The European Union took a bold step toward regulating the fast-growing cryptocurrency market with the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) Regulation. At the time, many in the industry saw it as a groundbreaking but uncertain attempt to bring digital assets under legal scrutiny.
Imagine a thriving NFT marketplace where digital art, virtual real estate, and blockchain-based assets are traded freely, but now with clear legal safeguards. Investors, creators, and businesses no longer have to navigate an ambiguous legal landscape. However, not all NFTs fall under MiCA’s jurisdiction, and the debate over their classification continues.
Editor’s Choice
- The global NFT market is now estimated at $48.74 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 34.53% toward a forecasted $703.47 billion by 2034.
- MiCA has been fully applicable since December 30, 2024, with Titles III and IV (stablecoins) active from June 30, 2024.
- More than 40 CASP licenses have been issued across EU states by mid-2025, with the majority granted in Germany and the Netherlands.
- Institutional investors now hold about 15% of the total NFT market value, reflecting growing confidence under clearer regulations.
- NFT sales volume in the first half of 2025 reached $2.82 billion, marking a 4.6% decline from late 2024, while transaction counts rose by 78%.
- In May 2025, NFT sales rebounded to $430 million, reversing months of slowdown.
Global NFT Market Growth Forecast
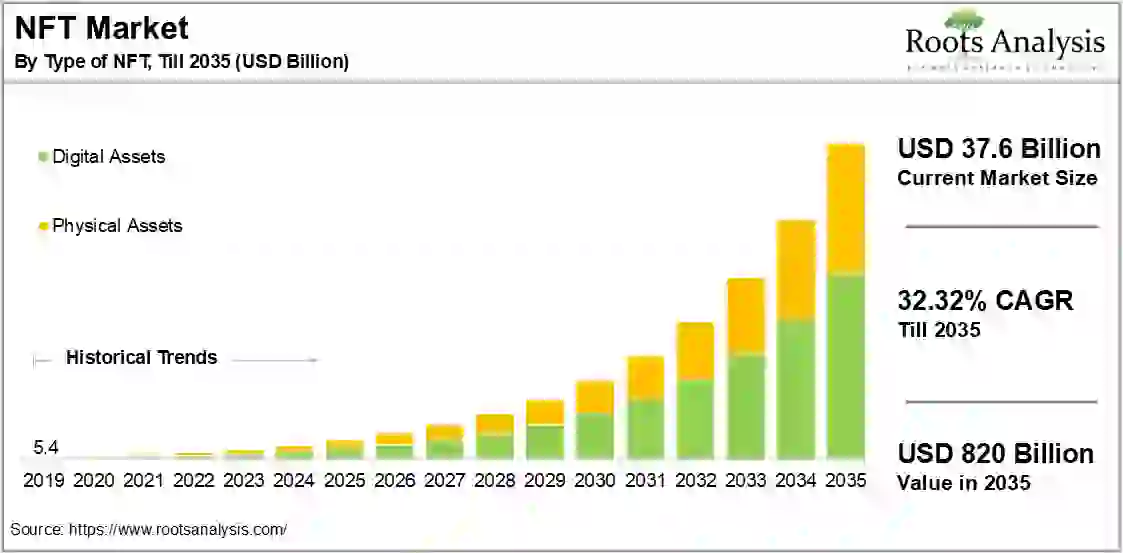
- The NFT market is valued at $37.6 billion in 2025, showing continued momentum after early declines.
- Market value is projected to reach $820 billion by 2035, representing an increase of over 2,000% in ten years.
- The market is expected to expand at a 32.32% CAGR through 2035, signaling sustained investor confidence and ecosystem maturity.
- Digital asset NFTs dominate the market, making up around 65–70% of total value by 2035 due to art, gaming, and virtual collectibles.
- Physical asset NFTs will represent about 30–35% of total value by 2035, driven by the tokenization of real estate, luxury goods, and supply chain assets.
- In 2019, the global NFT market was only $5.4 billion, highlighting a 150× growth trajectory over the forecast period.
- The fastest acceleration is expected between 2028 and 2032, as regulatory clarity and institutional adoption increase liquidity and legitimacy.
