025.
Valuations
- The average corporate bond yield stands at 6.1% as of July 2025, reflecting stronger income opportunities.
- Aaa-rated corporate bonds are yielding approximately 5.3%, slightly lower than prior year levels.
- Long-term high-quality corporate bond spot rates are around 5.9%, indicating solid return potential.
- The average corporate bond yield across credit categories is approximately 5.8% in mid-2025.
- IRS segment yield rates for April 2025 are 4.95%, 5.31%, and 5.55%, reflecting varying maturity structures.
Technicals and Trading Dynamics
- Corporate bond average daily volume reached $60.9 billion in early 2025, showing a 23% quarterly and 19% annual increase.
- Total ADV reported in April 2025 was $57.4 billion, including $18.4 billion in credit and $3.8 billion in credit block trades.
- Bid-ask spreads tightened significantly in early 2025, reflecting improved liquidity and trading efficiency.
- Institutional and retail trading trends converged, with smaller trade sizes and increased odd-lot activity.
- Liquidity for off-the-run corporate bonds deteriorated, with bid-ask spreads widening notably under stress.
- High-yield spreads narrowed to approximately 309 basis points, signaling greater investor confidence.
Technological Innovations in Bond Trading and Analysis
- AI-driven analytics are increasingly adopted, though still emergent in bond markets, enhancing risk management, efficiency, and uncovering new sources of alpha.
- AI tools have delivered efficiency gains estimated between 22%–40% across key fixed income functions, including pricing, risk modeling, and reporting.
- AI-powered pricing platforms like CP+ have improved intraday price discovery, especially for less liquid bonds and during high‑uncertainty periods.
- Patent filings with AI-related content for algorithmic trading have surged, rising from 19% in 2017 to over 50% annually since 2020, indicating growing innovation in AI‑driven strategies.
- The global AI trading platform market size is estimated at $13.5 billion in 2025, expected to grow at over 20% CAGR through 2034.
- As of 2025, approximately 50% of investment-grade and 33% of high-yield corporate bonds trade electronically, according to data from MarketAxess and Greenwich Associates, highlighting persistent fragmentation in bond market infrastructure.
Challenges in the Corporate Bond Market
- Interest rate volatility remains a key hurdle, with approximately 70% of issuers citing it as a major issue in 2025.
- Credit rating downgrades continue to rise, with high-yield bond downgrades up 5%, reflecting stress on lower-quality issuers.
- Liquidity challenges persist in the high-yield segment, where 35% of traders report difficulty finding buyers for low-grade bonds.
- Regulatory and disclosure pressures are increasing across the board, though specific 2025 metrics remain limited.
- Global economic uncertainty, from geopolitical tensions to currency risks, continues to add caution to the market.
- ESG compliance costs are climbing due to mandatory reporting frameworks such as the SEC’s Climate Disclosure Rule and Europe’s CSRD, pushing firms to invest in ESG audit, legal, and data infrastructure.
- Underwriting market concentration is contributing to cost pressures as top firms continue to dominate fee structures.
- Inflationary concerns are weighing on real returns, particularly in sectors like utilities and consumer goods.
- Cybersecurity threats persist in the fixed income space, with 25% of trading platforms reporting attempted breaches in the past 12 months.
Recent Developments
- The SEC has rolled out enhanced corporate bond disclosure standards in 2025, now influencing reporting practices for around 20 % of new issuers.
- Bond issuance has accelerated early in 2025 with corporates tapping record $83.4 billion in the opening week to preempt anticipated rate cuts.
- Green bonds continued to soar, with globally aligned annual issuance climbing to approximately $577 billion in 2024 and uptake expected to rise further in 2025.
- Federal stress tests now include corporate bond resilience factors, encompassing roughly 30 % of major corporate issuers.
- Cross-border bond issuance grew as regulatory easing lifted hurdles, contributing to about 5 % more foreign investment in U.S. corporates.
- The convertible bond segment saw breakout growth in Q2 2025, with issuance volume rising 36 % and deal count up 20 % versus Q2 2024.
- Merger and acquisition–driven issuance spiked, fueling approximately 12 % higher bond issuance as firms raised capital for strategic deals.
- Corporate bond maturity extensions became more prevalent, with around 20 % of issuers opting to push out maturities to avoid near‑term refinancing pressure.
- Blockchain pilot projects for bond settlement are underway at select firms, aiming to streamline settlement workflows and boost transparency.
Conclusion
The US corporate bond market is both a stabilizing force in the economy and a dynamic, evolving sector. With $10 trillion in market size, it plays a crucial role in corporate finance and offers diverse opportunities for investors. Today, key trends such as interest rate impacts, increased ESG participation, and technological innovations in trading continue to shape the landscape.
While challenges like rate volatility, regulatory changes, and liquidity constraints remain, the bond market’s resilience and adaptability keep it robust. As companies and investors alike navigate these changes, the corporate bond market will likely see further growth and innovation, marking its continued significance in the financial world.



































































