Imagine a world where every product journey, across oceans, continents, and currencies, could be traced with unmatched transparency and precision. That’s the promise blockchain brings to supply chain finance. In 2025, businesses are increasingly recognizing blockchain’s potential to reduce fraud, increase efficiency, and drive down costs in global supply chains. With complex networks spanning multiple stakeholders, blockchain’s impact is proving transformative, not just in theory but in practice. This article explores the essential statistics and insights that highlight blockchain’s expanding role in supply chain finance and its future trajectory.
Key Takeaways
- 1The blockchain supply chain finance market is valued at $3.27 billion in 2025 and projected to reach $21.29 billion by 2039 with a CAGR of 59.8%.
- 246% of North American supply chain firms have adopted or are adopting blockchain to enhance operational visibility and efficiency.
- 3Blockchain implementation reduces supply chain costs by up to 37% by eliminating intermediaries and automating processes.
- 4The pharmaceutical sector could save $218 billion annually with blockchain by reducing fraud and counterfeit drugs while boosting efficiency.
Blockchain Supply Chain Market Growth Outlook
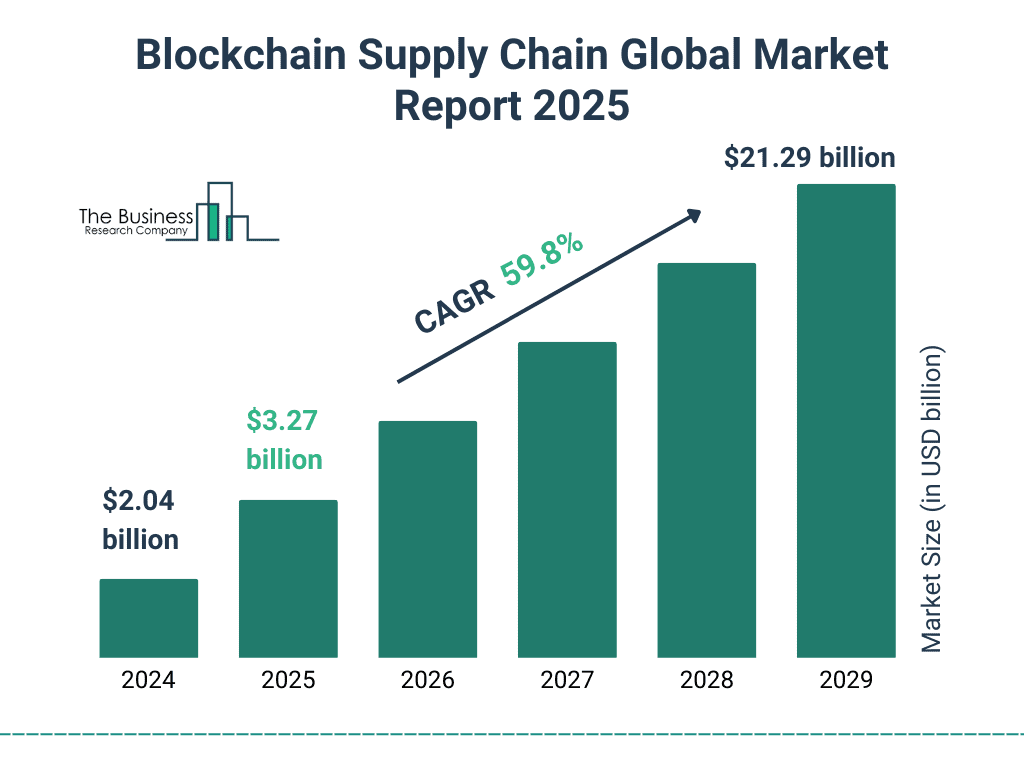
- The blockchain supply chain market is expected to grow to $21.29 billion by 2029.
- This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 59.8%.
- The market is projected to reach $3.27 billion in 2025, marking a strong early growth phase.
- Growth continues steadily, with significant jumps seen through 2026 to 2028, culminating in a tenfold increase by 2029.
Global Blockchain in Supply Chain Finance Market Dynamics
- 63% of companies now seek blockchain-based verification systems to boost transparency, traceability, and security.
- Blockchain adoption CAGR in finance and logistics stands at 53% from 2018 to 2025, reflecting strong multi-year growth.
- 46% of North American supply chain firms have already integrated or are planning to adopt blockchain solutions.
- Blockchain-based supply chain finance is set to generate $24.7 billion in transaction volume in 2025, projected to double by 2028.
- Transaction accuracy improved by 38% for blockchain-using firms, significantly cutting down global supply chain errors.
- 48% of companies report better risk visibility due to blockchain’s real-time transparency across their networks.
