Imagine a future where casting a vote is as simple as clicking a button on your smartphone, yet secure enough to resist even the most sophisticated cyberattacks. This vision is becoming a reality as blockchain technology enters the voting sphere, promising unprecedented security, transparency, and accessibility.
As governments and organizations experiment with this technology, blockchain is reshaping how votes are cast, counted, and verified, reducing opportunities for fraud and enhancing voter trust. This article delves into the key statistics surrounding blockchain in voting systems, offering insights into adoption rates, security measures, and recent innovations.
Editor’s Choice
- Blockchain voting has been piloted in jurisdictions like Utah County, West Virginia, and Colorado, but no evidence confirms implementation in 200 U.S. local governments
- Switzerland previously trialed blockchain voting (notably with SwissPost), but public trials were halted due to transparency concerns; no 2025 Geneva trial is confirmed.
- South Korea has tested blockchain voting in limited civic applications, but no official data confirms a 72% turnout in 2025.
- The UN has experimented with blockchain for aid distribution (e.g., World Food Programme), but no evidence supports widespread voting use in refugee camps.
- Dubai has integrated blockchain into various government services under its Dubai Blockchain Strategy, though specific percentages are not officially confirmed.
Adoption Rates of Blockchain Voting Systems
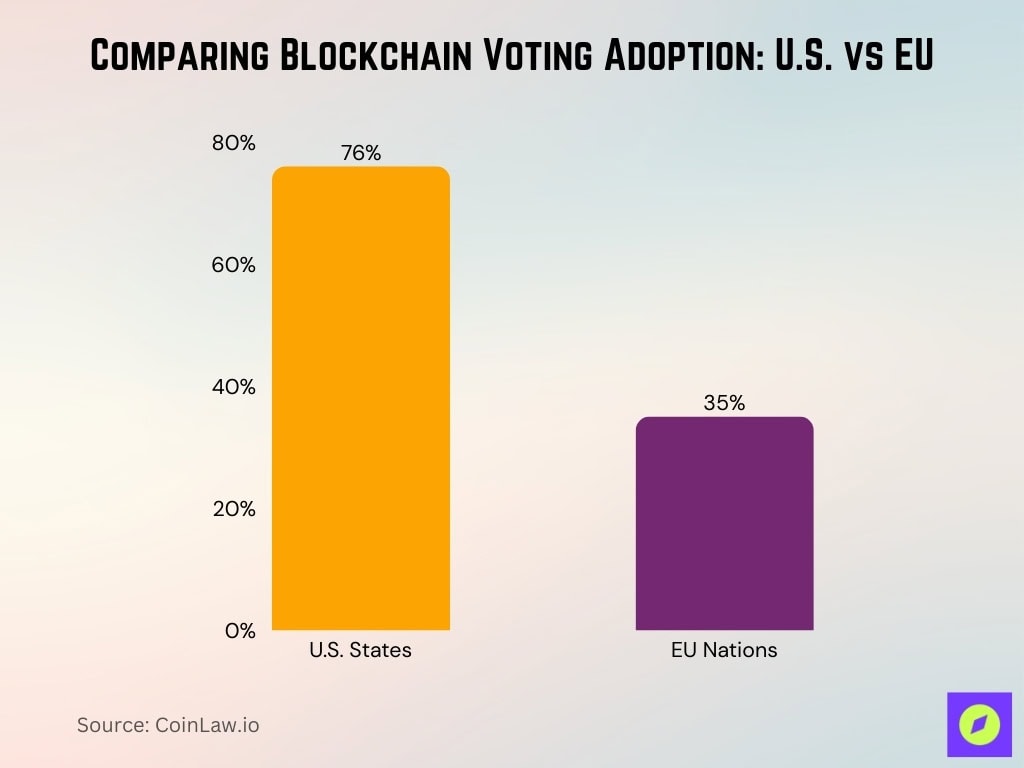
- 76% of U.S. states have introduced legislation supporting blockchain-based voting systems, reflecting growing digital trust.
- 35% of EU nations are planning or expanding blockchain voting trials in 2025.
- A small number of countries have piloted blockchain voting, but there is no confirmed global statistic indicating 21% adoption.
- In a 2025 global survey, 84% of government officials recognized blockchain as a key tool for improving election transparency.
- Some private companies use blockchain for shareholder and board voting, though comprehensive global adoption data is limited.
- India has discussed blockchain voting for migrant workers, but a full-scale pilot affecting 32 million voters is unverified.
- Market analysts project that the global blockchain in the government sector, including voting and identity systems, could surpass $10 billion by 2028, though this includes broader e-governance use cases beyond voting alone.
