Imagine a world where financial transactions are completely immune to hacking. This isn’t the distant dream it once was, but a potential reality with quantum cryptography, a groundbreaking technology poised to transform the financial industry. As we stand on the edge of this quantum revolution, understanding its impact and the shift it brings is crucial. In this article, we dive into quantum cryptography in finance, exploring its adoption, readiness, and the possibilities it opens for securing financial data.
Editor’s Choice
- The global quantum cryptography market is projected to reach $380.9 million.
- North America holds a 58% share of the quantum cryptography market.
- Quantum cryptography market valued at $1.15 billion with a 38.3% growth rate.
- North America dominates with 42% market share, driven by defense investments.
- Quantum computing unlocks $1 trillion cumulative value for end users by 2035.
- Quantum vendors are expected to generate $50 billion in revenue through 2035.
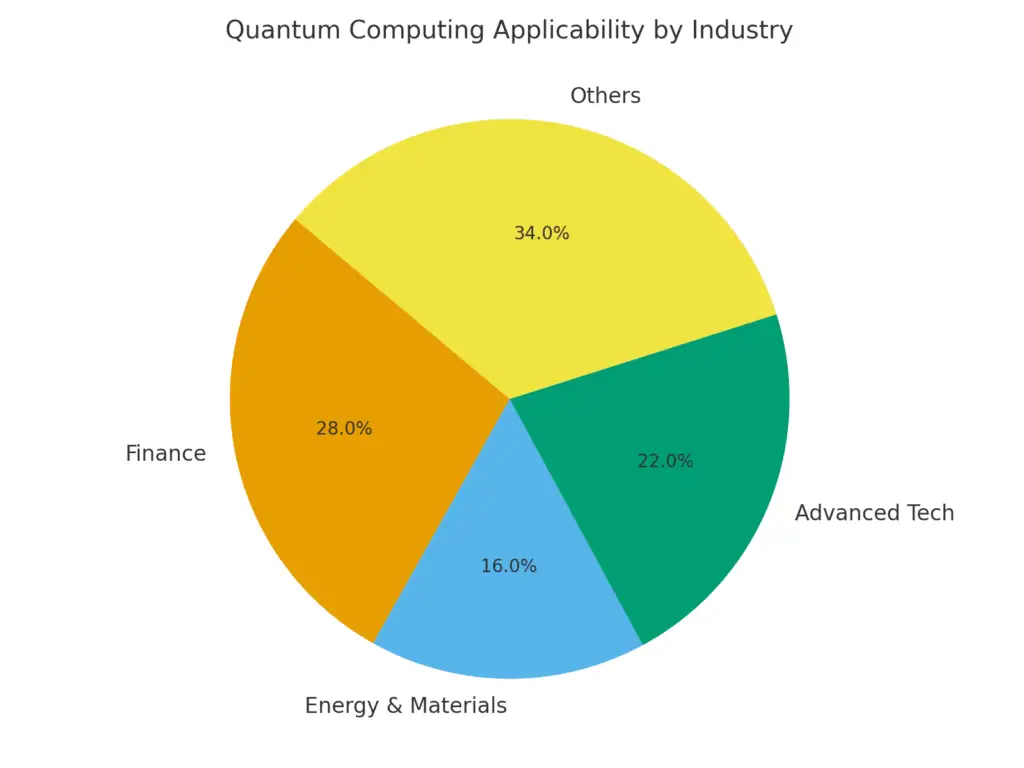
Quantum Computing Use by Industry
- Finance accounts for 28% of all quantum computing applications, reflecting strong interest in quantum-powered risk modeling, encryption, and portfolio optimization.
- Advanced Tech industries hold a 22% share, leveraging quantum for complex simulations, AI acceleration, and high-performance computing.
- Energy & Materials sectors represent 16%, applying quantum to optimize resource extraction, energy efficiency, and material discovery.
- Other industries make up the largest segment at 34%, showing growing experimentation in healthcare, logistics, pharma, and agriculture.
Understanding Quantum Computing Basics for Finance
- Finance sector quantum computing value estimated at $622 million, led by corporate banking at 31%.
- Quantum investments in finance surge 50% to $2.25 billion, driven by North America and Asia.
- 75% of hedge funds use quantum algorithms for real-time decision making.
- Demand for quantum professionals in finance rises 65% year-over-year, with salaries at $160,000.
- 55% of CFOs view quantum technologies as critical for long-term strategy.