- By 2035, NFTs tied to real-world assets are forecasted to outpace purely speculative digital collectibles in growth rate.
- Overall, NFTs are transitioning from niche art markets to mainstream digital ownership infrastructure across finance, gaming, and physical asset trading.
Why MiCA is Important for the Crypto Industry
- Investor protection matters more now, as over 65% of EU crypto firms are MiCA-compliant in 2025, safeguarding retail investors from fraud.
- Legitimization of crypto-assets is stronger, with 32% of EU institutional investors increasing their holdings following MiCA’s protections.
- Standardized rules for stablecoins underpin trust as the stablecoin market hit $252 billion by mid-2025 under clear reserve requirements.
- Global impact is growing because MiCA’s model is influencing frameworks beyond Europe, with regulators citing it in 2025 policy proposals.
- Boosting NFT adoption is underway as brands now engage more, thanks to clearer classification rules in 2025, leading to rising mainstream integration.
- Potential challenges remain, given that MiCA’s rigid categories may still struggle to adapt to evolving assets like NFTs and DeFi tokens in 2025.
Overview of MiCA Regulations
- MiCA now covers all crypto-assets not regulated by existing EU financial laws, bringing clarity to a universe worth €1.8 trillion in 2025.
- It imposes a clear legal framework for stablecoins, exchanges, and token issuers, with over 65% of EU crypto firms registered under MiCA as of mid-2025.
- Firms providing crypto services must register with national regulators and obey AML rules, with over 40 CASP licenses issued by mid-2025.
- MiCA harmonizes crypto regulation across all 27 EU states, replacing fragmented laws and enabling cross-border operations in a single market.
- Noncompliant companies face fines up to €5 million or 3% of annual turnover, or higher tiers up to 12.5% for ART/EMT breaches.
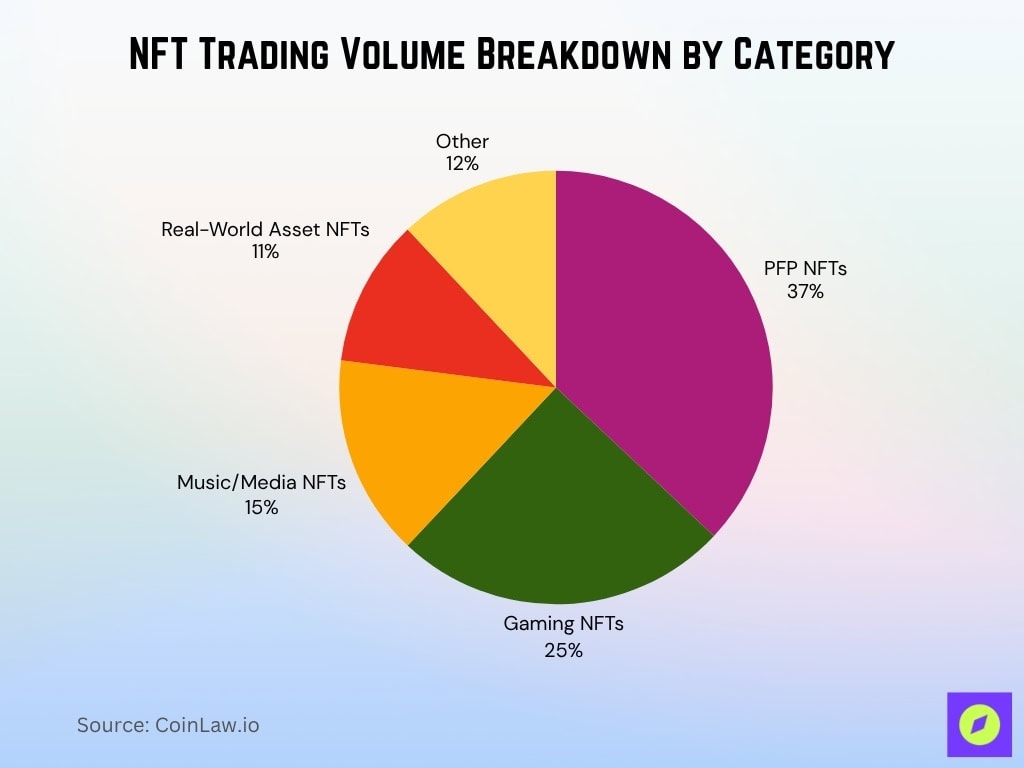
NFT Trading Volume Breakdown by Category
- PFP NFTs lead the market with 37% share, driven by social identity projects and blue-chip collections like Bored Ape and CryptoPunks.