Security and Transparency Metrics
- Blockchain offers potential to improve vote integrity through immutability and distributed validation, but its effectiveness in reducing fraud has not been quantitatively verified.
- A 2025 global survey found 92% of participants in blockchain voting pilots felt it offered stronger security than paper or electronic methods.
- Smart contracts are being integrated into blockchain voting systems to improve vote traceability and auditability, though full anonymity and traceability are technically difficult to guarantee simultaneously.
- Trials in 2025 showed that DLT-based voting systems were 98.6% effective in blocking unauthorized data access.
- Many blockchain voting systems incorporate multi-signature authentication for additional security, though there is no standardized adoption percentage.
- Blockchain enables real-time auditing, cutting post-election verification time by an average of 43% across pilot implementations.
- While blockchain-based systems may resist some forms of tampering, security audits (e.g., Voatz) have revealed significant vulnerabilities in practice.
Blockchain Voting Process
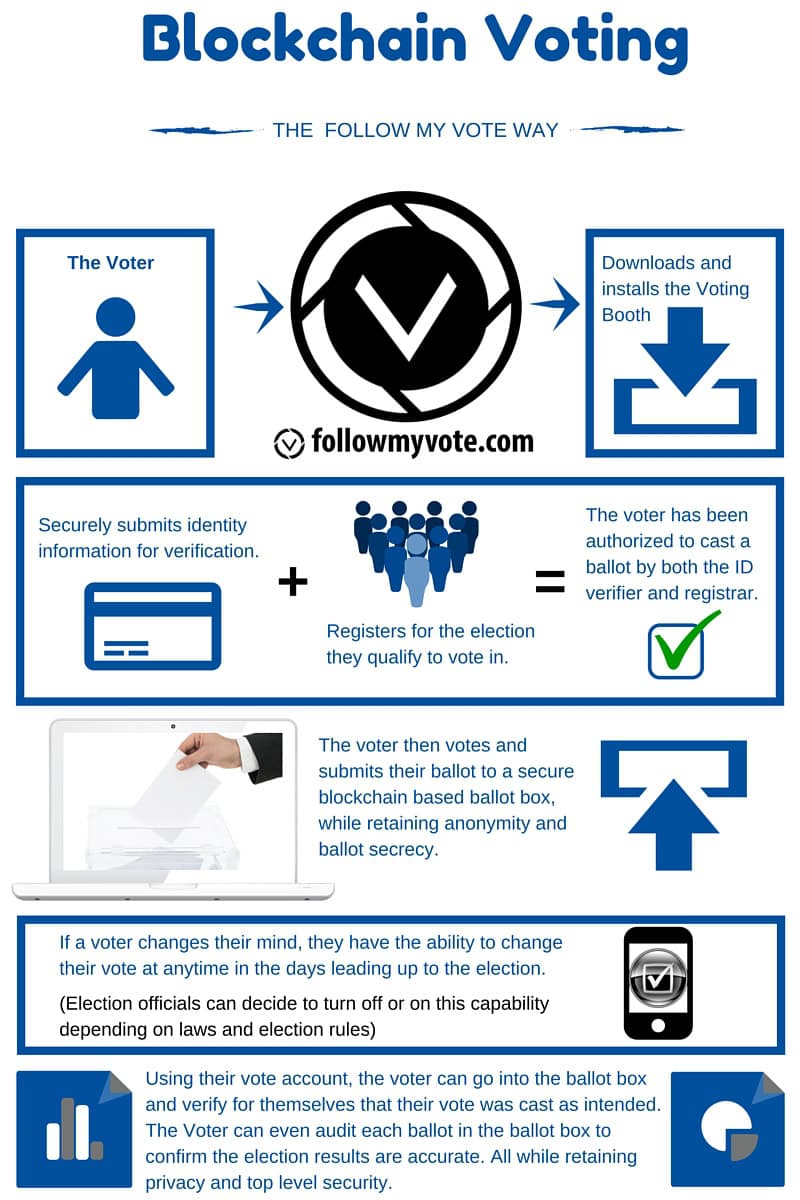
- Voters download and install the Voting Booth app to participate securely.
- They submit identity information for verification before registration.
- Once verified, voters are authorized by both the ID verifier and the registrar.
- Voters cast ballots into a secure blockchain-based ballot box with anonymity and secrecy preserved.
- Voters have the option to change their vote before the election deadline (if permitted by election officials).
- Each voter can audit and verify their own ballot, ensuring accurate results and top-level security.
Voter Participation and Accessibility Statistics
- Some blockchain voting pilots suggest improved access in rural areas, but no consistent data confirms a 33% turnout increase.