- Quantum computing market valued at $3.52 billion, growing at 41.8% CAGR to 2030.
- BFSI industry holds a 26% share due to complex financial calculations and security needs.
- Quantum security market reaches $1.7 billion with finance at 42% of spending.
- Post-quantum cryptography implementations rise 70% amid quantum threats.
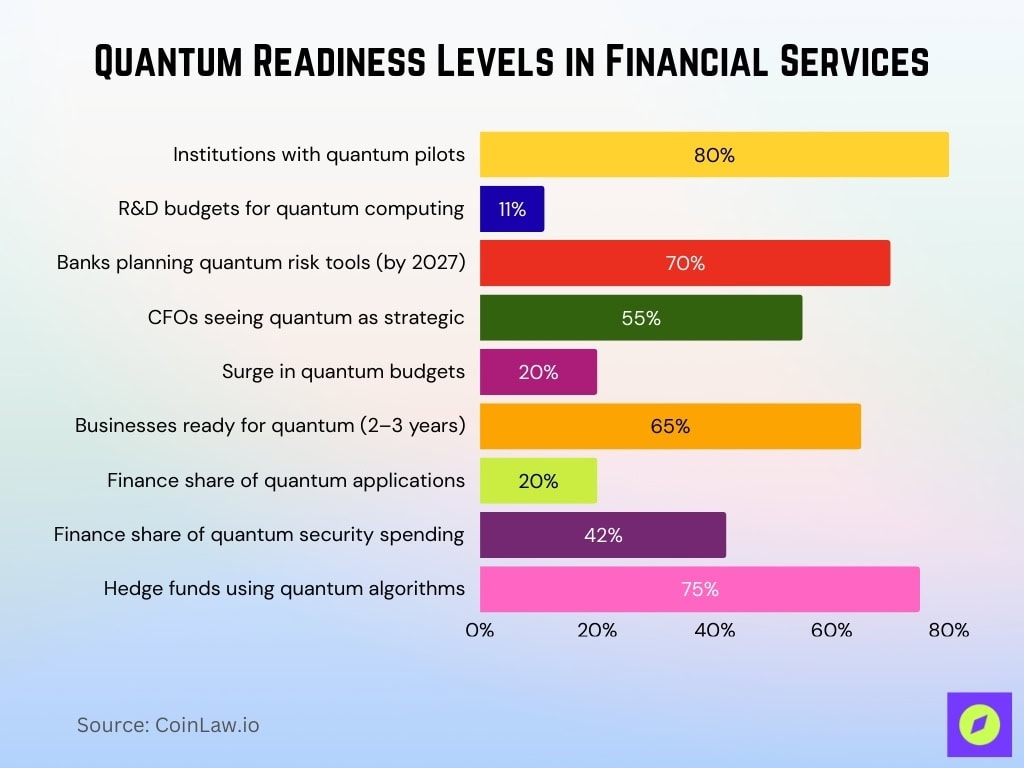
Quantum Readiness in Finance
- 80% of financial institutions globally had quantum pilots.
- Quantum computing captures 11% of average R&D budgets.
- 70% of banks plan to use quantum risk modeling tools by 2027.
- 55% of CFOs view quantum as critical for strategy.
- Global quantum budgets surge nearly 20%.
- 65% of businesses are ready to adopt quantum in 2-3 years.
- Finance holds 20% of quantum computing applications.
- Quantum security spending by finance reaches 42% globally.
- 75% of hedge funds use quantum algorithms for decisions.
Powerful Quantum Use Cases in Financial Services
- Portfolio optimization QAOA delivers ~40% better returns on diversification.
- Fraud detection cuts false alerts by ~65% using quantum machine learning.
- Risk assessment improves default prediction precision by ~35%.
- Quantum algorithms boost risk analysis speeds up to 25x faster.
- HSBC quantum simulations cut derivatives pricing errors by ~22%.
- Barclays’ quantum credit risk models yield ~25% better accuracy.
- Quantum machine learning improves fraud detection by 30%-50%.
- Quantum annealing reduces asset allocation compute times by ~65%.