- The Asia-Pacific blockchain market in supply chain finance is expanding at a 59% CAGR through 2027, driven by tech-focused investment.
Market Growth and Adoption Rates
- Global investment in blockchain technology for supply chain applications is expected to exceed $11 billion by 2025.
- 15% of logistics providers are now using blockchain to streamline supply chain finance.
- 45% of financial institutions involved in supply chain finance believe that blockchain can drastically reduce operational bottlenecks by automating verification processes.
- Blockchain-powered logistics platforms have increased in number by 30% year-over-year, reflecting heightened demand for efficient and transparent solutions.
- The number of blockchain-based platforms handling trade finance has grown 50% in the last year alone, supporting faster cross-border payments and trade settlements.
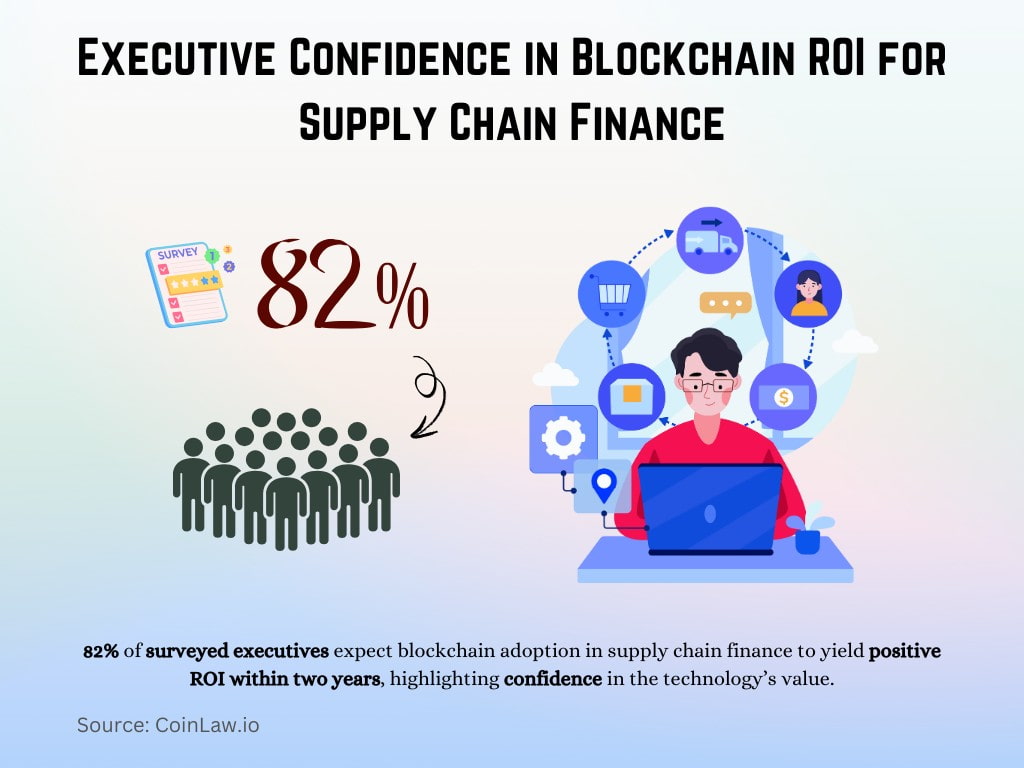
- 82% of surveyed executives expect blockchain adoption in supply chain finance to yield positive ROI within two years, highlighting confidence in the technology’s value.
Financial Impact and Cost Savings
- Blockchain implementation in supply chain finance can cut operational costs by up to 33% by removing intermediaries and manual checks.
- Digital ledger technologies are now saving businesses $3.8 billion annually by reducing fraud and preventing double financing.
- Smart contracts powered by blockchain have lowered administrative costs by up to 42%, especially in invoicing and settlements.
- Trade finance processing times are reduced by an average of 81% through blockchain-based systems, saving both time and money.
- Blockchain-based dispute resolution has led to a 25% drop in annual dispute management costs across major global supply chains.
- 43% of banks in supply chain finance report cost savings in 2025, especially in areas like compliance and regulatory automation.
- Increased transparency from blockchain adoption is projected to save the global economy $112 billion annually by minimizing fraud, errors, and inefficiencies.