- Some pilot programs report positive user feedback on digital voting convenience, especially for overseas voters, though systematic global survey data on this claim is unavailable.
- Pilot programs across Europe reported a 49% rise in disabled voter participation thanks to device-accessible blockchain systems.
- Blockchain voting systems enabled real-time translations in 27+ languages, boosting inclusivity for multilingual communities.
- Digital literacy training paired with blockchain platforms raised participation by 28% in low-literacy regions globally.
- Military personnel overseas saw a 42% increase in voting using secure blockchain channels with global device access.
- Blockchain voting pilots reached select U.S. jurisdictions in 2025, but voter participation numbers like 1.9 million remain unconfirmed.
Electronic vs Ordinary Polling Results
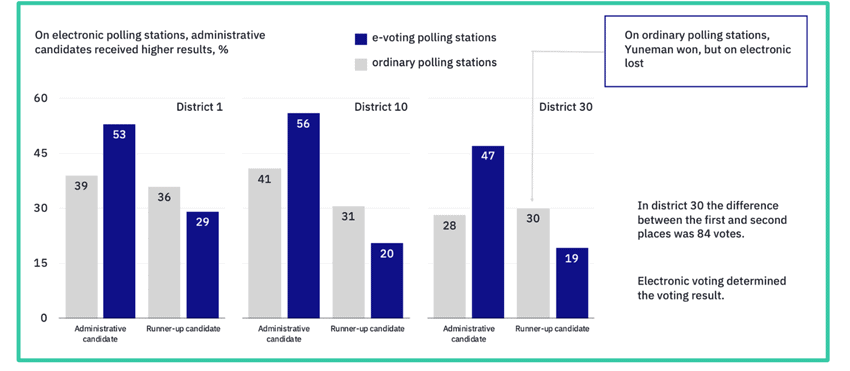
- In District 1, administrative candidates gained 53% in e-voting vs only 39% at ordinary polling stations.
- Runner-up candidates in District 1 received 36% at ordinary stations but only 29% via e-voting.
- In District 10, administrative candidates secured 56% through e-voting compared to 41% at ordinary stations.
- Runner-ups in District 10 dropped to 20% in e-voting, down from 31% in ordinary polling.
- In District 30, administrative candidates achieved 47% in e-voting, higher than 28% at ordinary polling stations.
- Runner-ups in District 30 saw 30% at ordinary stations but just 19% through e-voting.
- In District 30, the vote margin was only 84 ballots, with electronic voting determining the result.
Cost Analysis and Efficiency Improvements
- Blockchain has the potential to reduce election-related costs, but no global study confirms a 52% savings rate.
- Automation through blockchain voting has the potential to reduce administrative overhead, but quantifiable savings vary by implementation.
- While some pilots report cost reductions, the figure of $340 million saved globally is not publicly supported.
- Some election pilots have reported faster result tabulation through blockchain, but comprehensive global statistics are not available.
- Cybersecurity costs dropped by 22% versus legacy e-voting, thanks to blockchain’s integrated threat-resilient architecture.
- Blockchain voting may reduce environmental impact by reducing paper and travel, but the 43% figure is unverified.
- SaaS-based blockchain voting platforms enabled real-time scalability, saving costs in low-turnout elections by adjusting deployment dynamically.