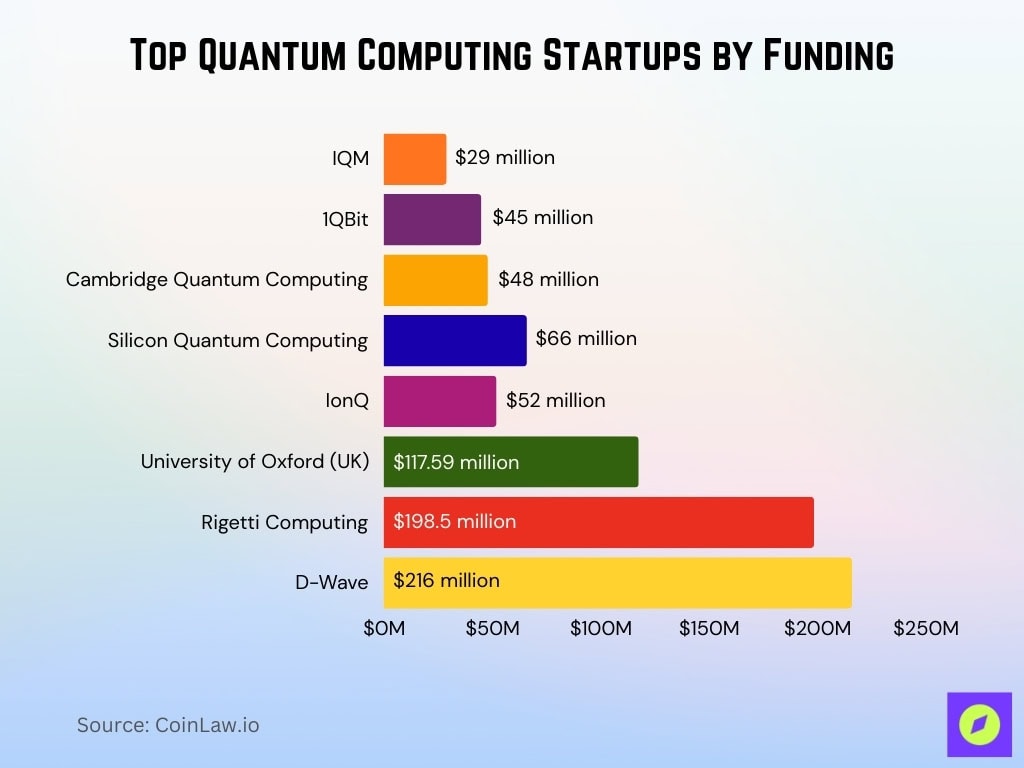
Top Quantum Computing Startups by Funding
- D-Wave leads with $216 million, showing the strongest investor confidence in commercial quantum solutions.
- Rigetti Computing has secured $198.5 million, positioning itself as a key player in superconducting quantum systems.
- The University of Oxford (UK) received $117.59 million, underscoring academia’s growing role in quantum innovation.
- Silicon Quantum Computing raised $66 million, focusing on silicon-based architectures.
- IonQ attracted $52 million, with a focus on trapped-ion quantum hardware.
- Cambridge Quantum Computing secured $48 million, driving advancements in quantum software.
- 1QBit received $45 million, contributing to quantum optimization and machine learning solutions.
- IQM closed $29 million, supporting its development of scalable quantum processors.
Impact on Financial Transaction Security
- Quantum cryptography reduces cyber fraud in finance by 40%.
- Financial organizations report a 50% drop in data breaches using quantum encryption.
- 90% of institutions identify quantum cryptography as key anti-threat technology.
- Quantum-secure transactions cut breach costs by $100 million annually.
- QKD secures 95% of cross-border payments against interception.
- Blockchain quantum encryption blocks 99.9% of DeFi attack vectors.
- POS quantum systems prevent 85% of credit card fraud attempts.
- Digital banking quantum security boosts transaction confidence by 65%.
- ATM networks with QKD detect 100% of interception attempts.
