As crypto adoption deepens globally, the cost of compliance has surged into the spotlight. Launching a crypto business isn’t just about innovation; it’s about surviving rigorous, high-cost regulatory environments. Some jurisdictions, while crypto-friendly in principle, impose licensing, capital, and audit burdens that push first-year expenses well beyond six figures. Below, we explore which countries have the most expensive crypto regulations, why they’re so costly, and what that means for startups and investors alike.
Key Takeaways
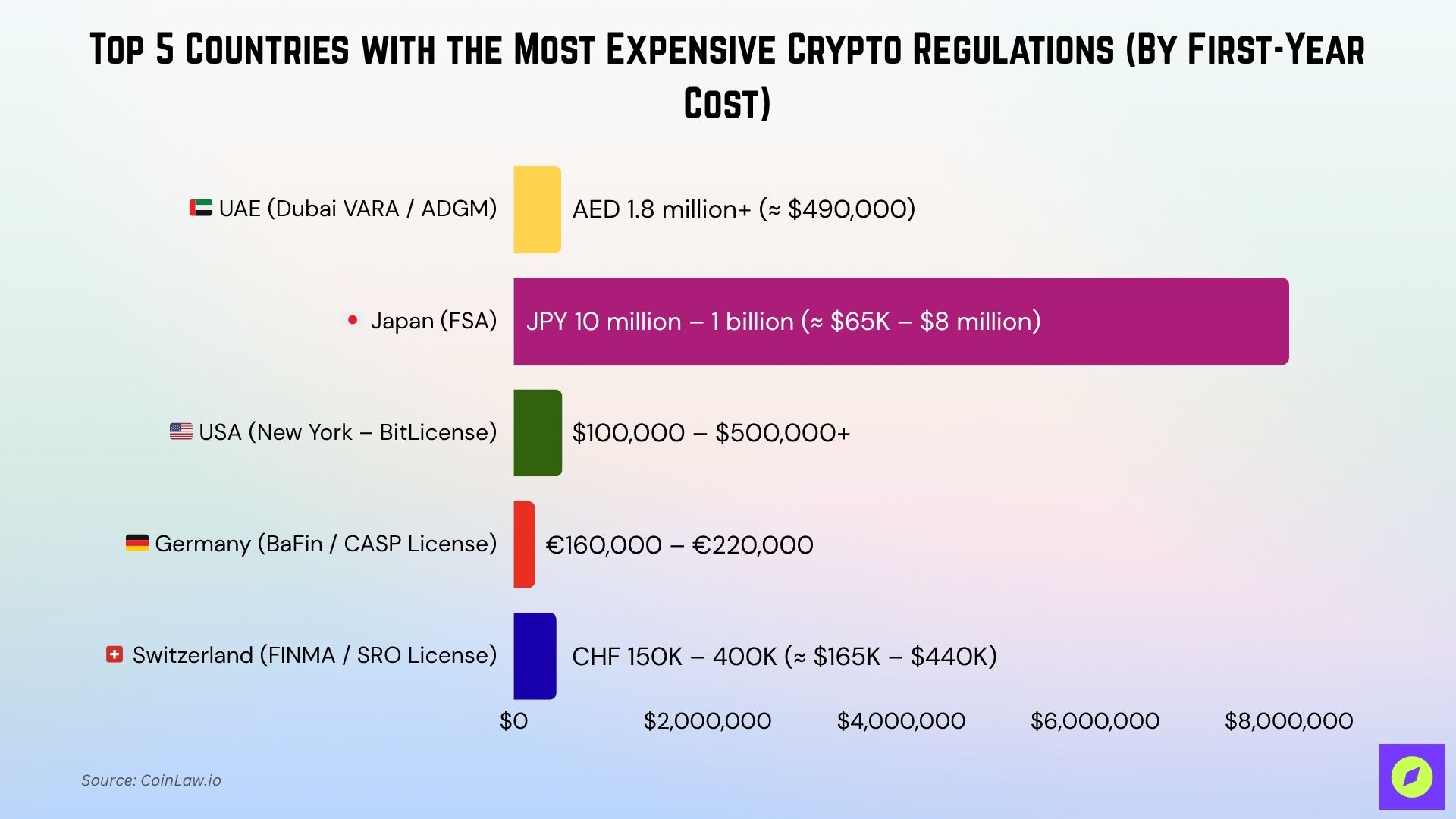
- UAE (Dubai) tops the list, with first-year crypto compliance costs nearing $490,000.
- Japan enforces strict crypto standards, with total first-year setup costs for large-scale operations reportedly reaching up to $6–8 million in rare cases, primarily due to extensive audits, legal fees, and compliance staffing
- New York’s BitLicense regime remains one of the most complex and expensive in the US.