Blockchain Technology Share in Sustainable Supply Chains
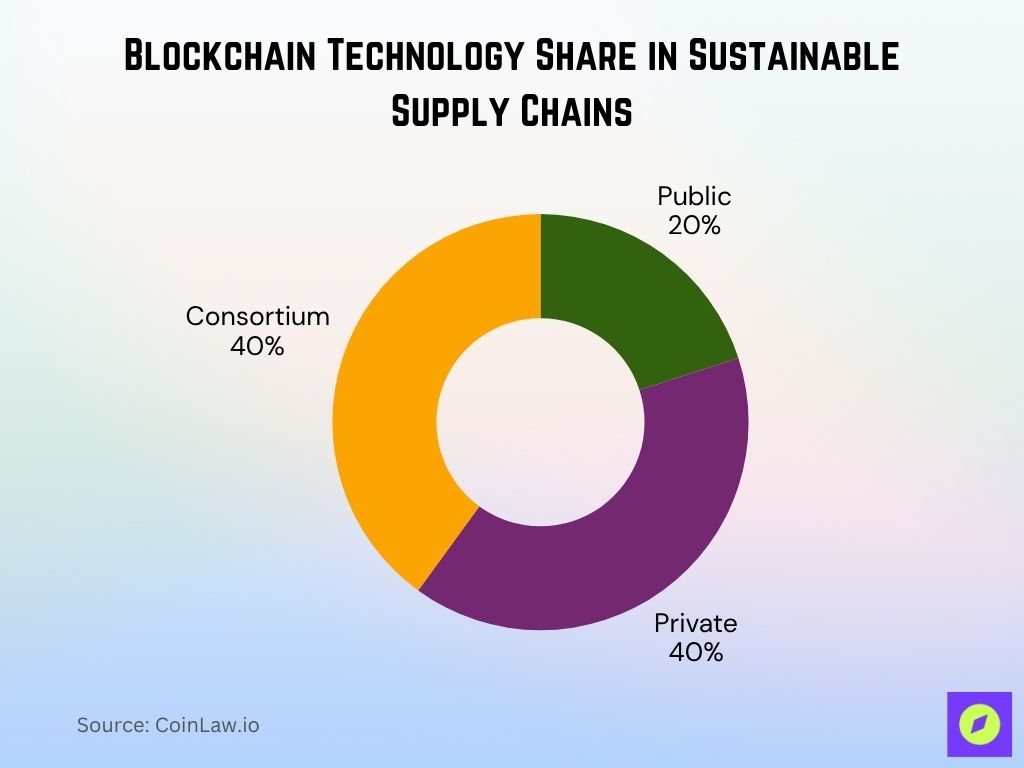
- Private blockchain leads the revenue share with 40%, indicating a strong preference for secure and permissioned networks in sustainable supply chains.
- Consortium blockchain also holds approximately 40% share, reflecting collaborative efforts across organizations to ensure transparency and traceability.
- Public blockchain accounts for an estimated 20%, suggesting limited but growing use in open, decentralized supply chain applications.
The data shows a clear industry tilt toward controlled-access blockchain models over fully decentralized systems for sustainable supply chain solutions.
Technological Developments and Innovations
- 32% of pilot programs in 2025 are exploring DeFi solutions for real-time payments in supply chain finance.
- Blockchain-integrated IoT adoption is growing at 34% annually, enhancing tracking and real-time data collection in supply chains.
- 17 major logistics firms are now collaborating on interoperable blockchain standards for seamless data exchange in global networks.
- Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) usage in supply chain finance has risen, with 39% of companies preferring BaaS for faster integration.
- Smart contract usage grew by 55% in 2025, enabling automated enforcement of trade agreements and payment terms.
- AI-powered blockchain systems are now used by 27% of blockchain-enabled firms for enhanced predictive analytics and decision-making.
- Energy-efficient blockchain protocols have lowered energy consumption by 44%, making them more viable for sustainability-focused companies.