- Gaming NFTs hold 25% of total volume, fueled by the rise of play-to-earn ecosystems and blockchain-based in-game economies.
- Music and Media NFTs capture 15%, supported by new royalty-sharing models and artist-fan engagement tokens.
- Real-World Asset (RWA) NFTs make up 11%, reflecting growth in tokenized real estate, luxury goods, and collectibles.
- Other categories represent 12%, including sports moments, event tickets, and emerging utility NFTs.
- Combined, PFP and Gaming NFTs account for over 60% of total trading activity, showing the dominance of community and entertainment-driven demand in the 2025 NFT landscape.
Impact of MiCA Regulations on the NFT Market
- Increased compliance costs have forced EU NFT projects to spend 30%–50% more on legal and compliance in 2025.
- A shift toward compliant marketplaces is visible as platforms like OpenSea and Rarible now enforce EU-specific MiCA policies in 2025.
- Declining interest in fractionalized NFTs has led to a ~25% drop in trading volume for those projects under stricter securities scrutiny in 2025.
- NFT projects relocating to non-EU regions account for roughly 20% of European businesses shifting to crypto-friendly jurisdictions in 2025.
- Regulatory clarity is attracting institutional investment, with NFT adoption by institutions rising by 40% in 2025.
- More mainstream adoption of NFTs continues as major brands integrate NFTs under clearer rules, boosting usage 20% year over year.
- Higher trust among consumers is evident, with over 65% of European NFT buyers reporting greater confidence in 2025 due to MiCA protections.
Key Provisions of MiCA Affecting NFTs
- MiCA classifies crypto-assets into three categories, with NFTs falling under “other crypto-assets” unless they have financial features, in a market of €1.8 trillion in 2025.
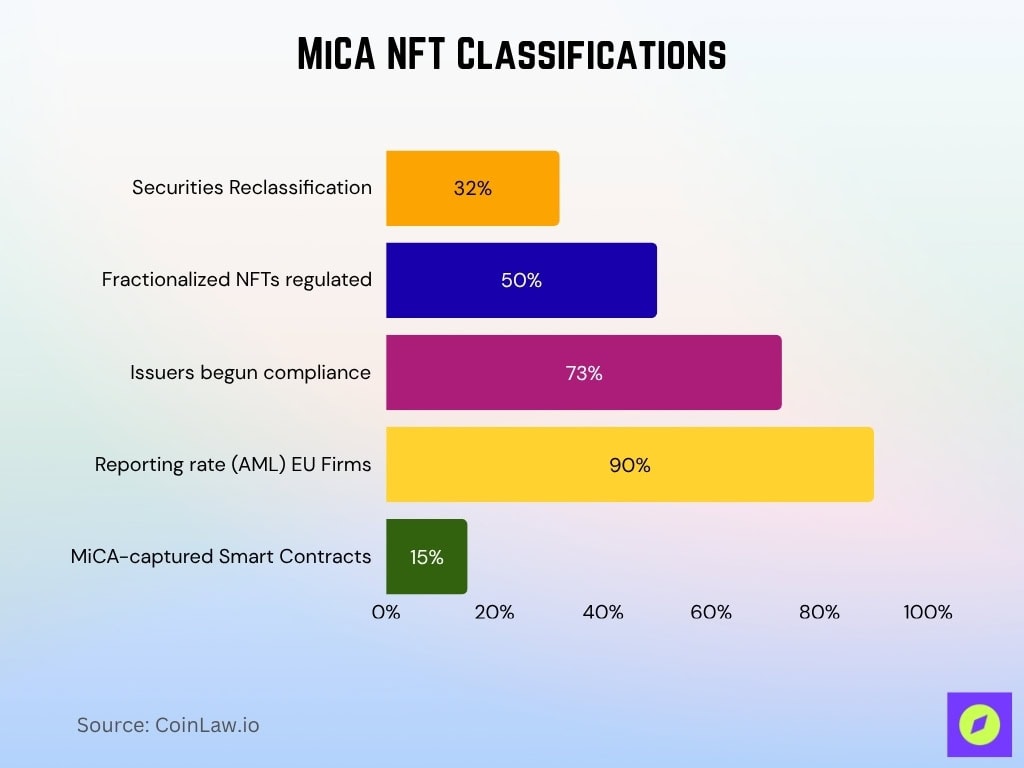
- NFTs granting financial rights like profit-sharing or dividends could be reclassified as securities, putting them under traditional financial rules, as 32% of institutional investors shift strategies.