- Germany’s BaFin demands high capital reserves and supervision fees, aligned with MiCA.
- Switzerland combines regulatory prestige with up to $440,000 in setup and compliance costs.
What Makes Crypto Regulation Expensive?
Crypto regulations are no longer loosely defined legal boundaries; they are formalized, tiered frameworks with direct monetary consequences. These are the primary cost drivers:
- Application & Licensing Fees: Jurisdictions now charge substantial fees just to process crypto license applications. In some regions, separate fees apply per activity (custody, exchange, advisory, etc.).
- Annual Supervision & Audits: Regulatory bodies demand yearly oversight, including independent audits, cybersecurity assessments, and detailed AML reporting.
- Minimum Paid-In Capital: Many regulators require a large sum of capital to be deposited or maintained, signaling financial stability.
- Legal and Compliance Infrastructure: Firms must invest in law firms, consultants, and internal teams to meet the layered requirements.
- Activity-Based Licensing: Some jurisdictions require different licenses for different services, making diversification costly.
The bottom line? A “crypto license” today can be as demanding and costly as a traditional banking license, especially in Tier-1 jurisdictions.
Top 5 Countries With the Most Expensive Crypto Regulations
These nations represent the pinnacle of regulated crypto ecosystems, where financial rigor meets institutional credibility. Their frameworks set the benchmark for transparency, compliance, and long‑term investor confidence in the digital asset economy.
| Country | First-Year Cost (USD) | Capital Requirement | Annual Supervision Fee | Major Regulatory Body | Why It’s Expensive |
| UAE (Dubai) | 💰 AED 1.8 million+ (≈ $490,000) | $408,000.00 | $54,500 | VARA / ADGM | Each crypto activity requires a separate license. Strong AML/KYC compliance, strict audits, and high paid-in capital requirements. |
| Japan | 💰 JPY 10 million – 1 billion (≈ $65K-$8 million) | $65,000+ | Varies | FSA | Extremely strict consumer protection, AML/KYC, and audit obligations under FSA oversight. |
| USA (NY) | 💰 $100,000-$500,000+ | Variable | Varies | NYDFS / BitLicense | Federal + state oversight, costly audits, background checks, cybersecurity rules, and capital requirements. |
| Germany | 💰 €150,000-€200,000 ($160,000 – $220,000) | €125,000 | Up to €500K | BaFin | High minimum capital, strict BaFin audits, MiCA compliance, and heavy documentation/reporting. |
| Switzerland | 💰 CHF 150,000 – 400,000 ($165,000 – $440,000) | Case-by-case | $55K – $110K | FINMA / SRO | Requires SRO membership, legal documentation, and strong AML audits. High legal and audit preparation costs. |
1. United Arab Emirates (Dubai VARA / ADGM)
Dubai continues to position itself as a luxury-grade financial hub where crypto regulation blends prestige with precision. Its frameworks are designed to attract serious institutional players looking for a globally respected jurisdiction with long-term operational stability.
- Estimated First-Year Cost: ≈ $490,000+
- Key Costs:
- Application Fee: AED 100,000 (~$27,000)
- Annual Supervision Fee: AED 200,000 (~$54,500)
- Minimum Paid-in Capital: AED 1.5 million (~$408,000)
Why It’s Expensive: Dubai’s Virtual Assets Regulatory Authority (VARA) enforces a modular licensing system where each activity, from brokerage to custody, requires a separate license. On top of that, applicants must comply with complex AML/KYC rules, provide audited financial statements, and maintain local operations. The UAE positions itself as a luxury destination for crypto finance, and the regulatory price tag reflects that ambition.
2. Japan (Financial Services Agency – FSA)
Japan remains a pioneer in structured digital asset oversight, reflecting its deep-rooted culture of consumer protection and technological discipline. Its mature crypto ecosystem has become a model for balancing innovation with investor safety.
- Estimated First-Year Cost: $65,000 – $8 million
- Key Costs:
- Minimum Capital Requirement: JPY 10 million (~$65,000–$75,000)
- Full Operational Setup (legal, tech, audits): Up to JPY 1 billion (~$6–8 million)
Why It’s Expensive: Japan is among the earliest and strictest crypto regulators. Exchanges must implement real-time monitoring, segregated customer funds, and undergo rigorous audits. Regulatory approvals take months, sometimes over a year. The FSA also mandates that all systems be thoroughly tested, with an internal compliance department often required even before license issuance. Japan’s framework, though precise and trusted, is prohibitively expensive for most startups.
3. United States (New York – BitLicense)
The U.S. regulatory landscape emphasizes accountability and systemic transparency, ensuring that only well‑capitalized, compliant firms enter the market. This approach cements the country’s influence in shaping global crypto governance standards.