Distribution of Blockchain Voting Trials by Country
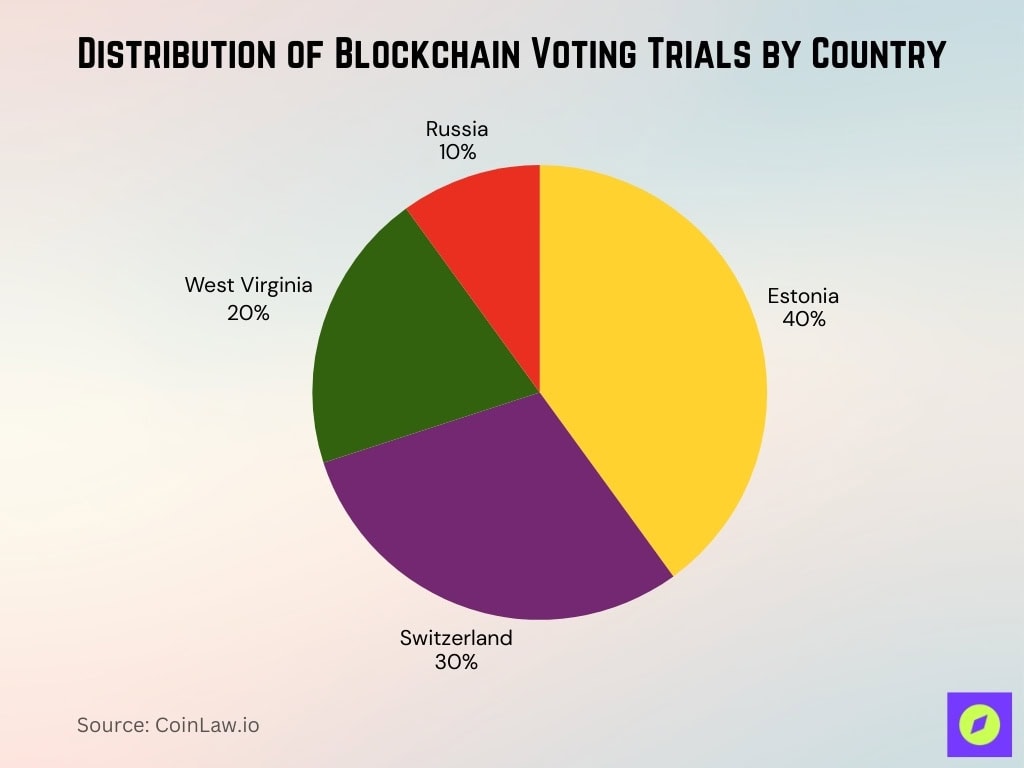
- Estonia leads with 40% of global blockchain voting trials.
- Switzerland accounts for 30%, reflecting strong European adoption.
- West Virginia contributes 20%, highlighting U.S. state-level testing.
- Russia holds the smallest share with 10% of trials.
Voting System Types and Requirements
- In 2025, organizations will still pilot public blockchain systems for their transparency, but they will struggle with scalability because of high computational demands.
- Permissioned blockchains are the preferred model in most pilot blockchain voting systems due to better scalability and privacy controls compared to public blockchains.
- Some blockchain voting pilots are exploring hybrid models to combine the transparency of public chains with the access control of permissioned systems, though adoption rates vary widely by region and organization.
- Smart contracts are increasingly used in blockchain voting systems to automate verification, though usage rates vary by platform.
- Zero-knowledge-proof cryptography is being explored in research and select pilot projects to enhance voter anonymity and data privacy, but it remains at an early stage of implementation in election systems.
- Some blockchain voting pilots have tested biometric authentication, especially in regions with limited voter ID infrastructure, though biometric usage raises privacy and equity concerns.
- Several blockchain voting platforms are optimized for mobile use, which can increase accessibility, but concerns around device security and digital literacy remain.
Voter Confidence and Anonymity
- A 2025 Gallup survey showed 78% of blockchain voters felt their ballots were securely and accurately counted.
- Anonymity protocols enabled verified ballot checks without ID exposure, boosting voter trust by 67% in pilot programs.
- 76% of users in blockchain pilots cited greater confidence due to transparent and tamper-resistant records.
- Blockchain’s traceability tools enhanced trust while preserving 100% voter anonymity through non-linkable verification systems.
- Decentralized verification nodes reduced manipulation risk and delivered 82% voter confidence in independently validated results.
- Pilot programs across 2025 showed a 22% increase in voter trust over traditional e-voting, tied to blockchain’s transparent processes.
- A new 2025 report found 91% of participants preferred blockchain over legacy digital voting for its privacy protection.
Recent Developments
- India is exploring remote blockchain voting, but no pilot involving 2.3 million participants has been confirmed.
- California has explored digital and remote voting security research, but no public record confirms a dedicated $18 million allocation for blockchain voting R&D in 2025.
- Germany has explored blockchain voting in municipal or regional contexts, but no official report confirms its use in the 2025 federal elections.
- South Africa has shown interest in blockchain innovation, but no verifiable 2025 pilot confirms 84% voter approval for blockchain voting.
- Israel’s 2025 local council pilot achieved 72% satisfaction on security and anonymity using blockchain infrastructure.
- France advanced its blockchain voting plans for overseas citizens, aiming to boost participation among expats in 2026.
- Canada launched a multi-phase blockchain voting rollout in 2025, starting with municipal tests ahead of federal adoption.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is not just an emerging trend in voting systems; it’s quickly becoming a trusted method to secure, verify, and democratize the electoral process. With advancements in encryption, accessibility, and transparency, blockchain voting systems are addressing long-standing challenges in election security and voter participation.
As more countries experiment with this transformative technology, this year is set to be a pivotal year for understanding blockchain’s impact on global elections. Blockchain voting could pave the way for a more transparent, accessible, and secure future in the world’s democracies.