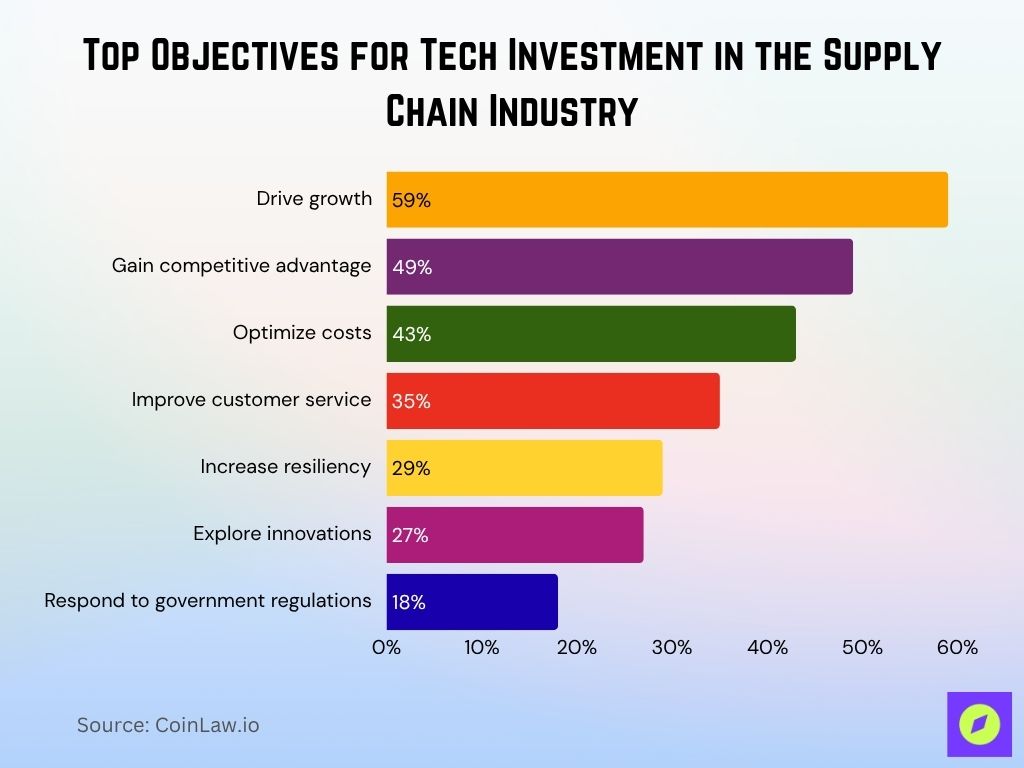
Top Objectives for Tech Investment in the Supply Chain Industry
- 59% of companies invest in technology to drive growth, making it the leading objective across the supply chain sector.
- 49% aim to gain a competitive advantage, showcasing the role of tech in strategic positioning.
- 43% focus on optimizing costs, reflecting the importance of efficiency and margin improvement.
- 35% prioritize improving customer service, underlining the shift toward consumer-centric logistics.
- 29% are investing in increasing resiliency, aiming for more robust and disruption-proof supply chains.
- 27% of organizations explore innovations, highlighting the need to stay ahead of emerging trends.
- 18% invest in response to government regulations, signaling compliance as a secondary driver.
Driving Factors and Restraining Factors
- Transparency demands are one of the leading drivers, as 78% of consumers now expect brands to disclose supply chain information.
- Rising data privacy concerns are restraining factors, with 45% of executives citing data security issues as a primary barrier to blockchain adoption.
- Government regulations are supporting blockchain growth, with 15 countries implementing policies that promote blockchain in supply chain finance.
- High implementation costs remain a restraint, with 60% of small businesses citing costs as a significant barrier to adoption.
- Blockchain’s potential for fraud prevention is a strong driving factor, as 85% of supply chain finance firms consider it essential for fraud reduction.
- The need for cross-border transaction efficiency is driving adoption, with 50% of trade finance companies pursuing blockchain solutions to reduce delays.
- Interoperability challenges among blockchain networks hinder adoption, with 30% of companies struggling to integrate blockchain with existing systems.
Latest Trends
- Real-time transaction tracking is now in demand, with 60% of companies aiming to implement blockchain to enable instant visibility.
- Blockchain-based carbon tracking has seen a 35% increase as companies seek to reduce their carbon footprints through transparent supply chains.
- Blockchain-based invoice financing has grown by 45% as it enables faster liquidity and reduces payment delays for small suppliers.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) integration is on the rise, with 25% of finance firms piloting DeFi solutions in blockchain-based supply chain finance.
- Blockchain-powered predictive analytics for supply chain disruptions is trending, with 30% of firms using blockchain data to anticipate delays and manage risk.
- Private blockchains for exclusive partnerships in supply chains are growing, with 40% of blockchain-using companies preferring private networks to protect proprietary data.
- Tokenization of assets in supply chain finance is gaining popularity, with 20% of companies exploring token-based assets for more efficient collateral management.

Recent Developments
- Blockchain enables full end-to-end traceability in supply chains, giving businesses and consumers real-time visibility through immutable digital records.
- Blockchain financing tools now support over 65% of SMEs in global supply chains, promoting inclusive funding access across all supplier tiers.
- Sustainability tracking pilots, like the TrackIt system, are aligning with new global ESG standards, improving data sharing and interoperability.
- In response to 2025 EU regulatory rollouts, Digital Product Passports (DPPs) are being adopted to boost compliance and product lifecycle transparency.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is redefining the future of supply chain finance with transparency, speed, and accuracy at its core. As more industries embrace blockchain, they’re not only transforming internal processes but also setting new standards for global commerce. In 2025, blockchain is no longer a novel concept; it’s an integral part of a forward-thinking, resilient supply chain strategy. With advancements continuing in technology, legislation, and market adoption, blockchain’s role in supply chain finance is set to expand even further, empowering businesses to meet the challenges of an increasingly interconnected and transparent world.