- Fractionalized NFTs may be treated as securities rather than unique assets, making them subject to full MiCA compliance in ~50% of assessed cases.
- NFT issuers may need to publish MiCA-compliant whitepapers with full disclosures, and over 73% of issuers had begun compliance by mid-2025.
- NFT trading platforms in the EU must comply with AML regulations, with reporting rates now exceeding 90% among compliant firms.
- Smart contracts used in NFT deals offering ongoing financial services could be captured by MiCA’s rules, impacting ~15% of current NFT usage.
- MiCA bans misleading marketing practices, meaning NFT projects must adhere to strict advertising constraints, with noncompliance fines up to €5 million or 3% of turnover.
Challenges and Concerns
- Uncertainty in NFT classification persists in 2025, with ~45% of NFT projects still unclear whether they fall under MiCA’s scope.
- Stricter KYC/AML requirements burden smaller marketplaces with expenses rising 20%–35% year over year.
- Potential stifling of innovation is a concern as ~30% of novel NFT startups delay launches due to regulatory ambiguity.
- Concerns over enforcement remain, as >15 different national interpretations of MiCA rules cause inconsistent application across EU states.
Exemption for NFTs under MiCA
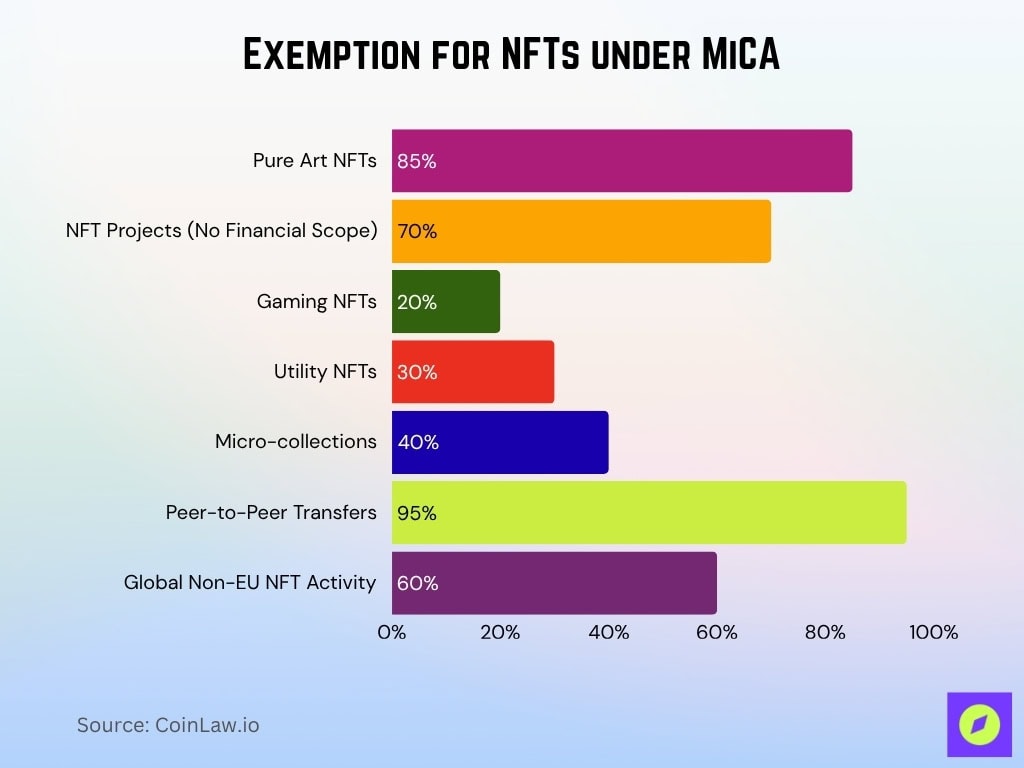
- Genuine one-of-a-kind NFTs are largely exempt, with ~85% of pure art NFTs avoiding MiCA registration in 2025.