- Estimated First-Year Cost: $100,000 – $500,000+
- Key Costs:
- BitLicense Application Fee: $5,000
- Legal, Compliance & Audit Setup: $100,000+
- Multi-State Licensing & Cybersecurity: Additional $100K+ annually
Why It’s Expensive: The United States features a dual regulatory system, federal and state, but New York’s BitLicense is considered the most demanding. To obtain one, applicants undergo background checks, provide detailed cybersecurity plans, submit audited financials, and maintain compliance reporting systems. Many firms spend over a year preparing before even applying. And because each state has its own rules, firms looking to operate across the U.S. face mounting multi-jurisdictional costs.
4. Germany (BaFin / CASP License)
Germany’s MiCA‑aligned regime reflects its focus on risk management and financial integrity across the digital asset sector. The country’s regulatory framework prioritizes prudence and governance, fostering confidence among traditional institutions.
- Estimated First-Year Cost: €150,000 – €200,000
- Key Costs:
- Minimum Share Capital: €125,000
- Application Fee: €10,750
- Supervision Fees: Up to €500,000 per year (based on complexity and assets)
Why It’s Expensive: Germany enforces EU-aligned Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) rules and is known for its conservative financial regulations. Crypto firms must undergo detailed AML audits, maintain full customer documentation, and hire locally for compliance roles. BaFin’s high standards require substantial documentation, board-level governance structures, and periodic supervision. Although entry is tough, Germany offers legal clarity that attracts institutional players.
5. Switzerland (FINMA / SRO License)
Switzerland blends financial heritage with blockchain innovation, maintaining its global reputation as a secure and forward‑thinking jurisdiction. It’s clear that legal structures continue to attract high‑value crypto ventures seeking credibility and investor assurance.
- Estimated First-Year Cost: $165,000 – $440,000
- Key Costs:
- Setup & Application Fees: CHF 50,000 – 200,000
- Annual Audit & SRO Supervision: CHF 50,000 – 100,000+
Why It’s Expensive: Switzerland’s FINMA combines Swiss-style regulatory precision with crypto-friendliness, at a cost. While the country has been a launchpad for major projects like Ethereum and Cardano, operating here demands a deep governance structure. Legal reviews, audited controls, and ongoing supervision by Self-Regulatory Organizations (SROs) make this one of the most expensive (yet prestigious) crypto jurisdictions in the world.
Impact on Startups and the Global Market
The rising cost of crypto compliance is transforming how innovation scales and where capital flows. As high‑cost jurisdictions favor well‑funded entrants, the global market is witnessing a clear divide between institutional growth hubs and emerging, agile crypto frontiers.
- Smaller Startups Are Getting Priced Out: Many early-stage ventures cannot afford a $200K+ upfront cost just to get licensed, forcing them to either go unregulated or operate in less reputable jurisdictions.
- Jurisdiction Shopping and Regulatory Arbitrage: Crypto firms are flocking to lower-cost nations like Seychelles, El Salvador, Lithuania, and BVI. While these offer lighter rules, they often lack credibility with institutional investors and banks.
- Market Consolidation: Well-funded players are gaining ground in top-tier jurisdictions, while undercapitalized firms are left behind or forced to pivot to DeFi, DAOs, or offshore structures.
- Compliance as a Competitive Advantage: In regulated hubs like New York or Zurich, full compliance now acts as a moat. Institutional investors, banks, and payment processors increasingly prefer licensed entities, regardless of the cost.
Cost vs. Trust: The Strategic Trade-Off
While these top 5 countries are expensive, they offer something critical: regulatory clarity and credibility. This is especially important for firms that:
- Want to serve institutional clients.
- Plan to issue regulated stablecoins or securities tokens.
- Intend to become listed on public markets or partner with traditional finance.
In short, compliance costs hurt short-term, but may offer long-term upside in the form of user trust, investor confidence, and global banking access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Approximately $620,000, reflecting a ~28% year‑on‑year increase in compliance expenditure.
Compliance costs increased by about 28% on average in 2025.
AML/KYC protocols account for 34% of total compliance budgets.
90% of centralized exchanges in North America achieved full KYC compliance.
The global crypto exchange market is projected to reach $71.35 billion in 2025.
Conclusion
As the crypto industry matures, the cost of legitimacy has never been higher. Countries like the UAE, Japan, the United States, Germany, and Switzerland are redefining what it means to operate a compliant crypto business, and the financial entry ticket can be steep. These jurisdictions offer stability, investor trust, and regulatory clarity, but at the cost of agility and affordability. For founders and investors, the message is clear: navigating the future of crypto will require not just innovation, but strategic capital allocation to survive and thrive in the world’s most demanding regulatory environments.