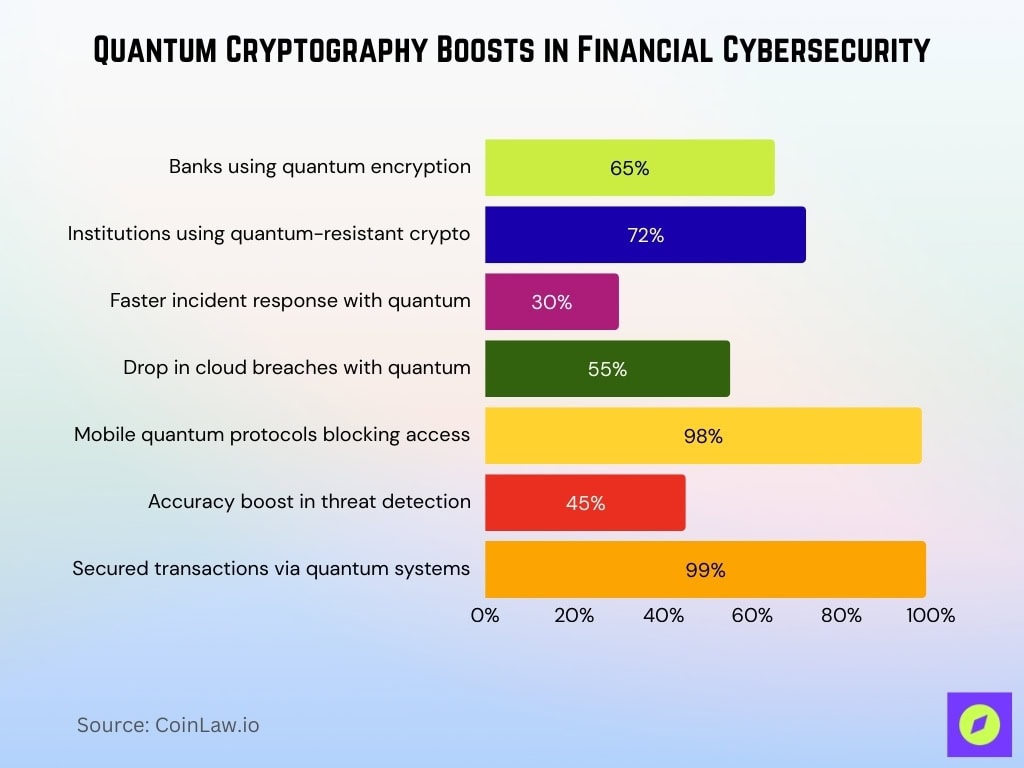
Cybersecurity Enhancements through Quantum Cryptography
- 65% of global banks integrate quantum encryption in cybersecurity.
- Quantum-resistant crypto is adopted by 72% of major financial institutions.
- Incident response times improve 30% with quantum analytics.
- Cloud security breaches drop 55% using quantum encryption.
- Mobile banking quantum protocols block 98% unauthorized access.
- Predictive threat detection accuracy rises 45% via quantum systems.
- Payment gateways secure 99% transactions against cyber threats.
Challenges in Implementing Quantum Cryptography
- Quantum cryptography deployment costs $10-15 million per financial institution.
- Global quantum talent shortage affects 85% of financial projects.
- 92% of banks cite scalability as the primary adoption barrier.
- Infrastructure compatibility issues impact 78% of quantum pilots.
- Regulatory uncertainty delays 65% of quantum security initiatives.
- 70% of executives fear data privacy risks from quantum threats.
- 45% of institutions report deployment complexity as a major hurdle.
- QKD hardware costs $500,000-$2 million per installation site.
- Commercial viability timeline averages 12 years for finance applications.
Recent Developments
- NIST PQC standards have been adopted by 68% of global financial institutions.
- Post-Quantum Cryptography Alliance serves 125 financial organizations.
- Banque de France-Singapore PQC experiment secures 95% quantum threats.
- WEF-FCA quantum tools are implemented by 42% of regulators worldwide.
- Quantinuum Quantum Origin is deployed in 35 banking networks.
- 82% of central banks accelerate PQC migration post-NIST standards.
- Quantum security patents filed by the finance sector surge 150%.
- Industry collaborations reduce quantum migration timelines by 24 months.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
North American financial institutions are predicted to account for 45% of global spending on quantum cryptography by 2025.
Financial blockchain applications for quantum computing are expected to attract $300 million in funding by 2025.
Over 65% of global banks plan to integrate quantum encryption into their cybersecurity frameworks by 2025.
Experts estimate that quantum technology adoption in financial services could reduce global financial cybercrime risks by up to 50% by 2030.
Conclusion
Quantum cryptography is transforming the finance sector, offering unprecedented security and efficiency. From enhancing financial transaction security to revolutionizing asset management, quantum technology is paving the way for a safer financial future. Despite the challenges, recent developments and collaborations signal strong progress, with major financial institutions around the globe taking steps toward quantum readiness. As this technology matures, it will be instrumental in building a financial landscape where data integrity and security are virtually unbreakable, meeting the demands of an increasingly digital and interconnected world.