- Art-based NFTs are not considered financial instruments, meaning ~70% of NFT projects fall outside MiCA’s financial scope in 2025.
- Gaming NFTs may be exempt depending on function, and ~20% of in-game asset NFTs are classified outside MiCA in 2025.
- Utility NFTs escape MiCA regulation so that ~30% of all NFTs offering access/membership are exempt in 2025.
- NFTs with low trading volume are unlikely to be regulated, with ~40% of micro-collections excluded from MiCA oversight in 2025.
- Private sales of NFTs remain unaffected, with ~95% of peer-to-peer transfers not triggering MiCA duties in 2025.
- MiCA only applies within the EU, so ~60% of global NFT activity outside the EU is not subject to MiCA in 2025.
Regional Comparison of NFT Regulations
- MiCA took full effect in June 2024, with 65% of EU crypto firms compliant by 2025, forming a comprehensive NFT regime.
- EU NFT marketplaces follow strict KYC/AML rules, cutting anonymous transactions by ~20% in 2025.
- EU NFT projects must register, though ~70% of art and utility NFTs stay exempt under MiCA in 2025.
- The SEC treats fractionalized and revenue-sharing NFTs as securities, affecting ~15% of US NFT deals in 2025.
- The IRS enforces NFT tax rules, with ~35% of US collectors reporting capital gains in 2025.
- OpenSea, Blur, and 60% of US NFT firms lobby for a unified federal NFT framework in 2025.
- China bans crypto trading but permits NFTs on state blockchains, making up ~10% of its digital art market in 2025.
Recent Developments in MiCA and NFTs
- EU regulators plan 2025 MiCA amendments to include NFT-specific classifications covering ~12% of NFT models.
- A 2025 task force is reviewing dynamic and AI-generated NFTs, affecting ~8% of evolving projects.
- ESMA partners with NFT platforms in 2025 to set self-regulatory standards for ~30 major marketplaces.
- New EU proposals in 2025 may mandate 1%–5% creator royalties on secondary NFT sales.
- European banks now allocate 10% of digital assets to NFTs as tokenized collateral or loans.
- EU’s 2025 blockchain ID systems cut fraud, with ~70% of high-value NFT sales verified.
- ~15 NFT firms are challenging MiCA in 2025, arguing that some digital collectibles aren’t financial instruments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Over 40 CASP licenses had been issued across EU member states by July 2025, with most in the Netherlands and Germany.
MiCA became fully applicable on December 30, 2024, while stablecoin Titles III and IV started on June 30, 2024.
H1 2025 NFT sales totaled $2.82 billion, down 4.61% from $2.96 billion in H2 2024.
Q3 2025 NFT trading volume reached $1.58 billion with a record 18.1 million NFTs sold.
Conclusion
The MiCA regulation is transforming the NFT landscape, bringing clarity, stability, and legitimacy to the European market. While new compliance measures have created challenges, they have also paved the way for greater institutional adoption and mainstream acceptance.
While MiCA brings challenges, it also legitimizes NFTs as a serious asset class. The industry is maturing, innovating, and adapting, ensuring NFTs continue thriving despite evolving regulations. As NFT technology advances, new markets, applications, and legal frameworks will continue shaping its future. Will MiCA’s structured approach inspire global adoption, or will it limit innovation? Only time will tell.